Lean Canvas Example: Lean Canvas Business Model Example in 2022. Lean Canvas Model Example. Example of Lean Canvas Business Model.
Lean Canvas Model
The Lean Canvas model refers to a business plan template outlining nine essential elements of the new business. In 2010, Ash Maurya developed the one-page business template and termed it the Lean Canvas Model. The lean canvas model assists entrepreneurship in pre-assume the nine essential critical ideas related to the Business.
Lean Canvas is adapted from Business Model Canvas introduced by Alex Osterwalder in 2005. Therefore, the lean canvas model is also known as the Lean Canvas Business Model. The alternative names of the Lean Canvas are the Lean Canvas Model, Lean Business Canvas, Lean Business Model, Lean Startup Canvas, and Lean Canvas Online.
Lean Canvas Business Model
Lean canvas business model refers to a one-page business plan template describing nine key idea elements related to the market: problem, solution, unique value proposition, unfair advantage, customer segments, key metrics, channels, cost structure, and revenue structure. However, the additional elements of the lean canvas model are existing alternatives, high-level concepts, and early adopters. It replaces detailed business plans with a concise and single-page business template.
History of the Lean Business Model
Lean Canvas Business Model is adopted from Business Model Canvas, and Business Model Canvas was adapted from Business Model Ontology. In 2004, Alex Osterwalder introduced Business Model Ontology for digital business. After one year, In 2005, he introduced the Business Model Canvas based on the previous theory “Business Model Ontology.” In 2010, Ash Maurya introduced the Lean Canvas model for entrepreneurship to start a new business with concise information regarding the business, including problem, solution, target audiences, competitors, and so more.
Lean Canvas Example
