Linear Communication Model Example Situation. Advantages and Disadvantages of Linear Model of Communication.
Linear Communication
Linear communication refers to one-way communication like reading books or newspapers, watching television, listening radio, and receiving no-reply emails. It is a particular type of communication that excludes receiver feedback. In this context, senders convey messages without expecting feedback from audiences. The receiver cannot respond to the sender immediately. For example, a company publishes a recruitment circular in a newspaper describing the application process. The authority wants to convey messages to applicants without expecting feedback.
Linear Communication Model
The linear communication model refers to the framework that explains the one-way communication process. Many communication systems are one-way directed, including disseminating news through radio. For example, print media spreads emergency news to readers; but readers cannot respond instantly or provide feedback to the authority. Conveying information through the radio, TV, newspaper, and book is an appropriate example of one-way communication. Therefore, many scientists designed linear communication models to explain these one-way communication processes. Linear means one way.
A linear model excludes Feedback, which is a mandatory element for transactional communication. In a communication process, senders transmit info to receivers. Similarly, receivers respond to senders, which is called Feedback. Effective communication occurs when both senders and receivers respond simultaneously. Feedback is an essential element of the communication process. Therefore, linear communication models have both advantages and disadvantages.
Different Between Linear and Transaction Models
The primary difference between the transactional and linear models is- the transactional model includes Feedback, but the linear model excludes it.
Additionally, the transactional theory can explain two-way communication, including face-to-face interaction. In contrast, the linear model can describe only one-way communication, like reading newspapers.
Finally, transactional models are developed from the linear model. The linear models are older than the transactional model.
Linear Model of Communication Example
The Four Examples of Linear Communication Models are:
- Aristotle Communication Model- 300BC
- Lasswell’s Communication Model- 1948
- Shannon-Weaver Communication Model-1949
- Berlo’s SMCR Communication Model in 1960
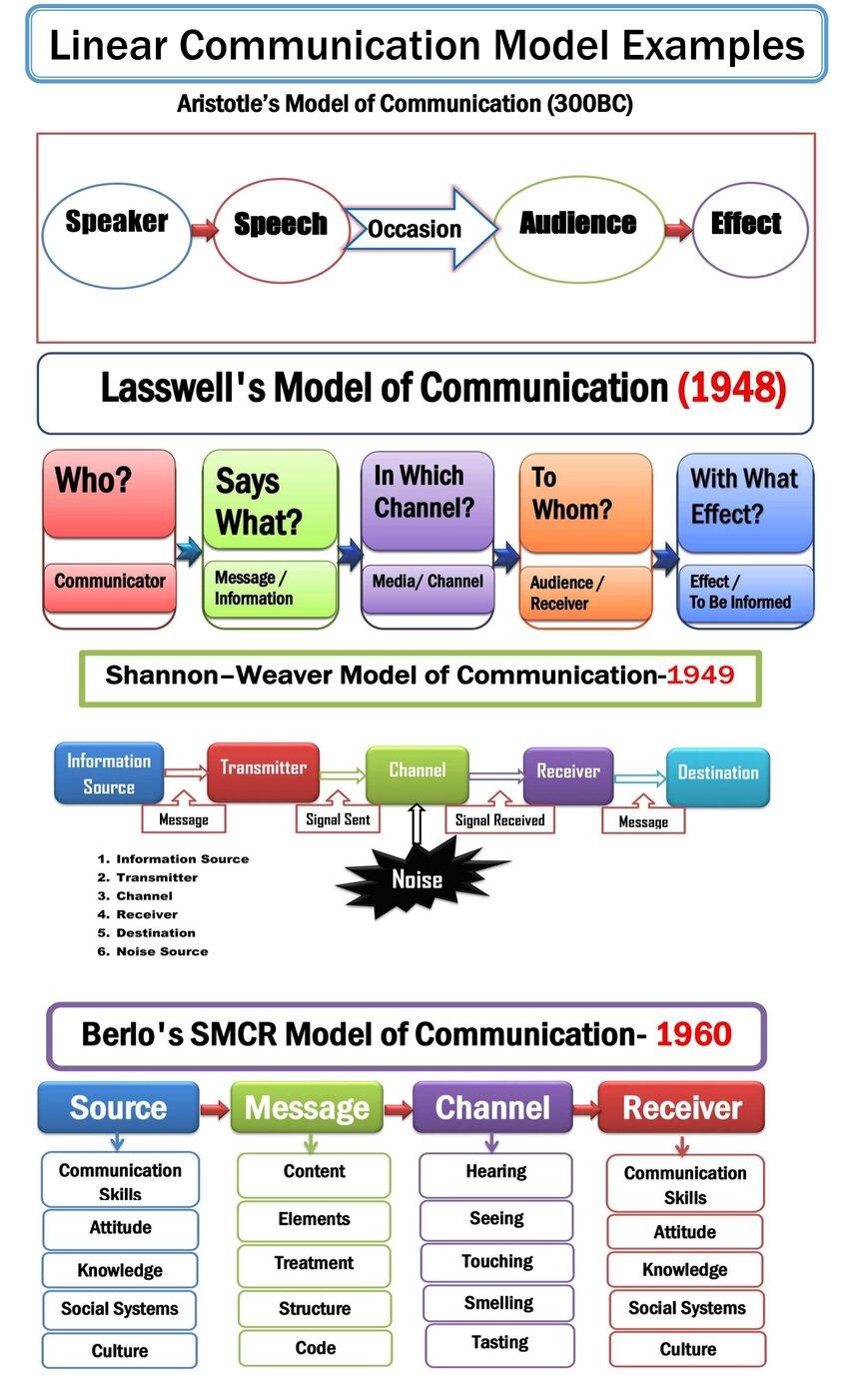
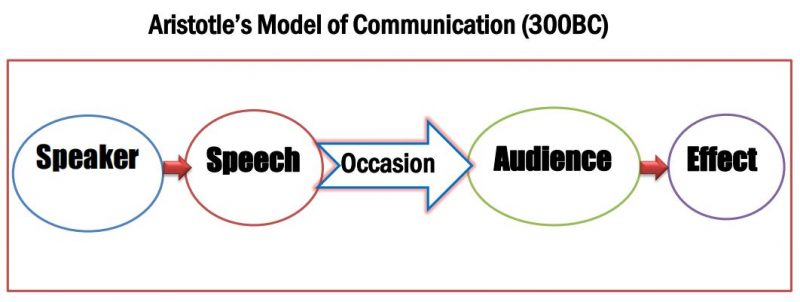
Aristotle Communication Model– 300BC
Aristotle’s communication model is a well-known example of a linear model of communication. Greek Scientist Aristotle introduced a linear communication model in 300 BC. He designed the model to explain how to provide political and social speech for audiences. The model is focused on the message and audience or receiver mainly. The five critical components of Aristotle’s communication model are speaker, speech, occasion, audience, and effect. This theory does not mention Feedback; hence, it is a linear communication theory.
