This Content Demonstrates the Natural and Human Causes of Climate Change in 2026.
List of Contents
Climate Change
Climate change refers to the long-term changes in weather conditions, such as temperature, precipitation, tsunamis, and drought, on Earth. It means different weather on the Earth compared to earlier decades. So, climate change refers to global warming on Earth. For example, now the Earth is warmer than it was thousands of years ago. NASA scientists have stated that the Earth’s temperature has increased rapidly in the past 150 years. It is estimated that the average temperature has risen by approximately 2 degrees Fahrenheit over the last 100 years. Although Earth’s temperature has been evolving, the previous five years were the warmest of the century. Therefore, climate change has been a much-talked-about topic for global leaders. Scientists mention the natural and human causes of climate change on the Planet.
Causes of Climate Change
The causes of climate change include natural factors and human activities that alter the Earth’s atmosphere. Scientists have identified many natural factors and human activities that influence the global atmosphere.
Natural Causes of Climate Change
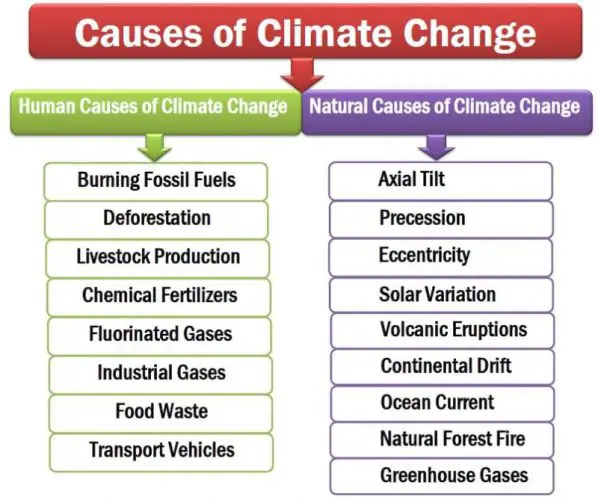
Natural causes of climate change refer to the factors and activities that change the Earth’s atmosphere. It might occur throughout the Earth’s cycle of motion, ocean currents, plate movement, volcanic eruptions, natural forest fires, and greenhouse gases. Natural causes are natural factors that occur mostly automatically, rather than people’s contributions.
What are the natural causes of climate change?
The Nine Natural Causes of Climate Change are:
- Solar Variation
- Volcanic Eruptions
- Axial Tilt
- Precession
- Eccentricity
- Continental Drift
- Ocean Current
- Natural Forest Fire
- Natural Greenhouse Gases.
Causes of Climate Change Diagram in 2024

1. Solar Variation (Sunspot)
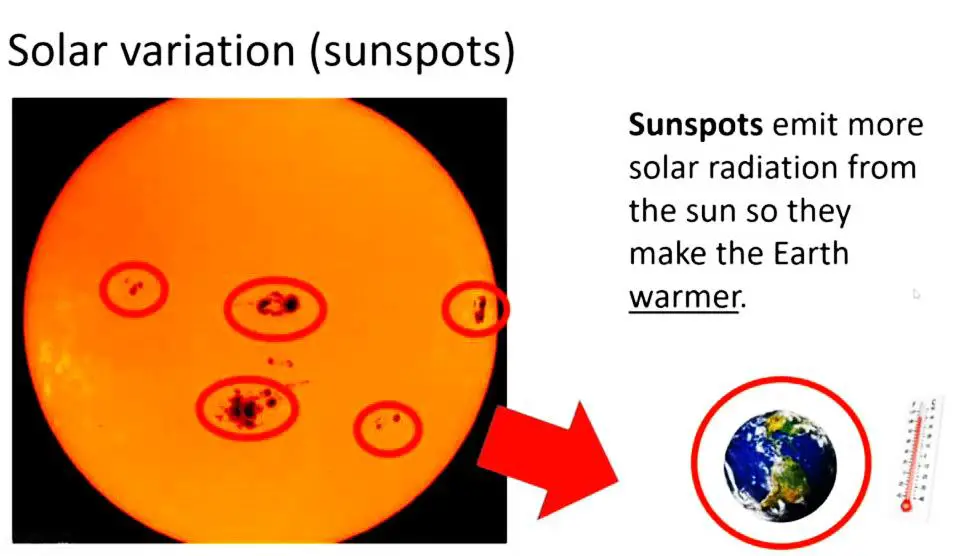
2. Volcanic Eruptions
Volcanic eruptions involve the emission of large amounts of gas, ash, lava, rock, and dust from the Planet’s surface. Volcanic eruptions are among the most devastating natural disasters, altering the environment in the disaster area. Therefore, it is another natural cause of climate change. The most adverse impact of the volcanic eruption is increasing the temperature of the Earth. Lava emitted during volcanic eruptions can raise the surrounding area’s temperature by about 1200 degrees Celsius.