The example of the lean canvas has been presented in this article so that students and viewers can understand how to create a lean canvas business model template for new businesses. Sometimes, lecturers provide assignments to students on how to create a lean canvas model template for starting up a new business.
Lean Canvas Example – Word File Download Link
Lean Canvas Business Model Example
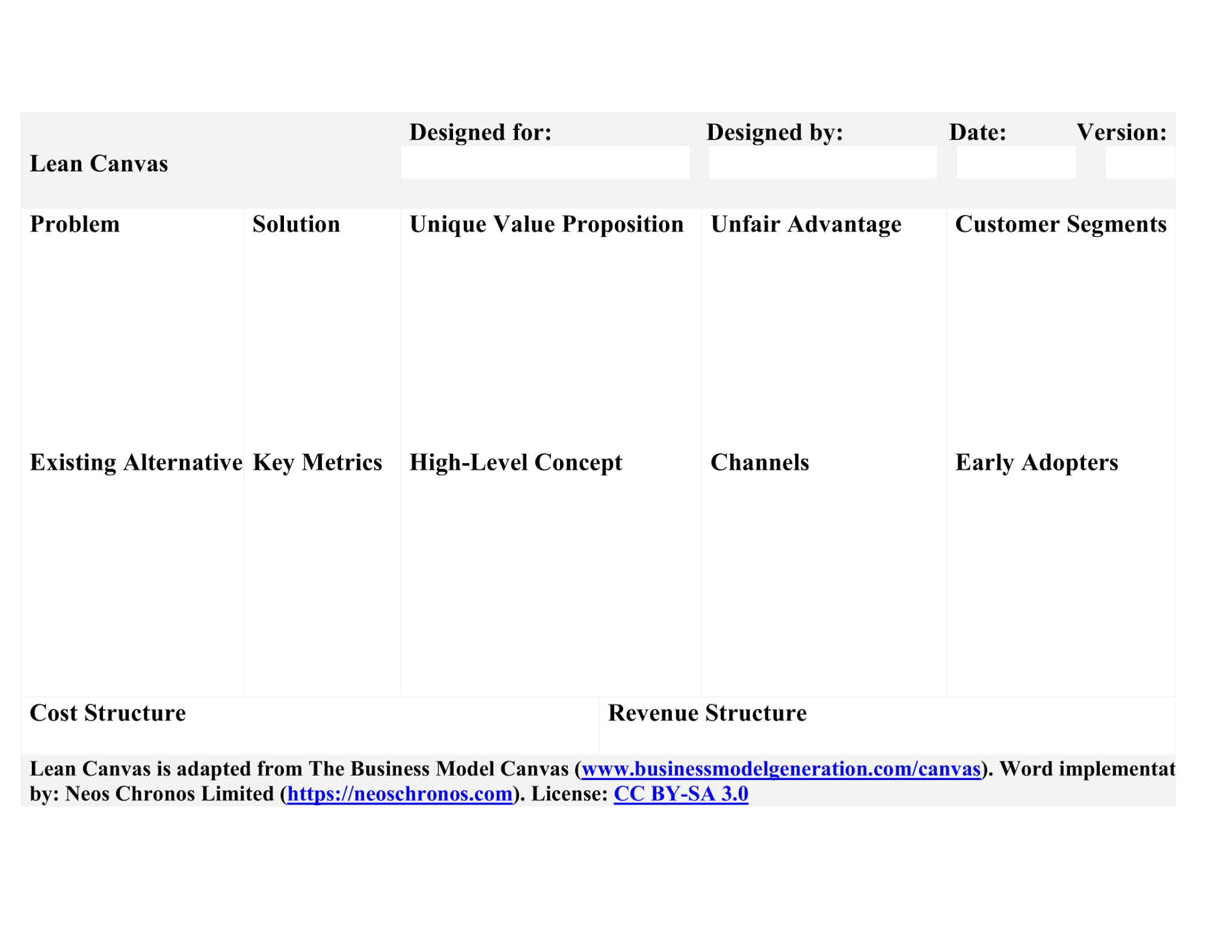
How to Fill Out a Lean Canvas
Lean Canvas Business Model Example
BambooS- An Eco-Friendly Company in Malaysia
BambooS is an environment-friendly company in Malaysia that produces bamboo straws. Nowadays, restaurants do not provide plastic straws due to polluting the ocean extremely. So, the BambooS has come up with straw made of Bamboo. These products are cheap, portable, reusable, and decomposable. The government of many countries, including Malaysia, has given directives to reduce the use of plastic. Therefore, many restaurants, including McDonald’s, KFC, PizzaHut, and Nando’s, do not provide plastic straws. It is challenging to drink juice without a straw; hence BambooS has started to sell portable and reuseable bamboo straws.
It is an example of a Lean Canvas template filled out by BambooS, an eco-friendly company in Malaysia. The student at University Putra Malaysia students completes these lean startups for assignment purposes. However, entrepreneurship also follows the same instructions to complete the lean canvas template. Hopefully, it will assist employees in obtaining ideas on how to fill out a lean canvas.
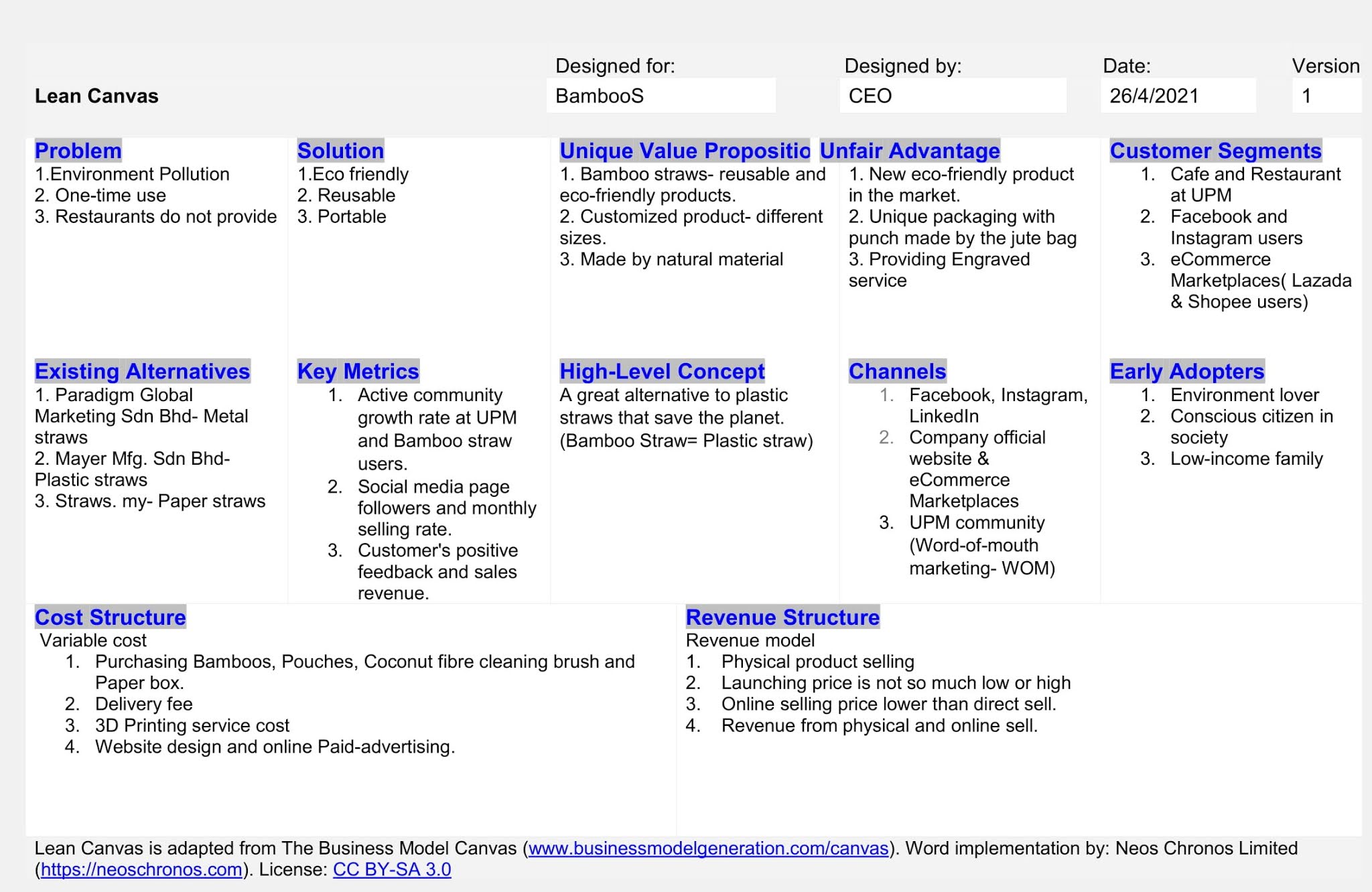
The Lean Canvas example will help students and employees to know how to fill the lean canvas word template. The author has attached a blank and filled lean canvas word template for entrepreneurship. It will definitely assist the new businessmen to start new businesses wisely.
Elements of Lean Canvas
The 9 Elements of the Lean Canvas Business Model are:
- Problem
- Solution
- Unique Value Proposition
- Unfair Advantage
- Customer Segments
- Key Metrics
- Channels
