Examples of STAR Interview Questions and Answers. STAR Interview Questions and Answers PDF
STAR Interview Questions and Answers
The STAR interview questions and answers refer to the organized statement that describes the interviewee’s Situation, Task, Action, and Result in a previous job. It is a structural method of answering questions. It is familiar as the STAR technique of interview questions. However, a few interviewers ask to be introduced during the job interview. However, self-introduction during the viva exam is common. The applicant needs to follow the STAR method of answering questions after self-introduction.
The STAR interview question-and-answer format helps the interviewee explain their previous job experience. It also allows interviewers to ask questions. It also helps the interviewer assess the interviewee’s skills and knowledge through the four specific situations. These answers are crucial for a self-introduction in a job interview, as they help prove the applicant’s potential. The STAR interview questions and answers help applicants explain their strengths precisely and are critical for assisting the interviewer in understanding the skills and experience relevant to the position. Hence, the STAR interview method benefits both the interviewee and the interviewer.
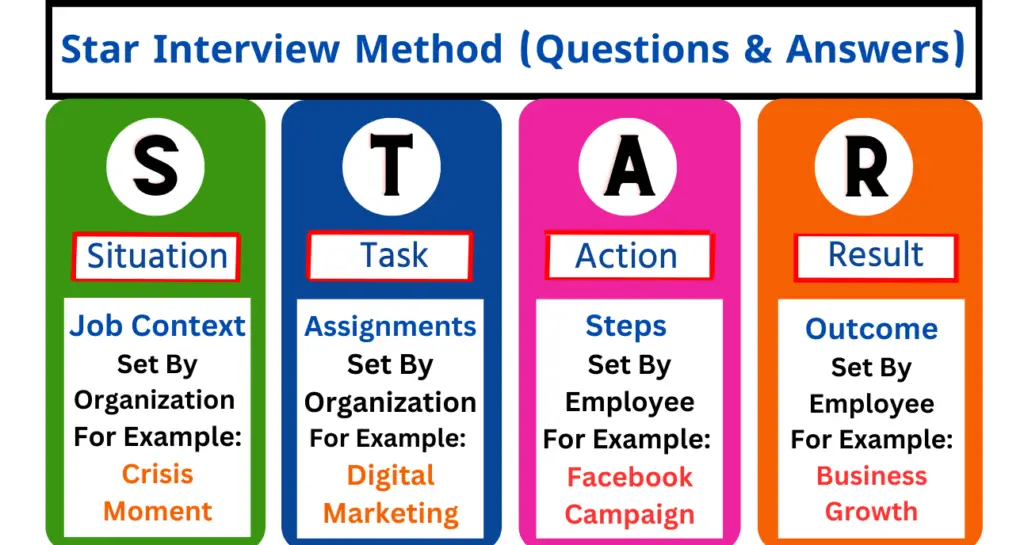
Star Interview Method Meaning
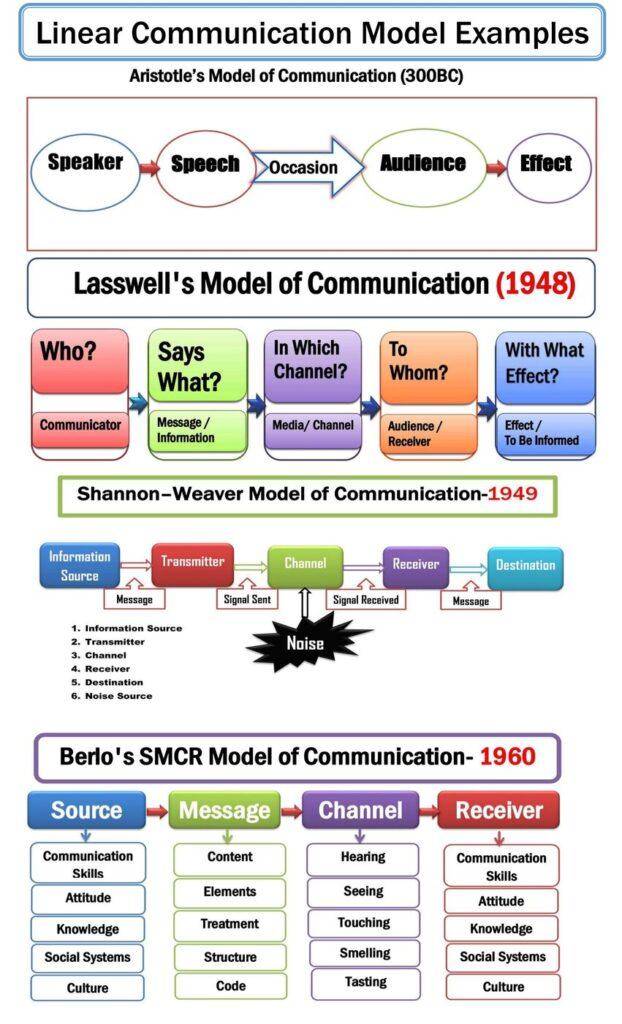
The STAR method interview involves explaining experience using the four key factors: situation, task, action, and results.
- Situation
- Task
- Action
- Results
1. Situation (Job Context)
The STAR interview method reveals the applicant’s job context. It refers to the job arena and scenario they encountered while working there. It highlights the problems, crises, and issues that the applicants overcame. The organization designs the situation and tasks for employees.
(The applicant can follow the answer example to describe the situation they have encountered previously.)
STAR Interview Questions and Answers Examples-1
For example, the organization’s sales growth decreased rapidly due to the natural crisis. Sales growth declined due to conflicts within the marketing department. The CEO appointed me to handle the situation. I worked very hard to recover business growth within two months.