However, it emits a considerable amount of flash and creates ash clouds in the sky. This ash cloud acts like a blanket in the sky, redirecting the Sun’s rays. The solar radiation is reflected on the ash cloud in the sky. The prolonged ash cloud reflects solar radiation; therefore, the Earth’s surface cools. In sum, volcanic eruptions are natural disasters that cause climate change.
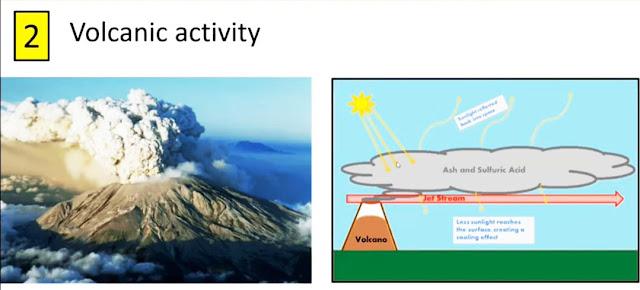
Does a volcanic eruption increase or decrease the Earth’s temperature?
Volcanic activity decreases the average temperature of surrounding areas. Although lava increases the surrounding area’s temperature, the ash cloud reflects solar radiation, reducing Earth’s temperature. So, a volcanic eruption cools the Planet and changes the climate.
3. Axial Tilt
According to Milankovitch Cycles, the Earth orbits the Sun, taking 365 days to complete one orbit. Additionally, the Sun takes 24 hours to rotate. Axial tilt is a crucial natural driver of climate change, as it determines how much solar radiation a region receives based on its position. Axial tilt is the angle between the Earth’s orbital plane and its equatorial plane during rotation. It is also known as obliquity, which represents the Earth’s angle. Axial tilt makes different seasons in the same area of the Planet.
According to statistical reports, the Earth has been tilted by 23.5 degrees relative to the plane. The axial tilt differs by 22.1 and 24.5 degrees from its orbital plane around the Sun. The seasons of the Earth depend on its axial tilt; therefore, the greater the axial tilt, the greater the seasons. The Sun provides more solar radiation when the Earth’s hemisphere tilts towards it in the summer. On the other hand, the Earth receives less solar radiation when it tilts away from the Sun’s orbital plane. According to Milankovitch (1930), it takes 41,000 years to complete the ice age cycle. So, the ice age comes back every 41,000 years.
For example, the Earth is currently tilted 23.45 degrees; therefore, one hemisphere receives more solar radiation, creating an extreme summer, while the other hemisphere experiences an extreme winter. The axial tilt is decreasing; thus, the Earth gets extremely hot in summer and extremely cold in winter. Based on the discussion, it is optimal to say that the axial tilt causes climate change on Earth.