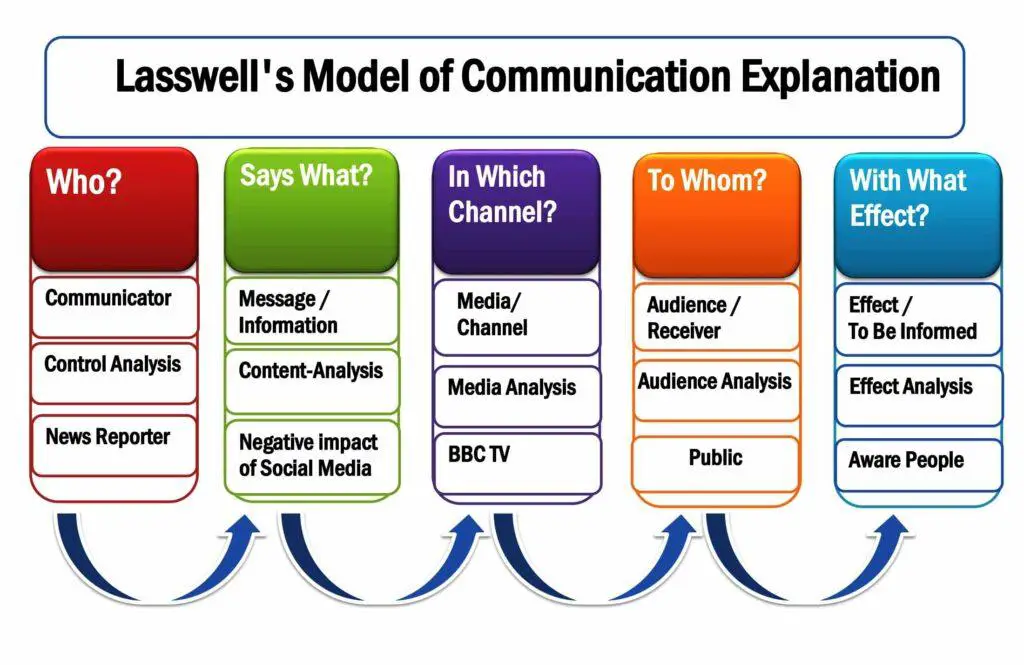
Lasswell’s Communication Model
In 1948, Harold Lasswell described a linear communication model with five elements: who says what, in which channel, to whom with what effect. It is another prominent model to illustrate one-way communication.
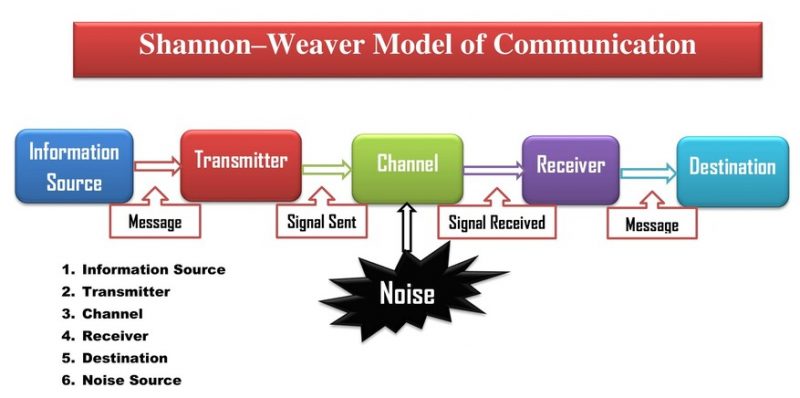
Shannon-Weaver Communication Model
The Shannon-Weaver model is the most notable theory in the communication arena for representing communication noise. It is known as the mother of all communication models. In 1949, Shannon and Weaver published this model to explain how signals are transmitted through channels. The six components of the Shannon-Weaver model are Information Source, Transmitter, Channel, Receiver, Destination, and Noise Source.
