Active and Passive Audience Definition, Theory, and Differences. Examples of Active and Passive Audiences.
List of Contents
Active Audiences
Active audiences actively receive media information and make sense of the messages based on their social and personal contexts. They listen to the media messages instead of hearing them. However active audiences receive media information actively, and the act of receiving media information is natural. So, active audiences pay full attention to receiving information and interpret it to give feedback. The most common listening styles are people, content, action, and Time-oriented listening.
Examples of Active Audiences
For example, people are the active audience who comment on social media content to express opinions.
Another example, based on the story shared in the example of the active and passive audience below, Ela is an active audience who scrutinizes the messages before accepting them and always tries to provide feedback.
Characteristics of Active Audiences
Active audiences actively listen carefully to provide feedback, making them complicated and critical thinkers. Additionally, they have good schemata. Feedback is an essential component of interactive communication.
Passive Audiences
Passive audiences are those who watch and observe the media information without making sense. Hence, they are recognized as inactive receivers. Passive audiences have low motivation to process information, low ability to process information and focus on simple cues (e.g., appearances instead of content)
Examples of Passive Audiences
For example, passive audiences dislike commenting on social media content. Audiences like to watch Television and read newspapers without providing opinions. They prefer a linear communication process where feedback is not essential.
Another example, based on the story shared in the example of the active and passive audience below, Bela is a passive audience that accepts the message without challenging them.
Characteristics of Passive Audiences
The Passive audience is inactively involved in hearing something rather than listening. Passive audiences merely observe the message; therefore, they are cognitive misers who are lazy to think.
Examples of Active and Passive Audiences
For example, Ela and Bela are siblings watching the news on television. The news reporter is providing tips on how to stay healthy. Ela actively listens to the news reporter’s tips to follow them. Then, she asks her sister Bela to confirm whether these tips work or not. In contrast, Bela accepts those tips readily. Here, Ela is an active audience who is a critical thinker. Therefore, she carefully focuses on the news presenter’s dress, speaking style, and messages’ meaning.
On the other hand, Bela watches the news without focusing on the content of the message. Here, Bela is a passive audience who is a cognitive miser. Therefore, she does not focus on interpreting the message; she only focuses on the news reporter’s appearance. As a result, she believes the news reporter’s tips quickly and becomes manipulated.
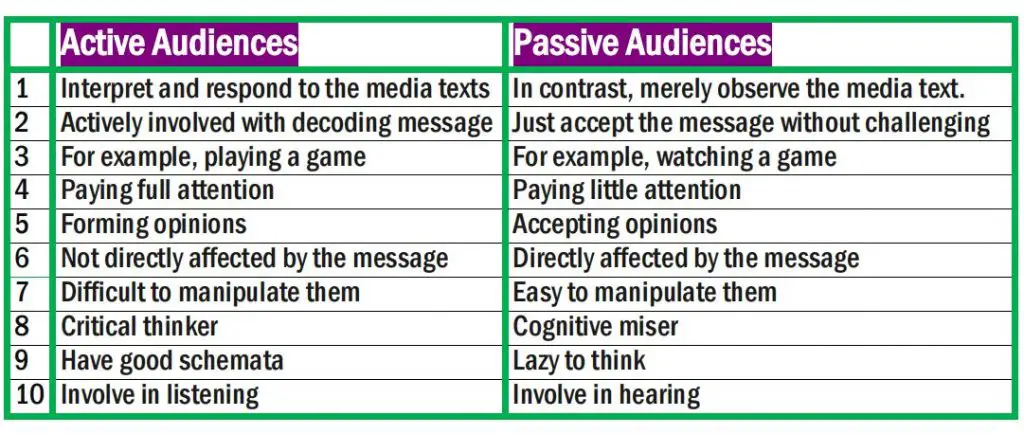
Difference Between Active and Passive Audiences
| Active Audiences | Passive Audiences |
| Firstly, active audiences interpret and respond to the media texts | In contrast, Passive audiences merely observe the media text. |
| They decode and evaluate the message. | On the other hand, they accept the message without evaluating it. |
| Active audiences form opinions and provide feedback in communication. | The passive audiences accept their opinions only. |
| Active audiences pay full attention to listening to the message. | In contrast, passive audiences pay little attention to hearing the message. |
| For example, Ela scrutinizes messages received from the news reporter rather than accepting them directly. | For example, Bela accepts messages received from the news reporter without scrutinizing them. |
| The message cannot affect the active audience directly. | The message affects the passive audience directly. |
| It is difficult to manipulate an active audience. | On the other hand, it is easy to manipulate the passive audience. |
| Active audiences are critical thinkers. | On the other hand, passive audiences are cognitive misers. |
| They have good schemata. | In contrast, passive audiences are too lazy to think. |
| The active audience is involved in listening, including discriminative and comprehensive listening. | However, the passive audience is involved in hearing. |
Active and Passive Audience Theories
Active Audience Theories
Active audience theory explains that active media audiences do not just accept media information passively but interpret the message based on their personal and social contexts.
Active Audience Theory posits that audiences are not passive recipients of media messages but rather actively engage with and interpret media content based on their own experiences, values, and beliefs. This theory challenges the notion of passive audience effects proposed by earlier media theories, such as the Hypodermic Needle Theory, and emphasizes the agency and autonomy of audience members in their interactions with media texts. According to Active Audience Theory, individuals actively select, interpret, and make meaning from media content, drawing upon their personal backgrounds, social contexts, and cultural frameworks. This theory acknowledges the diversity of audience responses to media messages and highlights the importance of audience participation and engagement in shaping the reception and interpretation of media content.
List of Active Audience Theories:
- Uses and Gratifications Theory
- Reception Theory
- Cultural Studies
- Active Audiences Theory
- Two-Step Flow Theory
- Agenda-Setting Theory
- Participatory Culture Theory
- Media Literacy Theory
- Social Learning Theory
- Social Cognitive Theory
Uses and gratifications theory shows a strategic approach to explaining how and why people or audiences actively find specific media to meet specific needs. It also represents an audience-centered strategy to perceive the process of mass communication.
The two-step flow of communication model argues that audiences accept media information more if the opinion leaders deliver the message. So, the audience gets influenced by mass media if the opinion leader supports disseminating the information.
Passive Audience Theories
Passive audience theories, also known as media effects theories, propose that audiences are passive recipients of media messages and are highly susceptible to the influence of mass media. These theories suggest that media content has a direct and powerful effect on shaping audience attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors without much active engagement or resistance from the audience.
List of Passive Audience Theories:
- Hypodermic Needle Theory (Magic Bullet Theory)
- Mass Society Theory
- Passive Audience Theory
- Limited Effects Theory
- Reinforcement Theory
- Encoding-Decoding Model
- Spiral of Silence Theory
- Dependency Theory
- Selective Exposure Theory
- Cumulative Effects Theory
The Hypodermic Needle Theory, also known as the Magic Bullet Theory or the Hypodermic-Syringe Model, is a communication theory that suggests that media messages are like a powerful drug injected directly into the bloodstream of passive audiences, influencing their thoughts, behaviors, and attitudes. According to this theory, audiences are seen as highly susceptible to media influence, and media messages are believed to have an immediate and direct effect on shaping audience perceptions
Citation For this Article (APA 7th Edition)
|
Kobiruzzaman, M. M. (2025). Active and Passive Audience Definition, Theory, Differences & Examples. Newsmoor- Educational Website for Online Learning. https://newsmoor.com/active-passive-audience-differences-example-active-audience-theory/ |