5 Gap Model of Service Quality With Examples. Gaps Model. Service Quality Gap Model Example. Gap Model of Customer Satisfaction.
Gap Model of Service Quality
The gap model of service quality refers to the five gaps model that describes gaps in service quality of the organization’s customer experiences and service quality. In 1985, four scholars, A. Parasuraman, Valarie Zeithaml, and Leonard L. Berry, introduced the gap model of service quality in the Journal of Marketing manuscript titled “A Conceptual Model of Service Quality and Its Implications for Further Research.” It is also known as the service quality gap model.
This model articulates the gap between customers’ expectations and the organization’s service. It assists service-providing companies in identifying customer satisfaction in different stages of the service delivery process. The service quality will be high when the customers’ perception meets the expectations, but the quality is low when the customer’s perception cannot meet the expectations. The five-gap model of service quality ensures the organization’s total quality management thoroughly.
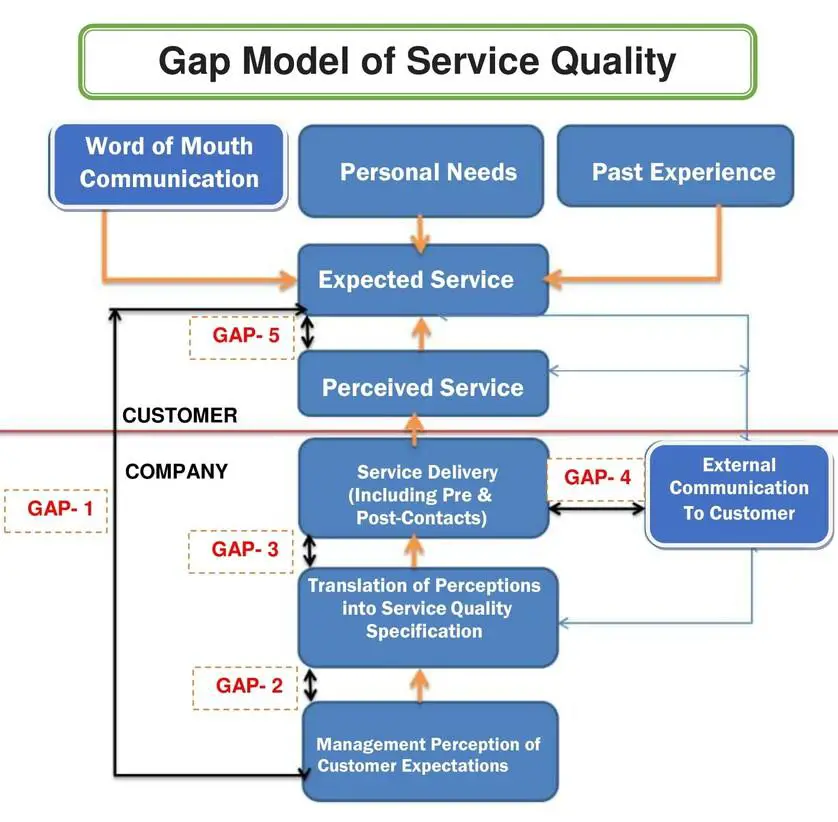
Servqual Gap Model
SERVQUAL model evaluates the gaps between clients’ expectations and perceptions of service quality with five major service dimensions: reliability, assurance, tangibles, empathy, and responsiveness. The Servqual model of service quality assesses the customers’ expectations and perceptions; therefore, many scholars call it the Servqual gap model. Hence, many service-providing companies utilize the gaps model to identify and improve clients’ satisfaction. The Servqual gap model or the five gap model of service quality represents a customer-satisfaction framework. However, the Survqual model is also known as the five service quality dimensions.
5 Gap Model of Service Quality
The 5 Gaps in Service Quality are
- Knowledge Gap
- Policy Gap
- Communication Gap
- Delivery Gap
- Customer Gap
5 Gap Model of Service Quality With Examples
Gap- 1. Knowledge Gap
The knowledge gap in service quality refers to the gap between customers’ expectations of the company and its action of providing that service. It identifies what customers want from the industry and what the company typically offers to the customers. This gap can grow if management doesn’t thoroughly focus on the customer’s expectations.