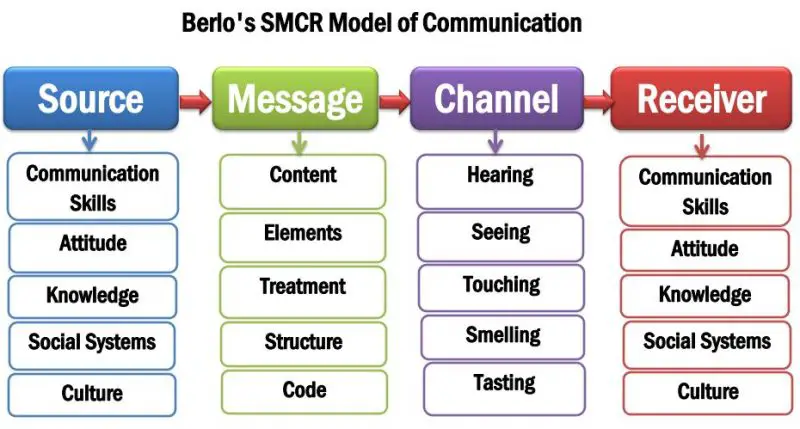
Berlo’s SMCR Communication Model
In 1960, David Berlo developed another linear communication model with four key elements Source, Message, Channel, and Receiver. Therefore, it is known as the SMCR communication model. Berlo describes five more elements under every critical component. For example, Source includes Communication Skills, Attitude, Knowledge, Social Systems, and Culture. Additionally, the message comprises Content, Elements, Treatment, Structure, and Code. Moreover, the channel contains hearing, seeing, touching, smelling, and tasting. The receiver includes the same elements as the message sender.
Linear Communication Examples
The five examples of linear communication are: (1) Reading books and Newspapers, (2) Watching Television, (3) Listening Radio, (4) Receiving no-reply emails, and (5) Public Speech.
Reading newspapers Example of Linear Communication-1
Reading newspapers is another example of a one-way communication process. The readers can receive the information but cannot respond.
Watching TV Example of Linear Communication-2
For example, Joe Biden, the 46th U.S. president, delivers a speech on CNN after returning from Ukraine. People are watching television to hear the president’s statement. He announces $500 million for military support in Ukraine. The speaker is the message’s sender, and the audience is the receiver. The message has been transmitted through the CNN television channel. However, audiences can not respond to the speech instantly. The feedback is not presented in this type of communication; hence, it is a one-way communication process.
Listening Radio Example of Linear Communication-3
Listening radio is an example of linear communication because the audience cannot respond. The audience can listen to news, music, and advertisements.
No-Reply Email Example of Linear Communication-4
A no-reply email is also an example of a linear communication process. The receiver receives the messages in email but cannot reply to them. A no-reply is sent from the company domain email that doesn’t receive feedback.
Public Speeches Example of Linear Communication-5
Donald Trump (politician) gave a speech at an election campaign in 2024 repeating the slogan “Save America Win Back The White House Make America Great Again I was indicted for you!”. The audience listens to the speech but cannot provide feedback on the speaker’s speech instantly.
Linear Communication Model Advantages and Disadvantages
The author explains the strengths and weaknesses of the linear model of communication. The linear model has pros and cons for the theoretical and practical implications.
Advantages of the Linear Model of Communication
Firstly, the linear communication model is easy to understand and describes the entire process thoroughly. The communication is straightforward and targeted to specific audiences.
Additionally, the linear model of communication was the initial theory that explains the communication process. The interactive and transactional communication models are designed based on linear models.
Moreover, a linear communication model is inevitable to explain the communication process through print media, TV, letter, Fax, and no-reply email.
Disadvantages of the Linear Model of Communication
Firstly, linear models do not represent Feedback; therefore, these models are incomplete. It can explain only the one-way communication process, but not two-way interactions. However, feedback is a significant component of interactive and transactional communication.
In addition, linear communication models cannot describe face-to-face communication as the most effective interaction. Nowadays, people prefer transaction communication systems like face-to-face, phone conversations, video conferences, and more. However, linear theories like Aristotle’s, Lasswell’s, Shannon-Weaver’s, and David Berlo’s SMCR communication model are unable to explain interactive communication.
Moreover, linear communication is inappropriate for problem-solving, bargaining, and dealing. One-way communication creates miscommunication between sender and receiver, sometimes disseminating misleading information. Linear models are designed to explain the inappropriate communication process that might create misconceptions about the message delivered by senders.
Furthermore, the Linear model distinguishes the sender and receiver in which the sender always send, and the receiver only receives messages. Naturally, in the communication process, senders work as sender and receiver, and receivers also work as receivers and senders of the message.