Types of Research Design- Different Types of Research Design & 10 Types of Research Design in Research.
Types of Research Design
Nobody can deny the importance of sophisticated research. Research is the process of discovering new knowledge and ideas. Recently, the researcher has become more advanced by skilled and trained. At present, researchers conduct the mixed method of research by applying both non-experimental and experimental designs. Usually, there are two types of research design such as experimental and nonexperimental research. Experimental research is divided into many designs, including Descriptive, Historical, Correlation, qualitative, et cetera. On the other hand, experimental research is divided into two methods: true experimental and Quasi-experimental research methods.
Difference Between Nonexperimental and Experimental Research
| Nonexperimental Research | Experimental Research |
| Firstly, Nonexperimental research determines the natural relationship between variables. | In contrast, experimental research investigates the cause-and-effect relationship between variables. |
| Additionally, the researcher does not control the setting of the study. | On the other hand, researchers control the setting of the study. |
| In this research design, researchers do not introduce external variables. | In this research design, researchers introduce external variables. |
| Researchers do not manipulate the independent variable. | Nonetheless, the researcher manipulates the independent variable methodically. |
| For example, Investigating the perception of the children in the COVID-19 pandemic. | For example, Testing the effect of the COVID-19 vaccine among children. |
| Usually, Nonexperimental research is both quantitative and qualitative. | On the other hand, experimental research is quantitative. |
| Nonexperimental research is intended to explain the subject’s characteristics, including the current situation, comparative position, and prediction. | However, experimental research is used to solve problems, create advanced innovation, and progress in medical science. |
Types of Research Design
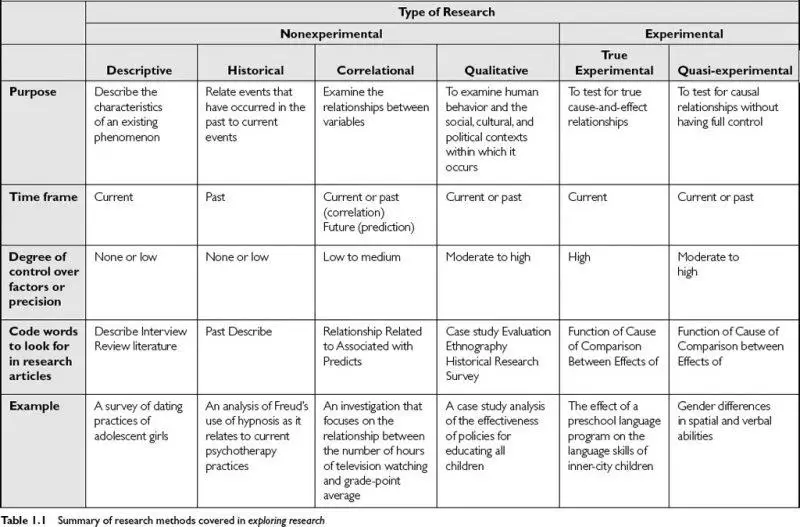
1. Nonexperimental Research
Nonexperimental research explains the researcher’s observation describing the natural condition of the study phenomenon. The nonexperimental research determines the normal relationship between variables but is not intended to identify the cause-and-effect relationship between variables. It only describes relationships between variables without testing causal relationships among them. This research is not involved in the manipulation of the independent variable. Therefore, it does not introduce any external variable, and variables are not manipulated. Researchers do not control the setting of the research.
For example, a researcher wants to investigate the relationship between the awareness of fake news sharing and the brand trust of Facebook among youth. Here, the researcher wants to determine the relationship between awareness of fake news sharing and Brand trust of Facebook. It does not indicate the causal relationship between variables.
Different Types of Research Design
The 10 Types of Research Design are:
- Quantitative Research Design
- Descriptive Research Design
- Correlational Research Design
- Historical Research Design
- Qualitative Research
- Case Study Research Design
- Mixed Methods Research Design
- Review Research Design
- Developmental Research
- Experimental Research Design
Descriptive Research Design
The descriptive research method describes the characteristics and features of existing phenomena at the time of research. It also provides a broad picture of the phenomena to convey a better understanding through the study. The time frame of the study is present. Descriptive research is the foundation of all other types of research. It does not involve control variables or treatments. However, the correlation between variables is characterized. There are many types of descriptive research, for example, Survey research, Correlation research, Developmental research (Longitudinal approach & Cross-section approach), Normative research, Naturalistic observational research, Comparative research, Data analysis research, Action research, etc.
For example, a researcher wants to survey students’ practice of social media-based citizen journalism. Based on the topic, the researcher should apply the descriptive research method to explain the feature of social media-based citizen journalism among students. Another example of the descriptive research design is ” the perception of Malaysia people on the use of social media to spread fake political news.”
Survey Research Design
Survey research examines the relationships and frequency between sociological and psychological variables. It assesses psychological factors such as beliefs, values, attitudes, prejudices, discriminations, opinions, and preferences.
Examples of the survey research are evaluating the following:
- Student’s attitudes toward the use of smartphones in the classroom.
- Teacher’s opinion in conducting online classes
- The perception of teenagers in the advantage of social media platforms
How to Conduct Survey Research
Any survey research begins with a general (flow) plan that shows the entire process of survey research.
- Clarify the purpose of the study
- Defining the sample plan
- Define a method also part of the interviewing session
Defining method stage of survey research will determine the answer to the following questions
- How will the questions be structured?
- What types of questions will be asked?
- How will the sample be defined?
- How will the data be collected?
4. Finally, Coding and scoring
Tools of the Survey Research- Interview
The interview is the primary tool of the survey research design. However, a Face sheet is an essential element to conducting an interview session properly. Face sheet information represents neutral information about the study respondent, such as age, gender, living place, educational level, income, etc.