Many reasons can increase the knowledge gap, for example:
Firstly, the knowledge gap in service quality increases when the industry does not carefully focus on what customers expect. Secondly, the knowledge gap increases due to a lack of upward communication and customer interaction. Thirdly, the preliminary market analysis also raises the knowledge gap.
The additional reasons for increasing the knowledge gap:
- Less focus on relationships.
- Failure to understand customer complaints.
- Lack of interaction between management and customers.
Knowledge Gap in Service Quality Example-1
The user of Netflix wants to see the upcoming movie trailers on Netflix’s official website. However, Netflix shows only the movie list on the site without knowing the customer’s expectations. Netflix would suffer this knowledge gap if it did not provide upcoming movie trailers on the site. Netflix’s organizational management fulfills the gap between customer perception and expectation to achieve competitive advantages.
Knowledge Gap in Service Quality Example-2
Consider a hotel chain that prides itself on offering exceptional customer service. The management team conducts regular customer satisfaction surveys to gauge guests’ perceptions of their stay. However, despite consistently receiving positive feedback on staff friendliness and cleanliness, the surveys reveal a recurring complaint about slow response times to guest requests.
Upon further investigation, the management team discovers a knowledge gap between guests’ expectations and the organization’s understanding of those expectations. While the hotel staff is trained to prioritize tasks based on urgency, they may not be fully aware of guests’ specific expectations regarding response times for requests such as room service, housekeeping, or maintenance.
Gap 2: Policy Gap
The policy gap is the difference between management perceptions of customer needs and the translation of those perceptions into service delivery policies and standards. This policy gap appears because of the dissimilarity between what the customer wants and what management provides for the customers.
Many reasons can grow the policy gap, for instance:
Firstly, the policy gap in service quality rises when the company is not committed to providing quality services. Secondly, the lack of task standardization extends the policy gap. Moreover, the lack of goal setting raises this gap.
The additional reasons for increasing the policy gap:
- Shortness of customer service standards.
- Inadequately described service levels.
- Failure to continually update service level standards.
Policy Gap in Service Quality Example- 1
Netflix will suffer from a policy gap if it uploads the upcoming movie trailers after releasing the movie. People want to watch the movie trailer before releasing the film. Netflix should be more responsive to the customers and commit to uploading the film trailer soon.
Policy Gap in Service Quality Example- 2
For example, a telecommunications company that advertises 24/7 customer support to assist subscribers with any service-related issues. The company’s policy dictates that customers should be able to reach a live representative at any time, regardless of the day or hour. However, upon closer examination, it becomes evident that there is a policy gap between what is promised and what is delivered.
Customers frequently report difficulties in reaching a live representative outside of standard business hours. Despite the company’s policy of round-the-clock support, they often encounter long wait times, automated messages directing them to visit the website or call back later, or even outright unavailability of customer service agents during evenings and weekends.
To address this policy gap and improve service quality, the telecommunications company implements the following measures:
- Staffing Adjustments: The company hires additional customer service representatives to cover peak call times, including evenings, weekends, and holidays. This ensures that there are enough agents available to handle customer inquiries promptly.
- Technology Upgrades: The company invests in advanced call center technology, such as interactive voice response (IVR) systems and chatbots, to handle routine inquiries and provide basic assistance outside of regular business hours. This helps reduce wait times and improve the overall customer experience.
- Training and Empowerment: The company provides comprehensive training to customer service representatives on effective communication, problem-solving, and conflict-resolution techniques. Agents are empowered to resolve issues quickly and efficiently, even during non-standard hours.
- Monitoring and Feedback: The company implements systems to monitor call volume, wait times, and customer satisfaction levels in real time. Management regularly reviews this data to identify trends, address bottlenecks, and make continuous improvements to service delivery.
By closing the policy gap between its stated commitment to 24/7 customer support and the actual provision of that support, the telecommunications company can enhance service quality, build customer loyalty, and maintain a competitive edge in the market. This example underscores the importance of aligning organizational policies with customer expectations to deliver consistent and reliable service.
Gap 3: Delivery Gap in Service Quality
The delivery gap is the dissimilarity between the standard of the company’s service delivery policies and the service’s actual delivery. The delivery gap in service quality arises when the company cannot maintain the standard of products and services provided to customers. This gap may occur because of the communication gap, poor technology, and inappropriate supervisory on productions in the industry.