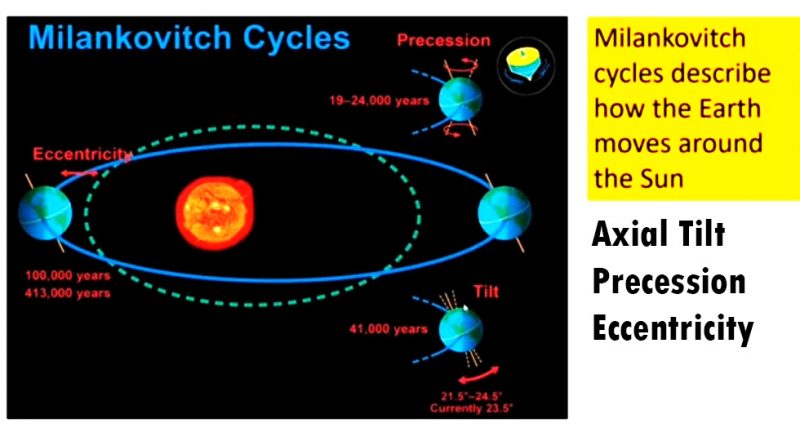
4. Precession
Precession refers to the movement in the orientation of the rotational axis due to the gravitational force of the Sun and the Moon. It is a type of movement that occurs when it starts to wobble and change the direction of the first axis. The Earth rotates once every 24 hours. However, it wobbles slightly roughly after every 19 to 24 thousand years. If it’s leaning towards the Sun, it gets more heat. On the other hand, the Earth receives less heat if it leans away from the Sun. The Earth’s precession affects climate change; hence, precession is another natural cause of climate change.
5. Eccentricity
6. Continental Drift by Plate Tectonics
Continental drift refers to the slow movement of Earth’s tectonic plates, also known as the shifting of Earth’s crust. Initially, Alfred Wegener proposed continental drift in 1912. There are seven continents on Earth; however, their positions are not fixed. Some continents are getting closer year by year; on the other hand, some are growing farther apart. The movement is a prolonged process. The motion of the continental drift movement is around 0.6 cm to 10.5 cm per year. Hence, continental drift is the critical natural cause of climate change on the Earth.
The tectonic plates are the separated pieces of the Earth’s crust. The outer face of the crust is rocky and solid and consists of two types of material: less-dense oceanic crust and more-dense continental crust. These tectonic plates can move freely, causing earthquakes and volcanoes on Earth. Most ocean volcanoes and Earthquakes are the direct consequences of continental drift. The movement of tectonic plates can be described in four patterns: transform faulting, spreading, subduction, and collision.
For example, the collision between the Indian and Eurasian plates has extended the Himalayan Mountain range. Magma is created from molten rock beneath the crust and is emitted from volcanic vents, which can change the climate. In sum, continental drift by plate tectonics is a natural cause of climate change.
7. Ocean Current
Ocean currents are a natural driver of climate change on Earth, formed by the continuous movement of ocean water. It is generated by ocean winds, the moon’s gravitational pull, breaking waves, temperature, and the rotation of the Earth. Ocean currents play a crucial role in driving climate change by warming the Earth. The ocean absorbs most of the solar radiation, while land areas receive some. The land surface radiates some heat back into space after sunset. However, the sea absorbs solar radiation and eventually redistributes it around the Planet. The heat from the sun evaporates ocean water continuously, raising the temperature and humidity in surrounding areas on Earth. Ultimately, the evaporation process creates rain and storms that reduce the temperatures.
If the current system collapses, it will lead to dramatic changes in worldwide weather patterns. Ocean currents could rapidly freeze parts of North America. If this circulation shuts down, it could bring extreme cold to Europe and parts of North America.
8. Natural Forest Fire
Natural forest fires are a significant natural driver of climate change, increasing temperatures in surrounding areas. There are two causes of forest fires: natural and human. A natural forest fire is a wildfire that burns thousands of acres, including trees and animals. According to the Environmental Protection Agency report, 20 percent of forest fires occur naturally, while around 80 percent are caused by human activities.

Natural forest fires can be sparked by lightning or by drought that sets trees ablaze. Usually, warm temperatures encourage setting fires, and strong winds spread them rapidly to surrounding areas. A forest fire transforms green vegetation into a desert for a while.
Forest fires release large amounts of greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, and ash. These gases trigger atmospheric warming and deplete soil nutrients. Therefore, a natural forest fire is a significant natural cause of climate change.
9. Natural Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases are gases that change the climate by trapping infrared radiation, or heat, in the atmosphere. GHG is the short form or abbreviation of greenhouse gases. There are two types of causes of greenhouse gas emissions: natural and human-induced. Natural greenhouse gases are produced on Earth without human activity. For example, permafrost is frozen ground that naturally contains and releases greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4).
