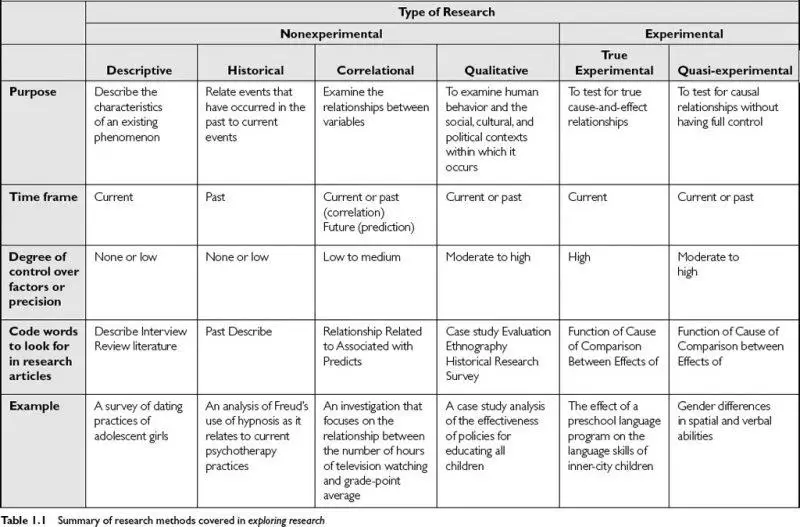
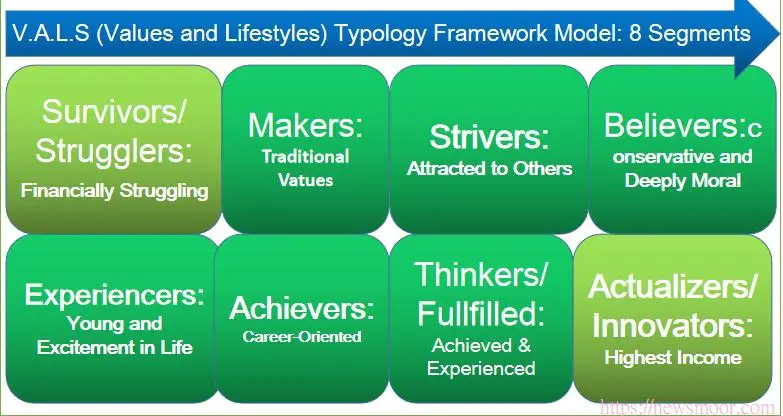
VALS Model in Consumer Behavior Examples. The eight elements of the VALS Segmentation Model are survivors, makers, strivers, believers, experiencers, achievers, thinkers, and innovators.
VALS Model
The VALS Model categorizes people into eight groups based on their lifestyles, psychological characteristics, and consumption patterns. It is also known as the Vals framework of psychographic segmentation, which segments people for marketing purposes. It is the most crucial framework for understanding clients’ values and lifestyles. Therefore, it is called the Vals audience segmentation model in consumer behavior. The VALS is the acronym for Values, Attitudes, Lifestyles, and psychographic factors.
VALS-2 is the extended model that renames strugglers as survivors, actualizers as innovators, and fulfilled as thinkers.
However, demographic and geographic psychographic segmentation is the most significant market segmentation technique for dividing people into homogeneous subgroups.
In 1978, the research institute Stanford established Maslow’s hierarchy of needs to develop a VALS (Values and Lifestyles) typology to categorize American consumers. In 1989, they created a quietly modified system that takes into account individuals’ lifestyles, psychological characteristics, and consumption patterns.
