Types of Journalism- 21 Different Types of Journalism are Print Journalism, Broadcast Journalism & Digital Journalism. Journalism Categories. Types of Print Journalism, Broadcast Journalism, and Digital Journalism.
Journalism
Journalism is a combined process of collecting, processing, and disseminating information through print, electronic, digital, or online media. Print media are printed publications such as books, newspapers, magazines, billboards, etc. Electronic media in journalism are mass media such as the telephone, television, and radio. Digital media are internet-based outlets such as websites, blogs, and social media. Journalists are the people who collect, analyze, process, and distribute information via the media.
According to the Dalai Lama, Writers and journalists are very influential in society. Even if human life is short-lived, written texts can survive for
Centuries. In Buddhism, for example, it is because the teachings of Buddha, of Shantideva, and other great masters have been put into writing that they have been able to guide people for so long about love, compassion, and the altruistic attitude of the enlightened mind; and this is why we study chemistry today. Unfortunately, other texts have been at the we can still root of tremendous suffering, such as those which spread the Extreme ideologies of fascism and communism. Indirectly, writers have the power to create the happiness or the unhappiness of millions of beings.
Journalism Types Diagram
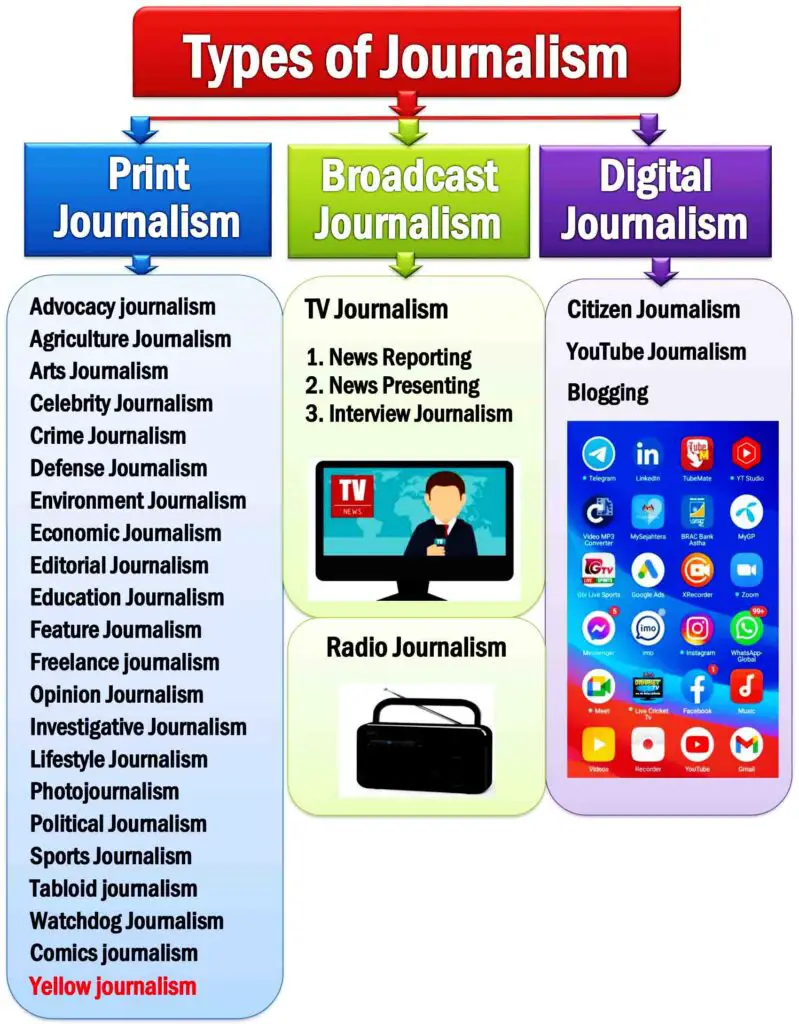
Types of Journalism
Types of journalism refer to the journalism categories or kinds of journalism. The three most common kinds of journalism are print, broadcast, and online.