The most common natural greenhouse gases on the Earth are water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and ozone (O3). Greenhouse gases help sunlight reach the Earth’s surface and block heat from returning to the atmosphere. These natural gases prevent the heat released from the Earth’s surface from escaping. Natural greenhouse gases contribute to the atmospheric temperature rise directly and indirectly. In essence, natural greenhouse gases warm the Earth’s atmosphere by trapping the heat. So, it is another natural cause of climate change that warms the atmosphere.
There are two sources of greenhouse gases: natural and human. Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, contribute to the emission of greenhouse gases. They also produce greenhouse gases such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and Perfluorocarbons (PFCs). People cut down forests for agriculture, which also contributes to global warming. Now, researchers and political leaders are working together to reduce human-induced causes of climate change. They raise awareness to prevent global warming. Social etiquette and social awareness among people can protect the environment from pollution. In a nutshell, greenhouse gases cause global warming and alter the global climate.
Conclusion
In conclusion, these nine natural causes of climate change (Solar Variation, Volcanic Eruptions, Axial Tilt, Precession, Eccentricity, Continental Drift, Ocean Current, Natural Forest Fires, and Natural Greenhouse Gases) contribute to changes in the global atmosphere. These factors are natural contributors to global warming, altering the atmosphere and the Earth’s environment directly and indirectly.
What are the human causes of climate change?
The Major Human Causes of Climate Change are
- Burning Fossil Fuels
- Deforestation
- Livestock Production
- Fluorinated Gases
- Chemical Fertilizers
- Fluorinated Gases
- Industrial Gases
- Food Waste
- Transport Vehicles.
These are the crucial human activities that cause climate change on the Planet.
1. Burning Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuel burning is the most significant human cause of global warming. Fossil fuels contain carbon and hydrogen gases beneath the Earth’s crust. They are made from the remains of animals and plants. The most common examples of fossil fuels are natural gas, bitumen, oil, coal, tar sands, and petroleum. People burn fossil fuels to generate electricity and power transportation. Fossil fuels release greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide (CO2), that trap heat in the atmosphere. So, burning fossil fuels is a catastrophic cause of global warming. They are the source of 80% of Earth’s energy, which is not renewable. The Earth’s average temperature has risen by about 1 degree Celsius, and sea levels have increased. As a result, people experience scorching summer weather. It is also caused by biodiversity destruction, plant and animal extinction, and global health conditions.
2. Deforestation
Deforestation is another human-caused environmental change on the Planet that results from people’s activities. People are directly associated with deforestation, which affects biodiversity and the Earth’s ecosystems. Deforestation is the cutting down of forest areas by humans. People cut trees in the forest for urbanization, crop cultivation, and mining. Since 1960, deforestation has reduced forest areas worldwide, contributing to changes in the atmosphere. According to the oxygen cycle, people inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide that trees consume. On the other hand, trees take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen during respiration.
The more trees on the Planet consume, the more carbon dioxide (CO2) is produced. Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere are increasing due to deforestation. Deforestation destroys the carbon stores and releases carbon dioxide into the Planet. It is a primary human cause of rising greenhouse gases and climate change. According to a 2019 study, deforestation is responsible for a 11 percent increase in carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions.
3. Livestock Production
Livestock production is another primary human cause of climate change. It contributes to the production of greenhouse gases that trap heat in the atmosphere. Livestock production is the agricultural process of farming domestic animals, including breeding, caring for, and raising them. Nowadays, people farm domestic animals for commercial purposes to produce meat, milk, leather, etc. The most common animals in livestock farms are cows and sheep. These animals generate methane(CH4) when they consume and digest food. A report shows that cows generate around 150 billion gallons of methane gas daily.
Methane is one of the greenhouse gases that contribute to rising global temperatures. Livestock production accounts for 14.5 percent of greenhouse gas emissions. Domestic animal farming has a large carbon footprint that contributes to climate change. Given people’s close association with livestock, it is reasonable to say that livestock production is an essential human driver of climate change.
4. Chemical Fertilizers
Chemical fertilizers are responsible for altering Earth’s climate. People produce chemical fertilizers to use in modern agriculture.
