Lewin’s Change Model Real-Life Example is Netflix. The Example of Three Stages of Kurt Lewin’s Change Management.
Lewin’s Change Model
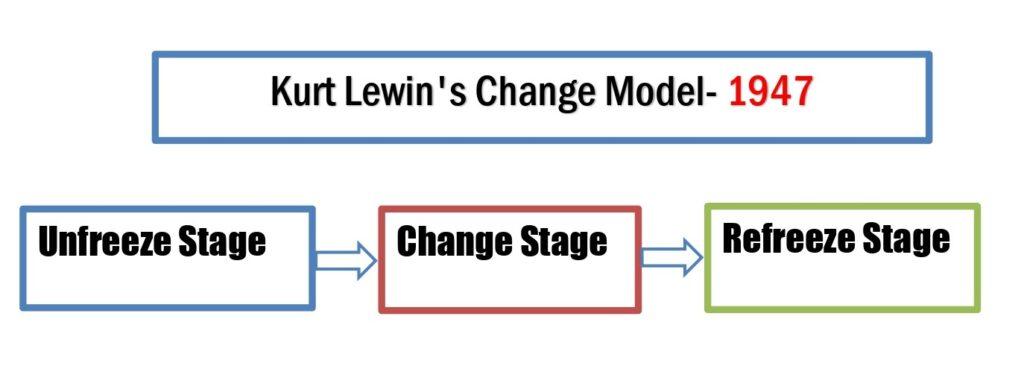
Lewin’s change model comprises three stages of management change theory. The three stages of Lewin’s change management model are unfreezing, changing, and refreezing. Therefore, the alternative name of the Lewin change management model is the unfreeze-change-refreeze theory. Lewin’s change model is one of the most well-known change management models that describes organizational transitions. It can explain how and why individuals accept organizational changes, such as business directions, technological, cultural, and leadership changes.
Who and When Established Lewin’s Change Management Model?
Kurt Lewin established the three stages of the organizational change model in 1947.
In 1947, Kurt Lewin introduced the three stages of the change management model, now known as Lewin’s change model. Subsequently, researchers and scientists developed numerous models to describe organizational change, including Kotter’s Change Management Model, Kübler-Ross’s Five-Stage Change Model, the ADKAR Change Model, McKinsey’s 7-S Change Model, and Lewin’s Change Model. However, Lewin’s change management model has become the most popular for its simplicity and fewer phases, for example, unfreeze, change, and refreeze.
Researchers have developed multiple theories based on Lewin’s change management model. So, it is the foundation of all modern change management theories. For example, John Kotter’s 8-stage change model was developed from Lewin’s change model. The management system is more complex than it was when the model was introduced. Therefore, Lewin’s change management model is controversial in modern organizations. It has excellent theoretical significance in the research arena rather than practical importance.
Lewin’s Change Model Real-Life Example
Many reputed companies apply Lewin’s change management model to survive in the current situation. For example, Netflix has used a change model to adjust to the digital era. Netflix’s organizational change process handled the force of organizational change to achieve a competitive advantage. Netflix transformed its business strategy in 1998 1998 and 2007. The management encountered multiple barriers to getting outcomes. They are now among the most successful companies globally. Netflix is a real-life example of Lewin’s change management model. It is known as Lewin’s Change Model Business Example.
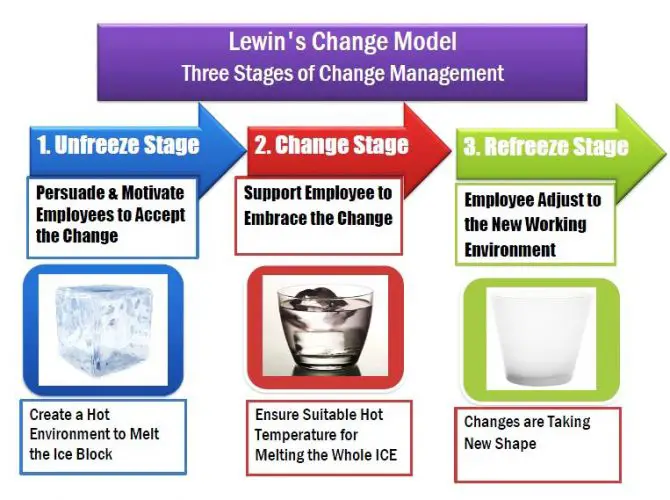
Lewin’s Change Model Stages
Three Stages of Change Management are:
- Unfreeze stage
- Change stage
- Refreeze stage
Unfreeze Change Refreeze
1. Unfreezing Stage of Change
Unfreezing is the initial stage of Lewin’s change management model. At this stage, employees mentally prepare to accept organizational change. In the management system, the unfreeze stage involves breaking down existing circumstances to facilitate organizational change. Employees are usually comfortable with the organization’s current state; therefore, some do not readily accept management changes due to uncertainty. The unfreezing stage consists of educating people about opportunities for organizational change. The organization should implement a change-management communication strategy to prepare employees for the change.
The key point of this stage is to compel employees to accept management change through effective change communication. Maintaining effective communication within management is essential to persuading employees to accept change. Employees will receive the change if they understand that the new things cannot prevent the company or organization from surviving. Additionally, they must recognize that change is essential to sustain the organization and to achieve competitive advantage.
A high level of positive motivation among employees helps to understand the reasons for organizational change and development. Next, the organization needs to persuade stakeholders that the change will benefit everyone. Some people will receive it quickly, whereas others will initially deny it. Finally, everyone will identify the motivation to make the change.