Different Types of Journalism
- Print Journalism
- Broadcast Journalism
- Digital Journalism.
Journalism differs into three categories: Print, Broadcast, and Digital.
1. Print Journalism
Print journalism is the process of news reporting through print media such as newspapers, magazines, books, etc. Newspapers are the most significant print outlets for publishing diverse types of news together. A newspaper has many spaces to disseminate different types of news; for example, national, international, editorial, advertisement, and sports. The print media authority assigns expert journalists for each space. Print media is a journalism category for publishing massive amounts of information to the audience.
Example of Print Journalism
For example, print journalism includes newspapers, magazines, books, flyers, and academic journals. It denotes printed documents that convey information.

21 Types of Print Journalism
The 21 types of print journalism are advocacy journalism, agriculture journalism, arts journalism, celebrity journalism, crime journalism, defense journalism, economic journalism, editorial journalism, education journalism, environmental journalism, feature journalism, freelance journalism, opinion journalism, investigative journalism, lifestyle journalism, photojournalism, political journalism, sports journalism, tabloid journalism, comics journalism, and watchdog journalism. The author does not acknowledge yellow journalism as a part of journalism because it is a malpractice of journalism.
1. Advocacy Journalism
Advocacy journalism is the process of reporting news from a non-objective viewpoint. It refers to a common type of journalism that combines reporting with a social or political viewpoint. The reports are generated by advocacy journalists dealing with social events, corruption, and corporate and government policy. This report appears as a potential jolt for the audience. Somewhat it is another type of investigative journalism. Advocacy journalists practice journalism from an ideological viewpoint to support the nation and society.
For example, “Vaccination better way to combat COVID-19 than lockdown.”
2. Agriculture Journalism
Agriculture journalism is a genre in which the journalist collects agriculture-related data and processes them to publish as informative information through mass media. It compares the traditional and new ways of cultivation. It also includes the challenges of the agriculture sector of the country.
For example, “Canadian farmers produce organic vegetables.”
3. Arts Journalism
Art journalism refers to the common type of journalism in which journalists analyze and report arts events such as theatre, architecture, movies, drama, visual illustration, music, and so more. It discusses traditional events of the community, society, country, and sub-continent areas. Art journalists focus on artistic features.
For example, “New art hub for Bournemouth.”
4. Celebrity Journalism
Celebrity journalism is the category of journalism that covers events related to celebrities such as sportspeople, royal family people, singers, T.V. stars, and opera stars.
For example, “Jennifer Lopez Goes From Business to Pleasure in Two Dramatically Different Looks.“
5. Crime Journalism
Crime journalism refers to covering sensational news stories related to offensive incidents in society. It is mainly associated with wrongdoing issues related to police, victims, and criminals. It is also part of objective and investigative journalism. Crime journalism is also known as crime news reporting; sometimes, it includes taking the interview of the crime stories. The journalist keeps a good relationship with the police, lawyer, and admin officer to get the news quickly. Crime events are crucial issues that add news value in journalism; therefore, journalists are interested in reporting those events.
For example, “Haiti President Jovenel Moise killed.”
6. Defense Journalism
Defense journalism refers to specialized journalism covering events related to the Army and Navy. It is an exceptional type of journalism that builds the relationship between the media and the military. Defense journalist gets special training to report war news from the spot. Usually, journalists write articles and generate content regarding military events and information to entertain soldiers. Defense journalists should know military history, rules and regulations, languages, and international relations.
For example, “the U.S. troops return from Afghanistan.”
7. Economic Journalism
Economic journalism is a significant type of journalism that covers the country’s financial issues, events, systems, and policies. It also includes an analytical report and comparative analysis of the financial state of the country. The reporters must have good knowledge of the economy in the country to report these types of news. The businessmen are the fundamental readers of this column. The journalists collect information by interviewing the finance manager, owner, investor, and company employee.
For example, “Lockdown hit the economy during the the Eid ul Adha Festival.”