Chemical fertilizers are modern fertilizers produced by chemical synthesis, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur. These ingredients contain nutrients for the plants—fertilizers containing nitrogen produce nitrous oxide emissions. Farmers use chemical fertilizers to get greater benefits from their farms. Although these fertilizers help plants grow and produce more corn and fruit, chemical fertilizers can harm the environment.
For example, nitrogen-based chemical fertilizers emit nitrous oxide (N2O), a greenhouse gas (GHG). It is said that nitrous oxide (N2O) is a long-lived greenhouse gas produced by agricultural activities. Chemical fertilizers contain nitrate (NO3–) and ammonia (NH4+). As a result, chemical fertilizers in agriculture generate the critical greenhouse gas nitrous oxide (N2O). Nitrous oxide (N2O) traps the heat in the atmosphere, allowing shortwave Infrared to enter the Earth and obstructing the longwave Infrared from returning toward the sun. The percentage of nitrous oxide in greenhouse gases is 10-14 percent. People are responsible for producing 80% nitrous oxide through modern agriculture. The scientists warned modern farmers to reduce the use of chemical fertilizers in agriculture to combat climate change.
5. Fluorinated Gases
Fluorinated gases are also a human-caused contributor to climate change, as people produce them for commercial purposes. The most common fluorinated gases are hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), nitrogen difluoride, perfluorocarbons (PFCs), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6). People produce these fluorinated gases as the elements of aerosol cans, air conditioners, refrigerators, and so on. These gases are crucial materials for producing semiconductors in the factory.
Fluorinated Greenhouse Gases
- Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
- Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6)
- Nitrogen trifluoride (NF3)
- Perfluorocarbons (PFCs)
The fluorinated gases are also powerful GHGs that trap heat in the atmosphere. Fluorinated greenhouse gases, also known as F-gases, contribute to global warming. According to the report, fluorinated greenhouse gases cause more than 23,000 times as much global warming as carbon dioxide (CO2).
6. Industrial Gases
Industrial gases include carbon dioxide, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, helium, and noble gases. Two types of human activities can produce these gases: people intentionally produce them, and industrial factories emit them. Firstly, these industrial gases are produced in factories for commercial purposes. They compress these gases into liquid in the cylinder to sell them in the market. Secondly, electrical factories generate carbon dioxide and nitrogen when producing goods and energy. In the United States, power plants emit 40 percent of carbon dioxide (CO2).
Industrial gases such as carbon dioxide and nitrogen are greenhouse gases that affect ozone depletion. The volume of industrial gas emissions is increasing as factories worldwide expand.
7. Food Waste
Food waste is one of the silent human causes of climate change that many people are unaware of. For example, many people intentionally waste food without realizing the negative consequences. Food waste occurs during processing and distribution from the seller to the buyer. It is estimated that Americans waste about 40 percent of their food each year. Additionally, Americans waste around 27,000 gallons of water annually by throwing away vegetables, fruits, eggs, and beef. Food waste produces methane(CH4) gas when it decomposes in landfills. Methane (CH4) is a potent greenhouse gas that contributes to global warming and climate change on Earth. The study shows that around 6-8 percent of methane is emitted from food waste. Therefore, food waste is a significant factor in climate change that many people do not know about.
8. Transport Vehicles
Transport vehicles consume fossil fuels and emit greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2). Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most devastating greenhouse gas, as it raises temperatures. It is estimated that vehicles account for around 30 percent of greenhouse gas emissions. Greenhouse gas emissions have increased rapidly in the last 30 years.
Significance of this Article
This article offers in-depth insights into the natural and human causes of climate change. It also provides ways for humans to prevent global warming from destroying this beautiful world. International organizations and global leaders highlight this issue. For example, the United Nations schedule for the 2024 UN Climate Change Conference (UNFCCC COP 29), to be held from 11 to 22 November 2024 in Baku, Azerbaijan. People from different groups in society have to come up with solutions to prevent global warming. Students can download the PDF.
Natural Causes of Climate Change PDF
Citation For This Article (APA 7th Edition)
| Kobiruzzaman, M. M. (2026). Cause of Climate Change- 9 Natural Causes of Climate Change in 2026. Newsmoor- Educational Website For Online Learning. https://newsmoor.com/natural-causes-of-climate-change-9-natural-causes-of-climate-change/ |