Pros of the Face sheet—Neutral background information
- First, it helps establish rapport with the respondents or interviewees. For example, where did you study? How many siblings do you have?
- Secondly, it establishes data frames or characteristics.
Two Types of Questions For Interviewees.
- Structured questions in which respondents can give explicit answers.
- On the other hand, open-ended questions permit the interviewee to give elaborative answers.
Advantages of the Interview
- Flexibility in collecting data
- The interviewer can set the tone and agenda
Disadvantages of the Interview
- Expensive
- Lack of anonymity, so responses might not be honest
- Lack standardized questions
Process of developing an Interview
- Firstly, describe the goals of the project.
- Secondly, select an appropriate sample.
- thirdly, develop interview questions.
- Fourthly, train interviewers.
- Finally, Conduct interviews.
The Ten Essential Commandments of Interviewing
- Do not begin the interview cold.
- Remember that you are there to get information.
- Be direct.
- Dress appropriately.
- Find a quiet place to conduct the interview.
- Don’t give up if your interviewee doesn’t give a satisfactory answer the first time.
- Use a tape recorder.
- Make the interviewee a part of the interview.
- To be a good interviewer, practice more.
- Thank interviewees for their help, and ask for questions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Survey Research
Advantages of Survey Research design
- Permits researcher to get a broad picture (good generalization)
- Efficient data collection
- Can yield very accurate results
Disadvantages of Survey Research design
- Bias (Interviewer bias and Interviewee bias)
- Non-response
Correlational Research Design
Correlation research design describes the relationship between two variables. It identifies the associated factors of the phenomenon that are co-related to one another. It also discovers how connected these factors are to each other and the strength of the relationship between variables. A numerical index measures the strength of the relationship called the correlation coefficient. The time frame of this research might be present or past, and future. Actually, it shows the past or present relationship between variables and offers predictions for the future. It implies that variables share something in common.
For example, a researcher wants to identify the relationship between social media addiction among students and their results in the final exam. Based on the topic, the researcher should use a Correlation research design to identify the relationship between social media addiction among students and their results in the final exam. Another example of the correlation research design is “Influence of Teenager’s Awareness of Fake News Spreading and Perceived Message Trustworthiness towards The Brand Trust of Twitter.”
Correlation Coefficient
The correlation coefficient measures the degree of linear relatedness between two variables. There are two types of correlation, for example, positive correlation and negative correlation. The positive correlation is good, yet the negative correlation is not bad. basically, both positive and negative correlation indicates the direction of the relationship; nothing else. The absolute value of the coefficient indicates the strength of the relationship. Variance increased when a stronger relationship between variables existed. Varies between –1.00 and +1.00.
Historical Research
Historical research investigates the past event and establishes the present concept of the event. It also describes the past fact of the event that affects the current situation. The objective of the historical research method is to collect and evidence from the past event to develop a fact that defends or refutes the hypothesis. Historical research is another term of historiography.
For example, researchers desire to identify the historical progress of women’s education in Malaysia. So, the historical research design will be the option to conduct the research.
Qualitative Research
Qualitative research design examines human behavior in the social, political, and cultural context in which it occurs. The qualitative research method is part of nonexperimental research; therefore, it never tests the cause and effect relationship between variables. The researcher applies different paradigms and tools to conduct qualitative research. The most important tools of qualitative research are interviews, ethnography, case studies, and ethnography. It provides nonnumerical qualitative data that is also known as primary data. In qualitative research, the researchers focus on the content of informants rather than the frequency of particular content. Here, the informant is the interviewees or people who the researcher has interviewed. The time frame is present and past.
For example, a researcher desires to identify the effectiveness of the government policy to educate all girl-children. So, they will implement the qualitative research method to identify the effectiveness of the government policy to educate all girl-children in the country.
Experimental Research
- Tries to discover causal relationships
- Two types:
- True experimental research
- Quasi-experimental research
True experimental Research
- For example, Comparing two different techniques
Quasi-Experimental Research
- For example, Participants are preassigned to groups
- Useful when the researcher cannot manipulate variables.
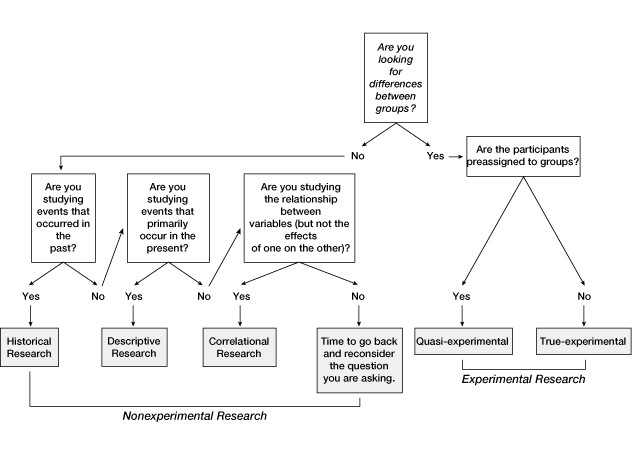
When to use what research design
Research design cheat sheet
The research design cheat sheet attached below will
Basis Research Design and Applied Research Design
Basic research has no instant execution to the world. Usually, researchers apply these basic types of research design to expand the knowledge of certain phenomena. Pure research is another name of basic research. For example, a study looking at how the online class during the COVID-19 pandemic increases depression among students. Researchers are intended to expand knowledge by this study or research; it has no instant application to society.
Applied research has immediate execution or application to the world. Researchers use this research to solve the problem. Therefore, it has an immediate practical use to resolve the problem or answer the question. For example, the research to invent the COVID-19 vaccine is an instance of applied research; because it has immediate application to the world.