8. Editorial Journalism
Editorial journalism refers to a genre of journalism where the chief editor expresses the opinion logically and ethically. In this respect, journalists play an important role in shaping public opinion by providing rational arguments. Although it is similar to opinion journalism, it is fixed only for editors to provide logical opinions. The editorial contents must include the news leads, body, and summary.
For example, “Effectiveness of the movement control order in Malaysia.”
9. Education Journalism
Education journalism deals with covering any news related to the Department of Education. It includes news related to the development of the education system. On the other hand, it also shows the discrimination that occurred in the education sector. The prime focus of the education journalist is to raise social awareness among students to get their rights properly. The educators and students are the main readers of this column. Additionally, students, teachers, and researchers become education journalists.
For example, “Education Ministry advises conducting online classes until 2022 in Malaysia.”
10. Environment Journalism
Environment journalism is reporting environmental issues, such as natural disasters, climate change, and global warming. Disaster journalism is one of the types of environment journalism because it includes news related to natural calamities and disaster management. Environment news covers natural conditions and calamities such as water layers, deforestation, global warming, floods, etc. It also includes the casualties and infrastructural damages. The reporters need to ensure safety while covering the news from the spot. It represents the victim’s wound that affects people’s emotions. The report also shows how the international and national disaster management authority plays its role in rescuing the people from the affected areas.
For example, “Cyclone hits Bangladesh and death toll rises to 200”.
11. Feature Journalism
Feature journalism means producing and publishing non-fiction articles dealing with events, issues, and trends. The aim of feature articles is not only to entertain but also to educate people. Feature journalism is also known as news feature article writing. The most common news feature articles are Personality Features, How-To Feature, Reviews Feature, Travelogue Features Article, Sports Features, and Obituary Features. Travel journalism includes travel articles and travelogue features.
For example, “3 idiots Film Review.”
12. Freelance Journalism
Freelance journalism is the process of generating informative content and selling them to media organizations. It is one kind of contract work; journalists complete newspapers, magazines, and commercial organizations. The content might be related to fashion, sports, products, and environments. Nowadays, many freelance journalists work to promote commercial products. Additionally, some of them are involved in investigative journalism.
For example, “How to earn money from Facebook.”
13. Opinion Journalism
Opinion journalism means publishing an author’s opinion regarding an issue. The author has good academic and or practical knowledge of the subjects. The content is a piece of article that is intended to clarify the issues elaborately.
For example, “The Importance of artificial intelligence in digital business.”
14. Investigative Journalism
Investigative journalism refers to a genre of journalism in which the journalist investigates a single case of interest, such as discrimination, corruption, wrongdoing, and critical crimes. An investigative journalist might spend a week, month, and year analyzing and reporting the news. They scrutinize the information thoroughly to identify the actual people behind the crimes or occurrences.
For example, “September 11 attract: who and why.”
15. Lifestyle Journalism
Lifestyle journalism is the process of reporting events related to people’s lifestyles such as food, travel, cooking, eating habits, yoga, home decoration, gardening, leisure, hobby, music, fashion, etc. It is one of the favorite types of journalism for the young generation. Lifestyle journalism has become more popular in recent decades. It provides tips and tricks for leading a life with happiness and avoiding common problems relevant to lifestyle.
For example, “Vogue brings new fashion at shop in 2021.”
16. Photojournalism
Photojournalism is a specific form of journalism that describes an event, issue, conflict, or story. A proverb says that a photo conveys more information than a thousand words. Photojournalism is a significant process of conveying emotions and stories via photos. It is an essential element of print journalism.
The most common types of photojournalism are spot news, general news, personality, illustration, pictorial photojournalism, and so more.
17. Political Journalism
Political journalism is a form of journalism in which journalists publish political news. The political news can be local or international. It presents deep information regarding democracy, royal families, elections, dictatorship, and so more. Political journalism reveals critical information about civil government how they rule the country. It also talks about the regional and international political powers. Political journalists should have greater knowledge of political science and the principle of democracy.
For example, “Political crisis in Myanmar.”
