Learn about the Two-Step Flow of Communication Model or Theory of Mass Communication, With an Example Situation
Two-Step Flow of Communication Model
The two-step flow theory is a famous interactive communication model in the communication field. The three veteran scholars, Paul Lazarsfeld, Bernard Berelson, and Hazel Gaudet, developed and published the two-step flow model in 1944. This two-step flow theory of communication was published in the People’s Choice book. The authors conducted this study based on the decision-making process in a presidential election.
The authors tried to find the impact of mass media messages on voting purposes. This study articulates that people strongly accept and believe mass media messages when influencers or opinion leaders convey them.
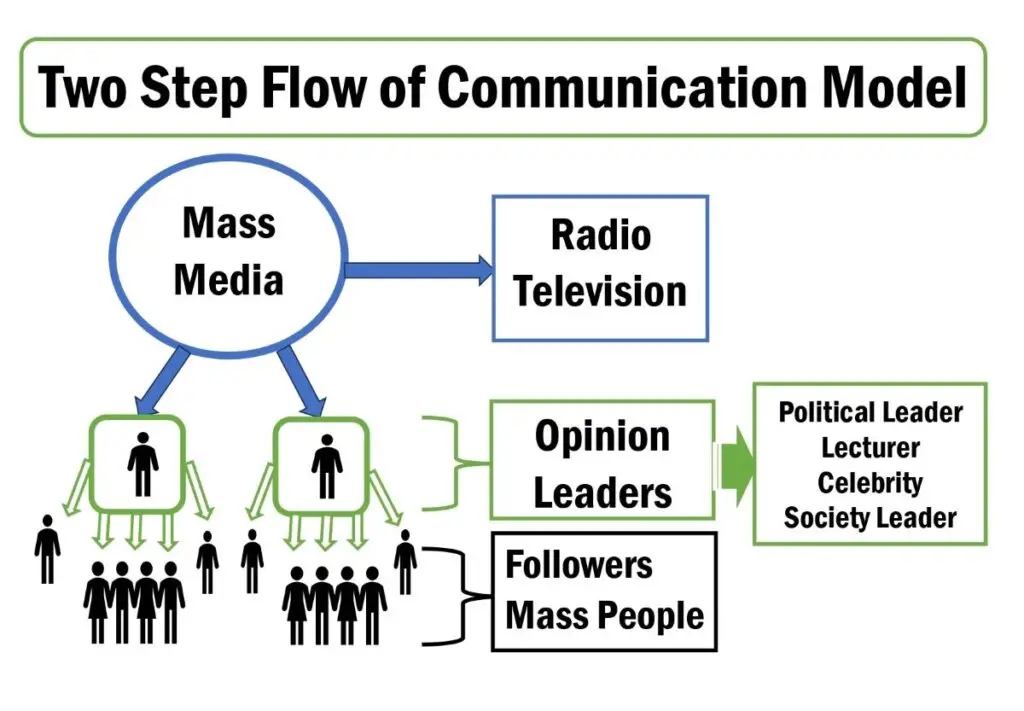
The two-step model illustrates that mass media do not directly influence the majority of people. Still, they are mostly influenced by their opinion leaders who interpret the media’s message. Opinion leaders are those who are first exposed to a specific media message and interpret this message based on their own opinions. Then , begin to infiltrate these opinions among the general public who are opinion followers. Therefore, the two-step flow theory is one of the active audience theories in the communication area.
Two-Step Flow of Communication Theory Major Findings
- Interpersonal and group communication are more effective than mass communication.
- We can find opinion leaders in every sector of society or community.
- Opinion leaders are influencers in our society.
- Opinion leaders are more exposed to the formal media.
Two-Step Model Statements
The two-step model proclaims that messages from the media transferred in two separate stages. First, opinion leaders who pay attention to the media and receive the information. Opinion leaders infiltrate their interpretations along with the actual media information.
The period ‘personal influence’ was invented to refer to the method of intervening between the media’s direct message and the people’s ultimate response to that message. Opinion leaders are quite persuasive in getting people to change their attitudes and manners and are quite alike to those they influence.
The two-step flow model has enhanced our understanding of how the mass media influences decision-making.
Two-Step Flow of Communication Model Elements
The three elements of the two-step flow theory are:
- Media
- Opinion Leader
- Receiver
1. Media
Media are news disseminating outlets that broadcast informative and recreational messages. Television and Radio is the most famous mass media.