- Cost Structure
- Revenue Structure
1. Problem
Firstly, as an entrepreneur, you have to identify existing problems that you want to solve with the new products and services. It is crucial to find out at least three essential problems that your product and service will completely solve. Therefore, the entrepreneur needs to list down three problems under the problem section in the lean canvas.
For example, according to BambooS’ lean canvas, the three problems are environmental pollution, one-time use, and restaurants do not provide plastic straws now. So, BambooS is a new company that has outlined these three problems.
2. Solution
The solution is the goal of your business. So, you have to outline the solution to the problems mentioned in the problem section. The solutions have to be concise, significant, and capable enough to resolve the problems.
For example, according to figure 3, the three solutions are eco-friendly products, reusable and portable. These three proposed solutions are sufficient to resolve the problems.
3. Unique Value Proposition
A unique value proportion refers to a commitment of value that the product or service will definitely provide. It is the fundamental reason for what the customer will buy the products or services. So, you have to differentiate your product or services from others to grab customers’ attention. The unique value proposition also represents the company tagline, somewhat relevant to the mission and vision.
For example, the unique value proposition of the BambooS products is bamboo straws- reusable and eco-friendly products, customized products- of different sizes and made of natural material. The tagline is Grab me with zero pollution to save the planet.
4. Unfair Advantage
Unfair advantage denotes something of the company that competitors will not be able to replicate. The exceptional quality of the product or services makes the company distinguished. However, it would help if you had to remember that your unfair advantages are sustainable.