18. Sports Journalism
Sports journalism covers the story related to a sports event and sportsperson. It enriches the newspaper by providing national and international sports events. The young generations are the primary readers of sports news due to having much interest in the sport. Sports photojournalism is a powerful element of sports news reporting. There are mainly two types of sports journalism: sports action and sports feature journalism. In this regard, the journalists understand the specific sport clearly and have practical communication skills to cover the story. Also, journalists must ensure safety and security while covering spot sports news.
For example, “Rio to allow fans for Brazil-Argentina final of Copa America.”
19. Tabloid journalism
Tabloid journalism is a different style of journalism in that journalism disseminates spectacular events via the small size of newspapers. The news is published in compact page format papers. It emphasizes sensational topics such as crime, corruption, celebrity gossip, and viral news on social media. Tabloid journalism is also known as rag publications.
For example, “Lionel Messi Join P.S.G.”
20. Watchdog Journalism
Watchdog journalism is another form of investigative journalism in which journalists ensure the authenticity of the news by interviewing responsible people. It is the process of monitoring the government’s actions and increasing the accountability of the news. Watchdog journalism has become the principle of the press media. It enforces the government official and authority to fulfill public interests as per responsibility. The watchdog journalists scrutinize the people in power to reveal the facts. Watchdog journalism works to inform people rather than entertain them.
For example. “Washington Post’s coverage of Watergate scandal.”
21. Comics Journalism
Comics journalism means graphic journalism in which journalists publish non-fiction events. The journalist draws a funny skeleton combined with pictures and words to convey a meaningful message and information to the audience. Therefore, the journalists are known as cartoonists or editorial cartoonists. It is also known as cartoon journalism. However, nowadays, journalist adopts technology such as computers and mobile to create visual graphics.
For example, “KAL’s cartoon.”
Illegal Yellow Journalism
Yellow journalism is a distinguished form that focuses on increasing circulation rather than news authenticity. It is a process of luring audiences setting eye-catching headlines that are not very relevant to the body content. Yellow journalism is a popular term in the American press; it is also known as yellow press. Journalists focus on exaggerating the news instead of identifying authentic news. The contents have not come from research and investigation. Journalist practices yellow journalism intentionally without following the code of conduct in journalism; therefore, it is unethical—people term yellow journalism as the negative role of journalists.

For example. “Spanish American War.”
2. Broadcast Journalism
Broadcast journalism is a process of reporting news and information through TV and Radio. Therefore, it includes T.V. and Radio Journalism. T.V. journalism is a special type of journalism that disseminates visual information via Television. It is a process of filming moments, and editing them to publish via television. Sometimes, T.V. journalists interview political, business people, or celebrities on-scene footage.
Types of Broadcast Journalism
- TV News Reporter
- TV News Presenter
- Interview Journalism
3. Digital Journalism
Digital journalism means collecting, generating, and publishing via digital platforms such as websites, blogs, and social media sites. It is also known as online journalism which includes citizen journalism. Citizen journalists gather the information and publish it through digital networking sites such as websites, blogs, and social media. So, citizen journalism is one of the types of online journalism.
Types of Digital Journalism
Digital journalism involves collecting and publishing information via digital platforms such as blogs, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn. The citizens are involved in collecting, processing, and reporting the news. They generate content to convey messages to society and the community. However, digital journalism has both adverse and positive consequences on society. Sometimes, people spread fake and fabricated information to the country via citizen journalism. Nowadays, many people collect, process, and publish news on social media, including Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, etc. The netizen generates and posts informative content on social media to create social awareness. There are many examples of digital journalism; however, the most common examples are Citizen journalism, YouTube journalism, Blogging, and Commenting.
For example, Arab Spring and Rebuilding Haiti.
The Three Examples of Digital Journalism are:
- Citizen Journalism
- YouTube Journalism
- Blogging
Citation For This Article (APA 7th Edition)
| Kobiruzzaman, M. M. (2024). Types of Journalism, Different Types of Journalism- Print, Broadcast & Digital. Newsmoor- Educational Website For Online Learning. https://newsmoor.com/types-of-journalism-different-types-of-journalism-print-broadcast-digital-journalist/ |