This gap occurs because of many reasons in the industry, for example;
Firstly, the lack of teamwork to deliver services or products triggers an increasing delivery gap. Secondly, the employee’s lack of knowledge about the product or service grows the delivery gap. Thirdly, insufficient human resources extend this gap.
The additional reasons for increasing the policy gap:
- Role ambiguity and role conflict are unsure of your remit and how it fits others.
- Poor employee or technology fit – is the wrong person or system for the job.
- Inappropriate supervisory control or lack of perceived control – too much or too little control.
Delivery Gap in Service Quality Example-1
Netflix may experience this gap if it uploads a lower video-quality film. Customers prefer to watch movies with high-quality regulations like HDR. However, Netflix streams films with 4K at 2160p, which reduces the delivery gap.
The Following Example Has Been Adapted From ChatGPT 3.5
Delivery Gap in Service Quality Example-2
A delivery gap in service quality occurs when the actual service delivered to customers falls short of what was promised or expected.
For example, you order a package online and the estimated delivery time provided by the company is two days. However, the package doesn’t arrive until four days later. In this scenario:
- Expected Service: The company promised a two-day delivery service.
- Perceived Service: You perceive the service as poor because it took four days instead of two.
- Delivery Gap: The difference between the promised two-day delivery and the actual four-day delivery represents the delivery gap in service quality.
Factors contributing to this delivery gap could include logistical issues, delays in processing orders, or inefficient delivery routes. Such gaps can lead to customer dissatisfaction, reduced loyalty, and negative word-of-mouth.
Gap 4: Communication Gap
The communication gap refers to the difference between what the company advertises about the products and what the customer delivers. It occurs when the company cannot provide services or products according to the commitment. It is an essential dimension to maintain because it may lead to customer disappointment. The employees have to ensure an effective communication process is inevitable to reduce the communication gap in service quality.
This communication gap occurs for many reasons in the industry, including;
- Over-commitment.
- Lack of integration between communication and production department.
- Inadequate communications between the advertising teams and the operations department.
Example of Communication Gap in Se
Netflix may suffer this gap if it cannot telecast the HDR video it promised to offer. So, Netflix should not commit to customers if they cannot stream HDR video on the site.
Example Adapted From ChatGPT 3.5
Communication Gap in Service Quality Example
A communication gap in service quality occurs when there’s a disconnect or breakdown in communication between the service provider and the customer, leading to misunderstandings, unmet expectations, or dissatisfaction.
For example, you visit a restaurant and inquire about the ingredients of a dish because you have food allergies. The server assures you that the dish is free of certain allergens. However, when the dish arrives, you notice one of the allergens listed in the ingredients.
In this scenario:
- Expected Communication: You expected accurate and clear information about the dish’s ingredients to ensure it’s safe for you to consume.
- Perceived Communication: The information provided by the server was incorrect or incomplete, leading to a misunderstanding.
- Communication Gap: The disparity between what you were told by the server and the actual ingredients of the dish represents the communication gap in service quality.
Factors contributing to this communication gap could include a lack of training for staff on ingredient awareness, miscommunication between kitchen and service staff, or inadequate systems for conveying accurate information to customers. Communication gaps like this can erode trust, lead to customer frustration, and harm the reputation of the service provider.
Gap 5: Customer Gap in Service Quality
The customer gap is the difference between customer expectations and perceptions of the service. This customer gap might appear if customers cannot understand the importance of the services and products.
In sum, the customer gap in service quality refers to the difference between customer expectations and perceptions of the service provided. It highlights how customers’ perceived service quality may deviate from their expected service quality. The customer gap also arises when clients misunderstand the service quality. Many organizations are unaware of this gap, losing many customers overnight.
Example of Customer Gap Adopted From ChatGPT
Conclusion
The five gaps in service quality are Knowledge, Policy, Communication, Delivery, and Customer. The five gaps model of service quality is known as the gap model. The gap model of service quality analyzes gaps and problems between organizations and their customers. Customer gratification will come out if the industry adopts the gap model diagram, which is a significant factor for continual improvement as well as the business. Therefore, the service provides industries like hospitals, hotels, restaurants, entertainment & recreational companies, and education consultants and tourism agencies focus more on the gap model to improve customer satisfaction.