For example, BambooS company’s unfair advantages are the new eco-friendly product, unique packaging with a jute pouch bag, and engraved service. These unfair advantages are sustainable and exceptional that no company offers now in Malaysia.
5. Customer Segments
The problems and customer segments are interconnected issues; because the customers create problems. So, the problem can not endure without customers. Additionally, customers are the consumer of your products and services. Therefore, you have to analyze your target customer before identifying the problems. Additionally, you have to keep in mind some issues related to the customers, such as where your customer lives, the economic conditions, the demographic factors, and so more. Customer segmentation is also known as geographics, psychographics, and demographics in marketing.
For example, the BambooS authority has chosen the University Putra Malaysia to target audiences. Additionally, they have included Cafe and Restaurant at UPM, Facebook and Instagram Users, and eCommerce Marketplaces (Lazada & Shopee Users) in the customer segment section.
6. Key Metrics
Key metric refers to the factors that the company owner measure to run the business properly. The key metric drives the performance of the business, so the owner must need focus on these factors to keep the record. Actually, key metrics are the statistical data related to market share, consumers, number of new users, revenue per customer, and so more. For example, how many followers of the social media pages and the monthly sales revenue. Sometimes, management invests in marketing based on the key metrics data. Every company invests to get
For example, the three key metrics of the BambooS company are active community growth rate at UPM and bamboo straw users, Social media page followers and monthly selling rate, and customer positive feedback vs. sales revenue. These data will definitely help the authority to adopt a strategic marketing policy to increase sales revenue. If the company can sell the product properly on social media platforms compared to offline sales, they definitely focus on increasing followers on social media pages to earn more.
7. Channels
Channels are the media in which management reaches the customers. The channel plays an essential media in conducting a marketing campaign. Many types of channels or media allow you to reach customers as well as regulate campaigns. The two most important types of communication channels are offline and online channels. The offline channels are face-to-face marketing, placard, banner, festoon, newspapers, TV, and radio.
On the other hand, online media are social media platforms, e-commerce sites, and website traffic. Usually, the market analyzer researches the customer’s background to decide which channels they want to use to conduct a marketing campaign. Nowadays, most companies utilize e-commerce and social media channels to conduct digital marketing. The covid-19 pandemic has changed people’s lifestyles, business patterns, and education procedures. Many organizations use online webinars to conduct organizational meetings and regulate business properly.
For example, the BambooS’ authority has chosen Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, company’s official website, Lazada, Shopee, and Word-of-mouth marketing- WOM for the UPM community.
8. Cost Structure
Cost structure refers to the costs of launching a new business, for example, equipment acquisition costs, marketing costs, operational costs, and website domain and hosting costs. According to a statistic report, around 90 percent of new companies fail to operate due to not considering the total cost of starting and driving the business. Therefore, the owner needs to launch a new business after arranging the full payment.
For example, the BambooS’ authority outlines the sectors where they have to initially invest money to launch the business. The list is following:
- Purchasing Bamboo, Pouches, Coconut fiber cleaning brush, and Paper box.
- Delivery fee.
- 3D Printing service cost.
- Website design and online Paid-advertising.
9. Revenue Structure
Revenue is the key performance indicator of a company. The factors of the company’s performance and the revenue has a positive relationship that influences each other. Revenue structure is also known as a revenue stream. You have to assess and set the price of the product before releasing it to the market. Many companies make the mistake of setting a meager price when launching the product in the market.
The minimum price may bring an adverse impact on business. It damages the future probabilities of your business. Firstly, you might lose a customer when increasing your product price later. The price module must be tested several times through multiple ways to catch the market by the products. The revenue structure depends on the type of business, whether you want to sell products or services. It also depends on whether the company is online platforms based or physical market-based.
For example, BambooS includes the factors to the revenue model, such as physical product selling, launching price is not so much low or high, and online selling price lower than direct selling.