2. Opinion Leader
An opinion Leader is a leader of individual group who provide details and message to lesser active people in the group. In office, the manager functions as an opinion leader, and in public, a political leader plays a role as an opinion leader. They interpret and infiltrate the information into their group. But one more thing is that the opinion leader is a leader only for their respective group not for all.
Katz and Paul give the impression of “the flow of media information from radio and television to opinion leaders and then the opinion leaders pass the messages into the lesser active users in the population”. Through this conversion of the message, the opinion leader may add their own opinion on the actual information, which may impact the low-active users. In some cases, the Opinion leaders are clarifying that the actual content certifies the information is needed by the people. Most opinion leaders are selective people, and they pass the information to the group (Schreiner, T. 2018).
Characteristics of Opinion Leaders
Generally, opinion leaders exist at every level of society. They ought to much more on money, education, and status than on opinion followers.
- Knew more than other people in the group
- Often had a certain location where they met with the general people
- They are positivists – beware of negativists
- They are activists – doing something
- Involved – they might not be the people you assume.
- Have trustworthiness – a combination of trust and expertise.
3. Receiver
Receivers in communication are followers and groups of people who receive information from opinion leaders and shape public opinion. The voters, students, patients, and the public are receivers in different contexts.
Example of the Two-Step Flow Communication Model
Two-Step Model Example Situation
People watching the News on CNN Channel flash the headlines with “Research exposes that Carrots protect people from hair fall”. People are receivers who listen to the news only. However, they believe and eat more carrots to protect from hair fall when a physician (dermatologist) conveys the same message to them. The physician (dermatologist) is the opinion leader in this context who influences others to believe the media message.
- Media: CNN Channel
- Opinion leader: Physician (Dermatologist)
- Audience: People suffering from hair fall
Two-Step Flow Theory Examples in Real Life
A political leader sharing TV news about the election date on social media to inform followers is a real-life example of a two-step flow theory of communication. Nowadays, people visit social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn more frequently than on television. They accept and believe information when they are conveyed by opinion leaders. The political leader is the gatekeeper or opinion leader in this context. Sometimes, mass media broadcast fake and fabricated news. Therefore, information becomes more authentic when influencers convey it through social media.
- Media: TV
- Opinion leader: Political Leader
- Followers: Voters and Supporters
Paul Lazarsfeld’s Empirical Research on Two-Step Flow Theory
In 1948, Paul Lazarsfeld, Bernard Berelson, and Hazel Gaudet distributed The People’s Choice, a paper investigating the voters’ basic leadership forms during a 1940 presidential election campaign. Amid the 1940 presidential race campaign, Franklin Roosevelt versus Wendell Willkie. Planned and directed the most detailed field try at any point led. More than 3000 individuals were chosen, and 600 were chosen to be on a board that was consulted with multiple times consistently from May until November. Concentrated consideration on changes in casting choices and made names for each.
- Early deciders – picked a competitor in May and never showed signs of change amid the whole campaign
- Waverers chose a contender and then were undecided or converted to another candidate, but in the end, they voted for their first choice.
- Converts chose one candidate but then voted for his rival.
- Crystallizers had not chosen an applicant in May, but chose by November.
Interview
- The detailed questionnaire was allocated to acquaintances with specific mass media content, such as candidate speeches.
- Results in slender Mass Society Theory.
- 53% of the voters were in early contests
- 28% were crystallizers
- 15% were waverers
- 8% were adapted
- He couldn’t find any indication that the media played an important role in manipulating the crystallizers, the waverers, or the converts
Voters said that they had been partial by other people.
- Many were politically uninterested
- No clear-cut voting conclusions b/c of low interest.
Two-step Model Strength
The model examines the way that personal relationships may help to facilitate messages from the media.
Two-step Model Weakness
- Surveys can’t measure how people use media on a routine basis.
- Surveys are a very affluent and unwieldy way to study people’s use of specific media, such as their reading of certain news stories or their observing of specific television programs.
- The research design and data analysis are intrinsically conservative in assessing the media’s power
- Monitoring for social and demographic variables
- Subsequent research on the two-step flow has produced highly conflicting findings.
Contrast with the hypodermic needle model
The hypodermic needle model or magic bullet theory, is the one-step theory of communication. This model explains that people are directly influenced by mass media, but the two-step flow of theory says that most people are not directly influenced by mass media.
Conclusion
In sum, the two-step flow theory is an interactive communication model. Scholars think the two-step flow of communication theory proposes that interpersonal communication is more effective than mediated distance communication.