Communication During the Unfreeze Stage
The primary communication objective is to prepare stakeholders, employees, and the organization to accept the change – “Readying” the organization. However, resistance will increase with the magnitude of the change and its impact on the organization. Effective communication can overcome resistance. To ‘ready’ the organization to accept the change, it is essential to declare the objective of the change. Additionally, you must ensure that everyone in the organization knows what will happen and why. Effective communication is essential for identifying the difference between actual and desired outcomes. The first message or declaration should come from the organization’s top-level management to avoid communication conflicts.
2. Change (Move) Stage
Change is the second stage of Lewin’s change management model. It is the middle stage of the three-phase change management model. Actual changes occur when everyone in the organization accepts the change with positive motivation. Employees adapt to the new work environment. Changes may be major or minor, depending on the organization’s needs. The organization must provide sufficient training and support for the employees to embrace the changes. It is the stage of implementing the change process; therefore, many issues must be addressed consciously. Some employees may spread misleading information due to having insufficient knowledge about organizational change. So, the organization needs to practice an effective communication process to avoid unwanted issues. However, employees will be focused on practicing the new work.
Communication During the Change Stage
The organization should ensure effective communication among employees to reduce uncertainty and organizational communication noise. People may spread disinformation and lies when they have limited information about the change process. Therefore, the communication must be more specific than in the previous phase. Communication at this stage is essential to provide authentic, accurate, and detailed information about what will happen to those with less detailed information about implementing changes. Finally, it distributes the new responsibility among the individuals assigned within the organization.
3. Refreezing Stage of Change
The refreezing stage of change is the third and final stage in Kurt Lewin’s change management model. At this stage, employees adjust to the change in management on a daily basis. Refreezing is a slow process of adopting the new culture and atmosphere of the corporate workplace. Employees and stakeholders may take considerable time to adapt to the new systems. The pace of the practice among employees determines the time of the refreezing stage. So, refreezing is the most crucial stage in the Lewin change management model. New attitudes and behaviors among employees become institutionalized as the norm within the organization. Finally, everyone starts to feel comfortable, as in the previous stage before unfreezing.
Communication During the Refreeze Stage
The communication process should address employees’ questions regarding rewards, control, efficiency, and roles within the relationship. At this stage, information flow should be concrete, continuous, and multidirectional to ensure that employees have a sufficient understanding of the personal associations with the change. Unavoidable misunderstandings may occur in this phase, so communication should focus on making the transition successful.
Lewin’s Change Model Example
For example, an ice block cannot be reshaped without melting it. So it would be best if you created a hot environment to melt the ice block. The temperature must exceed 32°F (0°C) to melt ice. So, here, increasing the temperature denotes the unfreezing stage.
According to Lewin’s theory, unfreezing refers to the preparation for adopting new workplace norms. It is the initial stage of preparing to accept the change. The management needs to motivate employees to accept change.
It will take time to transform the entire ice block into water. Keep the glass isolated and ensure the temperature is sufficiently high to melt ice. When the ice block completely transforms into water, pour it into a new pot to give it a unique shape. Here, pouring water into a glass constitutes a change of steps or a transition to a new stage. Melting the ice denotes the change stage of Lewin’s theory.
According to Lewin’s theory, change refers to the adoption of new norms and subsequent change. Thus, the employee begins to adapt to and accept the workplace’s new culture.
Finally, store the glass in a cold place to refreeze the water. It is the process of freezing water to transform it into a new solid form. It is called the refreezing process and the final stage of Lewin’s change management model.
Refreezing refers to the process of adapting to new workplace norms. The employee has already accepted the change and adapted to the new environment.
The model summarized that successful management change is accomplished through a three-stage process: unfreezing, changing, and refreezing.
Lewin’s Change Management Model: Real-Life Example
For example, the educational institution has closed due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Therefore, all organizations, including educational institutes, decided to conduct virtual or online classes to ensure the continuation of education for students. These educational institutions are using online videoconferencing platforms, such as Zoom and Google Meet, to conduct virtual classes and organizational meetings. It was a new experience for lecturers; therefore, they were afraid of uncertainty and interested in taking online courses. However, the university authorities compel them to accept the change.
The university administration maintains effective communication via social media platforms to motivate employees to effect change. They believed the organizational change would confer competitive advantages, as other educational institutions had adopted it. Finally, they accept the change and adapt to the new working environment. It is a perfect example of Lewin’s Change Theory.
Lewin’s Change Model Pros and Cons
Lewin’s Change Management Model Strengths and Weaknesses
Lewin Model Advantages
Firstly, Kurt Lewin’s model is straightforward to understand; any organization can implement it efficiently. Management does not need to hire experts to implement the model. Existing employees will be able to apply it and evaluate the outcomes. It has only three stages: unfreeze, change, and refreeze, so it is easy to understand and apply. For example, the McKinsey 7-S model has seven elements that are challenging to implement.
Lewin Model Disadvantages
Firstly, refreezing takes a long time to adapt to new norms. Additionally, many employees leave their jobs due to uncertainty about the latest norms and the work environment. Lewin’s theory excludes many crucial elements, such as staff, structure, strategy, system, and style.
Kurt Lewin 1951 References
Citation for this Article (APA 7th Edition)
| Kobiruzzaman, M. M. (2026). Lewin’s Change Model- Lewin’s Change Management Model of the 3-Stage. Educational Website For Online Learning https://newsmoor.com/lewins-change-model-3-steps-management-change-and-communication/ |