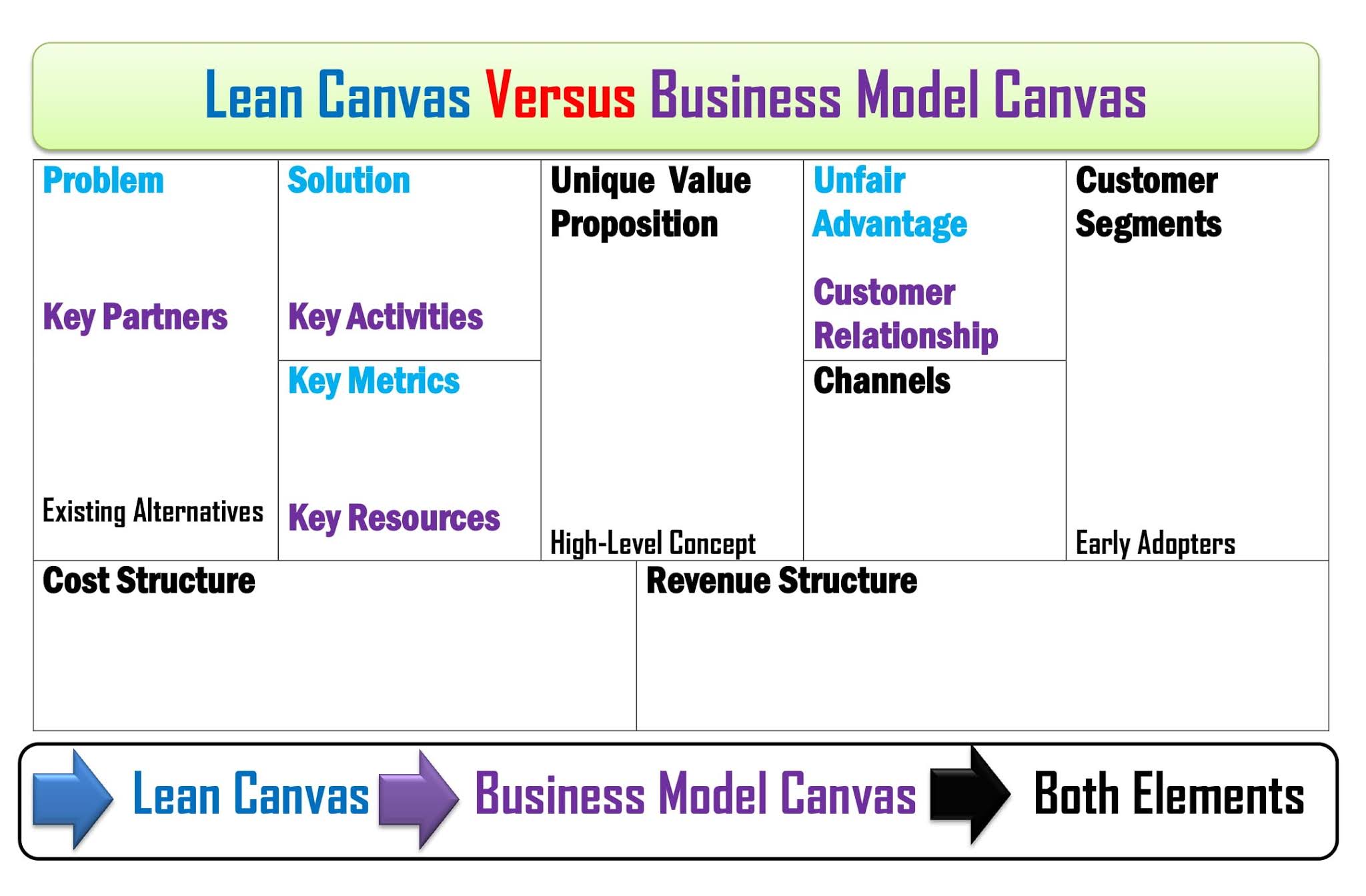
Difference Between Lean Canvas and Business Model Canvas
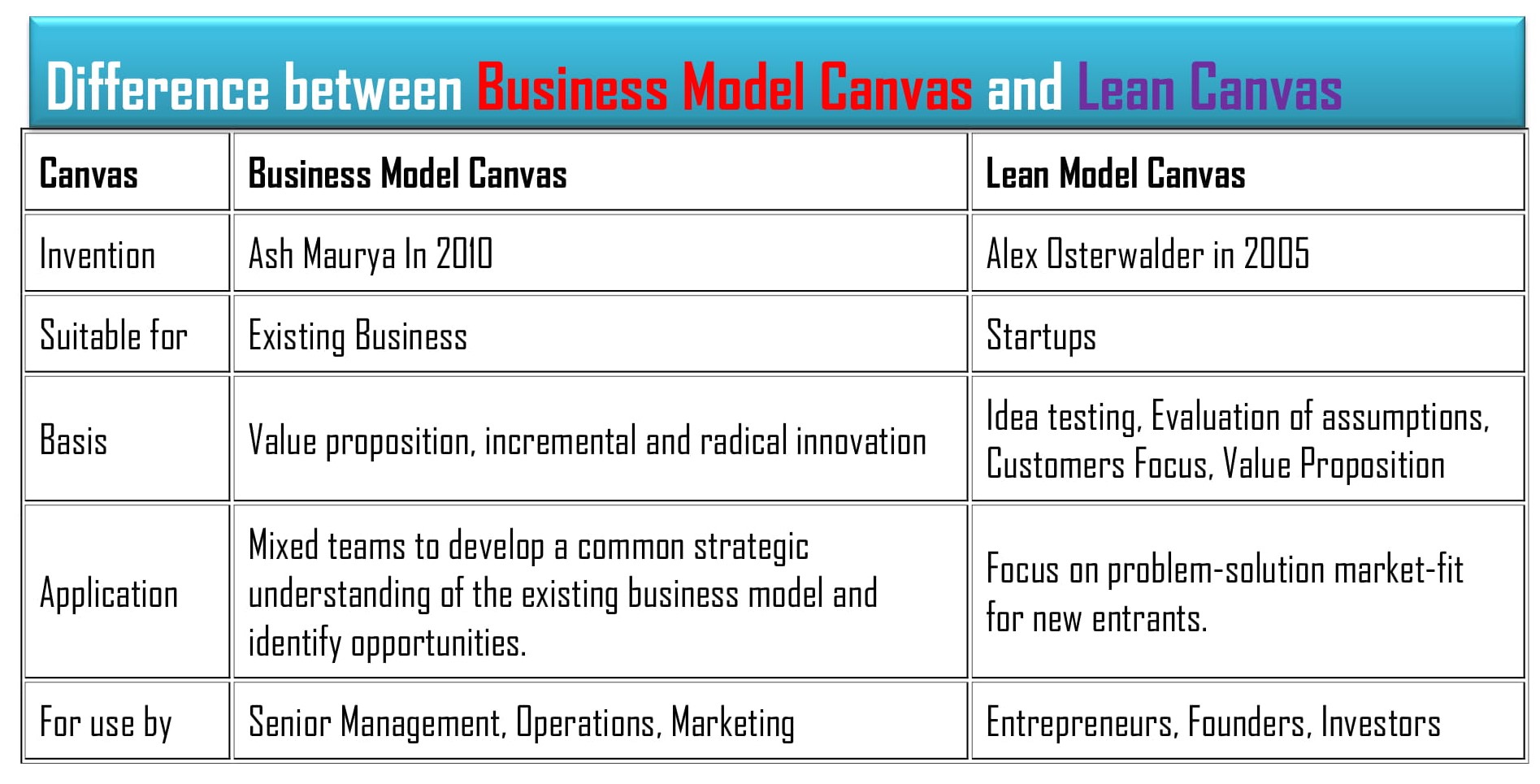
Firstly, Ash Maurya developed the Lean Canvas Model in 2010, whereas Alex Osterwalder introduced the Business Model canvas in 2005.
Secondly, the nine basic elements of the lean canvas model are the problem, solution, unique value proposition, unfair advantage, customer segments, key metrics, channels, cost structure, and revenue structure. On the other hand, the nine fundamental elements of the Business model canvas are customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure.
Additionally, the Lean canvas model is suitable for new entrepreneurs who want to start a new business and startup. In contrast, Business Model Canvas is suitable for an existing business.
Usually, entrepreneurs, founders, and investors of the company apply the lean canvas model. However, the senior manager, marketing manager, and operation manager utilize the business model canvas to yield positive outcomes from the business.
Moreover, applying lean canvas aims to identify the problem and solution to fit new entrants. On the other hand, using the Business model canvas understands the existing market and identifies opportunities.
Furthermore, the basis of the lean canvas model indicates testing ideas, assessing the assumption, and focusing on the value proposition. In contrast, the basis of the Business model canvas shows advanced and progressive innovation.