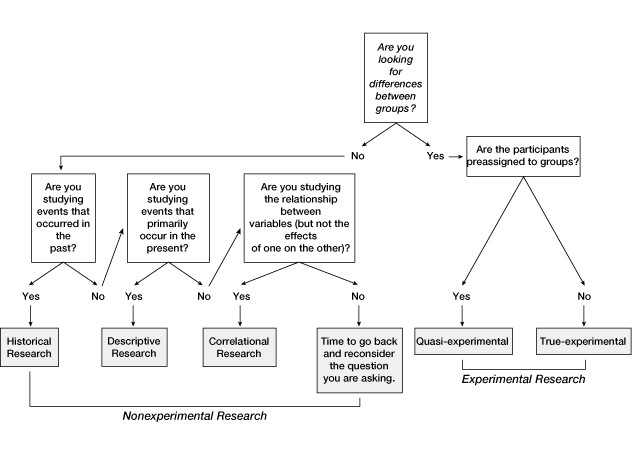
The difference between the VALS and the VALS-2 Model
The VALS model includes the following eight elements: Survivors, Makers, Believers, Achievers, Strivers, Experience, Thinkers, and Innovators.
Similarly, the VALS 2 Model divides people into eight categories: Strugglers, Strivers, Makers, Believers, Achievers, Experience, Fulfilled, and Actualizers.
VALS Framework Components
Eight Segments of the VALS Model are:
- Survivors
- Makers
- Strivers
- Believers
- Experiencers
- Achievers
- Thinkers
- Innovators
1. Survivors/ Strugglers
Firstly, Survivors or strugglers are financially needy people. In contrast to innovators, they are low-skilled, educated, without strong social bonds, and passive. They avoid risk because of feeling powerless. It seems their primary motive is to meet safety and security requirements.
For example, students are survivors because they are financially needy and powerless.
2. Makers
Makers are practical people with strong traditional values, constructive skills, self-sufficiency, and enough income. They live within a conventional context of family, practical work, and physical recreation. Makers are suspicious of new ideas, politically conservative, and respectful of government authority but resentful of government intrusion on individual rights.
For example, religious leaders uphold traditional values and operate within society’s conventional context.
3. Strivers
Strivers are attracted to others who exhibit qualities they don’t have but admire. They inquire about motivation and self-definition. They expect to achieve goals through wealth and often feel that life has dealt them a bad hand because of their lower income. Strivers feel easily bored because they are very impulsive.
For example, an unemployed person is looking for a job after completing graduation. Therefore, job seekers are real-life examples of strivers.
4. Believers
Believers share a very conservative, profoundly moral mentality with makers. They seem like makers because of their conservative, traditional values. They follow established routines organized by the family, social groups, and religious organizations. Their income, education, and energy are enough to meet demands.
For example, a retired government employee. The former person is an example of a believer.
5. Experiencers
Experiencers are young, energetic, enthusiastic, impulsive, and rebellious. They seek a variety of excitements but are politically uncommitted and highly ambivalent about their beliefs. They like being associated with outdoor, sports, recreational, and social activities.
For example, a teenager is an experience in the Vals segmentation model.
6. Achievers
Actually, achievers are work-oriented, successful people. They like to feel in control of their lives. They are also deeply committed to their work and to keeping promises to family, society, and their career. Achievers respect authority because they prefer to keep their promises, but are politically conservative.
For example, an employed person is an achiever. The CEO of the company, an artist, a political leader, and a businessman, is an example of an achiever in the Vals segmentation model.
7. Thinkers/ Fulfilled
Thinkers are enough adults, mature, well-educated, professional people with satisfying incomes. They stay current with international and national events and often deepen their knowledge. They are usually calm and self-assured because they depend on their decisions.
For example, a successful businessman is a thinker in the Vals segmentation model.
8. Innovators/ Actualizers
Finally, Innovators are highly successful people with self-esteem and considerable resources compared to strugglers. Innovators are supervised by both their principal and the dreams around them. They want to be government and business leaders because they have enormous power and social consciousness.
For example, a political leader is an innovator who can change society with power. Therefore, a political leader is an example of an innovator in the Vals segmentation model.
Conclusion
The Eight Categories of the VALS Segmentation Model are survivors, makers, strivers, believers, experiencers, achievers, thinkers, and innovators. The VALS Framework has become a crucial tool for targeting audiences in political campaigns and product marketing. Many organizations conduct digital marketing campaigns on social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and YouTube.