STAR Interview Questions and Answers Examples-2
I work as a website content writer for the Global Assistant Education Consultant. Google penalized the website for duplicate content, resulting in massive organic traffic loss and declining revenue. The managing director assigned me to recover the visitors.
2. Task (What Activities)
Task refers to the employee’s activities and assignments in a specific situation in the STAR interview method. Senior employees set the assignments. It does not point to where they work; instead, it means what you work on regularly. In the interview, the interviewee should discuss the tasks they used to accomplish. You have to mention the specific tasks that you have done before. The applicant should provide sufficient information about previous job duties so the interviewer can understand their capabilities. The task specifies particular job responsibilities, including IT specialist, Group leader, crisis management, content writer, social media marketing, graphic designer, etc.
The applicant can follow the Star interview answer example to describe the activities they have completed.
STAR Interview Questions and Answers Examples-1
For example, my senior manager instructed me to recover the website traffic. I paraphrased most of the duplicate content and republished it.
STAR Interview Answers Example-2
Social media marketing managers explain how they promote products and company brands on platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, YouTube, and WhatsApp.
STAR Interview Answers Example-3
A digital marketing manager should say that I used to regulate the Facebook page and WhatsApp group to communicate with potential and existing customers. Thus, the task in the STAR interview technique indicates daily assignments in the workplace.
3. Action (What Steps)
Actions in the STAR interview method represent employees’ steps toward achieving the goal. It specifies the individual contribution toward achieving the business goal. In this section, applicants should emphasize the number of tasks they have completed while working at a previous or current company to address the crisis. Action is the most crucial part of the STAR interview approach to explaining the applicant’s strengths.
The employees take action for positive outcomes, not management. Therefore, the applicants must emphasize these sections to ensure they are represented appropriately.
However, the interviewee should not mention what their team or group did to accomplish the project. You should use “I,” not “we,” when describing actions.
The applicant can use this question-and-answer example to describe the actions they took to overcome the critical situation.
STAR Interview Questions and Answers Examples-1
For example, a digital marketing manager should articulate that I design product banners and share them daily on Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and WhatsApp. Additionally, I communicate with our existing and potential clients to inform them about the new laptops.
4. Results (Achievements)
The result of the STAR interview method describes the outcome of the actions taken to achieve the goal. It is the most critical section, followed by the actions. You have to present personal credits that contribute to accomplishing business goals. The answers should contain multiple positive effects. You can list positive results. The interviewee must emphasize explaining the results, as this also reflects their capabilities. Therefore, the action and results of the STAR interview technique are critical to applicants.
For example, a marketing manager should state that I sold 200 laptops in a month. Additionally, my actions have increased the number of followers on social media pages and website visitors. Ultimately, it contributes to corporate reputation and image.
STAR Interview Questions and Answers Examples
The author provides examples of STAR interview questions and answers for applicants. These examples of interview questions and answers help fresher students and employees to face interview sessions.
STAR Interview Questions Examples
Based on the STAR interview, the author created the following questions for the interviewer to ask the applicants. The interviewers can ask these questions before, during, or after the introduce yourself speech.
- Describe a situation where you persuaded other employees to accept organizational change for a better outcome.
- Explain how you completed tasks when you were under immersive pressure.
- Describe a time when you were exhausted at work and recovered properly.
- Please provide a list of the tasks you regularly perform to achieve the company’s goals.
- Please give me an example of when you contributed to crisis management in the organization.
- Give us a specific example of a goal you set independently to achieve the company vision and that you ultimately reached.
- Tell a situation when you confronted a company’s rules and regulations but refused to comply with them to complete the tasks.
- Describe a time when you failed to complete the tasks. What lesson did you learn from it?
Examples of STAR Interview Questions and Answers
Situation (S): In January 2023, our company’s sales revenue decreased due to insufficient digital marketing. I enhanced social media marketing and customer service to improve revenue.
Task (T): My senior assigned me to improve social media marketing. My goal was to create a new marketing plan that would increase revenue.
Action (A): I designed promotional content featuring product banners and shared it on Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp. Additionally, I motivated my digital marketing team to regularly communicate with potential and existing customers.
Result (R): Finally, I achieved around $5 million in sales growth in February 2023. I also contributed to increasing the number of followers on our social media pages. Now we’re receiving more orders from social media as part of the new marketing strategy.
STAR Interview Questions and Answers PDF
The author connects the Star interview questions and answers PDF for employees and managers. It helps applicants prepare for interview sessions. You need to click on the following link to download the PDF format of the Star interview questions and answers.
Question-1
Describe a situation when you handled massive stress in a workplace.
Answer-1
At my previous workplace, our senior officer left just one week before delivering a project to clients. The senior manager handled the project and served as its chief. The managing director instructed me to complete the project within the period. The tight deadline put me under massive pressure to handle the project. However, I called upon an international meeting with coworkers and divided the task again. I had to accept additional tasks from the senior officer who left the job. I put extra time into coping with the situation and finally achieved it. This crisis moment allowed me to explore that I can work under stressful conditions. My dedication, commitment, plan, and complex work function ideally.
STAR Interview Questions and Answers Preparation
- The interviewee should remember situations that demonstrate strong skills, work experience, supervision, cooperation, planning, and customer satisfaction.
- They should briefly explain the situation to answer the questions.
- The interviewees must outline a story with a beginning, middle, and end. They must be ready to explain the situation following the task, action, and result.
- They have to present results that positively reflect the applicant’s credibility.
- Everyone must be honest while describing the story, even if the result is unfavorable. Do not make a fake story to enhance credibility.