Lean Canvas Versus Business Model Canvas Example
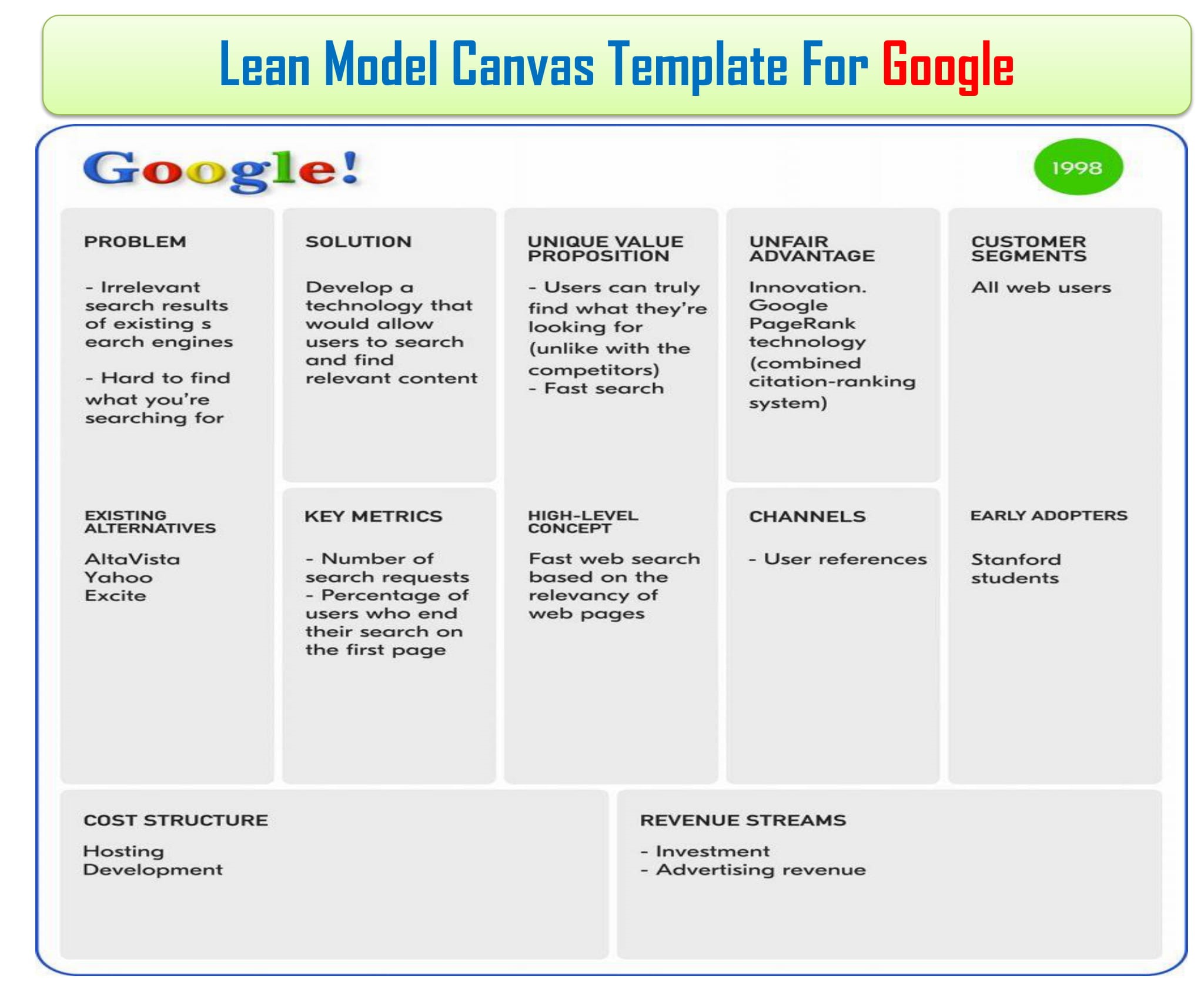
Lean Canvas Business Model Example For Google
A sample of a lean model canvas of Google has been presented here to better understand how to fill out the template.
Lean Canvas Business Model Example For YouTube


