This feature explains the discriminative, comprehensive, empathic, analytical, and appreciative listening with examples. It also describes the difference between discriminative and comprehensive listening.
Listening Definition
Listening means hearing and interpreting the message intentionally to provide feedback. It is an active process of giving attention to listening to the sounds. The active listening process has six steps: receiving, selecting, interpreting, understanding, evaluating, and responding to the message. Therefore, listening is the ability to receive, select, analyze, understand, assess, and react appropriately to the meaning of another person’s verbal and nonverbal messages. People use many types of listening to communicate with each other.
In communication, people spend enormous time listening (40 – 70%), speaking (20 – 35%), reading (10 – 20%), and writing (5 – 15%). People often listen in communication by using different types of listening strategies. Although there are many types of listening in the communication process, the author will discuss the five basic types of listening: discriminative, comprehensive, empathic, analytical, and appreciative Listening.
Types of Listening
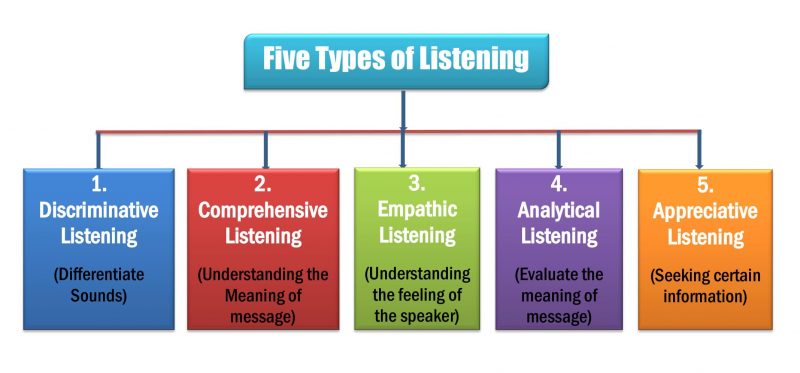
The 5 Types of Listening are Discriminative Listening, Comprehensive Listening, Empathic Listening, Analytical Listening, and Appreciative Listening.
The 5 Types of Listening
- Discriminative Listening (Differentiate the sounds of the voice)
- Comprehensive Listening (Understanding the meaning of the message)
- Empathic Listening (Understanding the feelings and emotions of the speaker)
- Analytical Listening (Evaluate the meaning of the message based on evidence)
- Appreciative Listening (Seeking certain information)
Discriminative and Comprehensive Listening
1. Discriminative Listening
Discriminative listening means only interpreting the sound of the message rather than understanding the meaning of the message. It is also known as a fundamental type of listening; therefore, people learn discriminative listening from their mothers’ wombs. This listening style involves hearing only the sound rather than listening to interpret the meaning of the message. It is the primary type of listening, where different sounds of words are recognized without understanding the meaning.
Example of discriminative listening
For Example, a Canadian person named Jon sits at Kuala Lumpur International Airport in Malaysia. At the same time, two Malaysian people are speaking in the Malay language beside him. Jon does not understand what they are talking about, but he distinguishes males and females based on their tone of voice. Based on the sound, he also identifies their age. Thus, discriminative listening helps identify age, gender, anger, and happiness based on the sound.
2. Comprehensive Listening
Comprehensive Listening means understanding the meaning of the message rather than interpreting only the sound of the message. It is an active process of seeking the meaning of the message. It is the initial process of meaning the verbal and nonverbal communication messages, thoughts, ideas, and opinions. Listeners use knowledge and vocabulary to understand the meaning of the speaker’s message. It is not only the meaning of the words but also something more than that. Active audiences use a comprehensive listening style to perceive the message’s meaning.
Listeners encounter obstacles or communication barriers to effective listening. These barriers or obstacles distract the listener from understanding the message’s meaning. They are also known as the communication noise to effective listening. The five types of noises or barriers to effective listening are physical, physiological, psychological, factual, and semantic barriers.
Example of Comprehensive Listening in Real Life
Students of the disaster management department join a lecture on climate change. The lecturer discusses the natural causes of climate change, citing scientific evidence. The speaker explains 11 natural causes of climate change, including Solar Variation, Volcanic Eruptions, Axial Tilt, Precession, Eccentricity, Continental Drift, Ocean Current, Natural Forest Fires, and Natural Greenhouse Gases. As the lecture progresses, the speaker moves on to the potential consequences of climate change, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and loss of biodiversity.
Students understand the keywords’ meaning and are actively involved with the contents. Some students ask questions for further clarification. Additionally, they take notes to memorize them for final exams.
Example of a Comprehensive Listener
For example, Isa is from the Philippines and joins to listen to motivational speeches in Filipino. The speaker talks about how to overcome stress in the organization. She understands almost all the advice that helps to reduce stress. She can understand the meaning of the message and speech. In this context of communication, Isa is experiencing a comprehensive type of listening; therefore, she is a comprehensive listener.
Similarly, what brand name comes to your mind when talking about soft drinks? Most of them answer Coca-Cola and Pepsi based on cognitive skills. It is also an example of comprehensive listening that is more than understanding the message’s meaning.
Difference Between Discriminative & Comprehensive Listening
Discriminative Listening |
Comprehensive Listening |
| Discriminative listening refers to translating sounds into words and sentences. | In contrast, comprehensive listening means making meaning out of words and sentences rather than translating only. |
| It is all about assuming meaning from the tone and body language. | On the other hand, it is about using knowledge and vocabulary to understand the speaker’s speech. |
| Discriminative listening is a process of hearing but not listening. | In contrast, comprehensive listening is a rather than just a hearing style. |
| For example, it identifies a boy and a girl based on the sound of the voice. | For example, understanding what the boy and girl are talking about is. |
3. Empathic Listening
Empathic listening is apprehended as understanding the feelings and emotions of the speaker; sometimes, the listener can feel what the speaker is feeling. Therefore, this listening needs close attention, discriminative listening, comprehensive listening, and a deep connection with the emotions of the speakers.
Example of Empathic listening
For example, the Audience is thinking about the same things the speaker is thinking.
4. Analytical Listening
Analytical Listening means evaluating and forming the appropriate meaning of the message based on evidence. So, It is related to critical thinking and analysis. However, It helps assess whether speakers are right, wrong, logical, or illogical. Analytical listeners understand why they accept or reject another member’s ideas and suggestions.
For example, speakers show a statistical report to persuade audiences, although audiences argue with others for a better understanding.
5. Appreciative Listening
Appreciative listening refers to the listening behavior where the listener seeks certain information to appreciate and meet their needs and goals. It is one kind of selective listening. Appreciative listeners are intended to listen to particular information that is important to them.
For example, I listen to a favorite song and poetry to seek the exciting words of the speech. I am also listening to a political speech to find motivational words.
In conclusion, the five types of listening are discriminative, comprehensive, empathic, analytical, and appreciative listening. They are distinguished from each other by the style of listening.
