Lasswell’s Communication Model Example. Advantages and Disadvantages of the Lasswell Model of Communication.
Lasswell Model of Communication
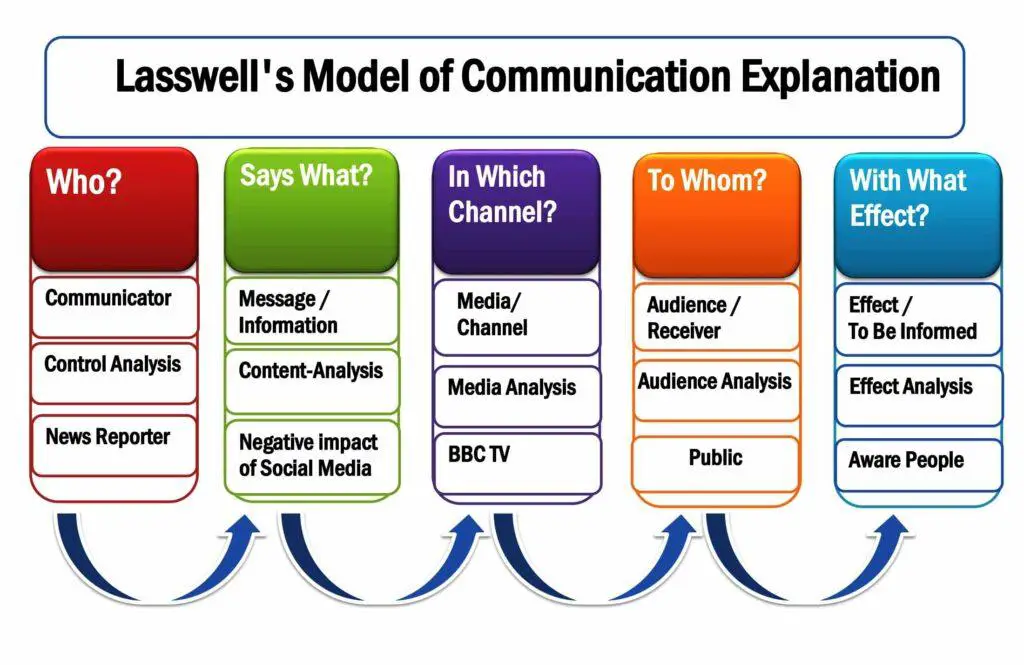
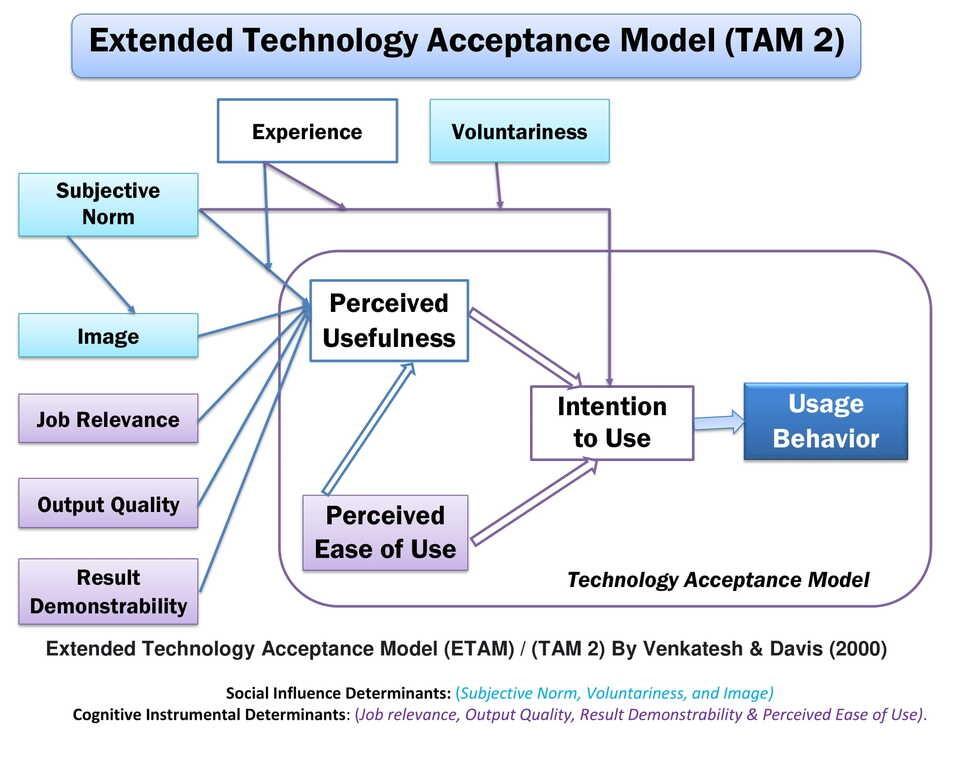
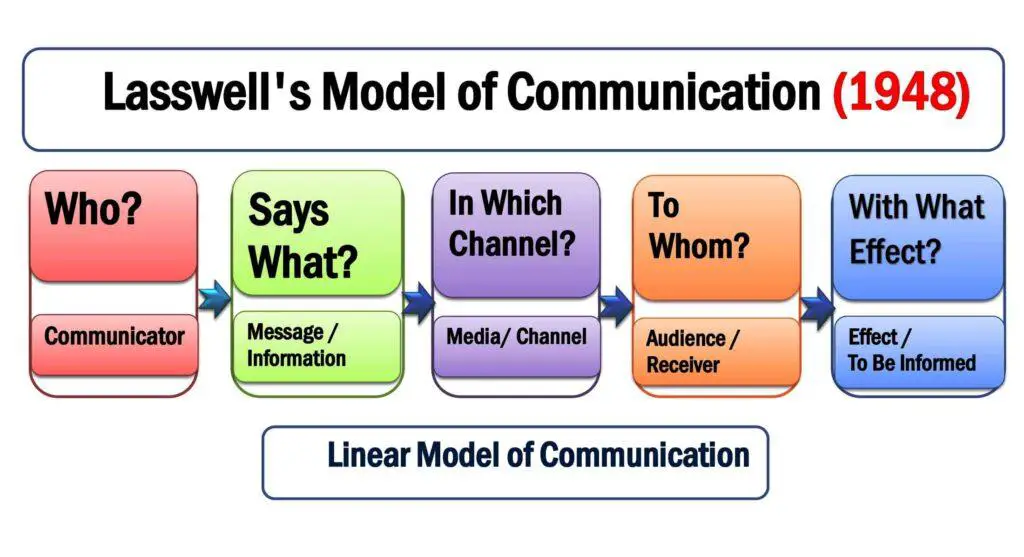
Lasswell’s linear communication model consists of five elements: who says what, in which channel, to whom with what effect. American psychologist and sociologist Harold Lasswell introduced a linear communication model in 1948. It is also known as the Action Model in communication. Harold Lasswell’s model describes the communication process with five questions; “Who? Says what? In which channel? To whom, and with what effect?” These are the five fundamental components of the Lasswell model. The researcher did not explain the feedback; therefore, it is a linear communication model. It was a significant model for explaining the verbal communication process. The message is directed to the audience and it is a way of conversation.
Example of Lasswell Model of Communication
A news reporter disseminates news regarding the negative impact of social media on BBC television to inform the general public.
Lasswell Model of Communication Components
The five components of Lasswell’s model are:
- Who
- Says What
- In Which Channel
- To Whom
- With What Effect
Harrold Lasswell’s model is also known as the 5Ws model for these five elements. This theory finds answers for the 5w and 1 h questions regarding the communication situation.
Who
Who refers to the sender of the message who initiates the communication. It also indicates the speaker and writer of the communication process. For example, the message’s sender is the news presenter, journalist, or political speaker.
For Example, A politician delivering a speech to mass people during an election campaign rally.
Says What
Says What refers to the message of the communication. The question “Says What” is intended to identify the sender’s statement. For example, a news presenter delivers a FIFA World Cup 2022 news update.
Another Example: The politician’s message may include promises of development and criticism of opponents.
In Which Channel
In Which Channel describes the message transmitting pathway. It shows how the information reaches target audiences. The channel of communication differs based on the communication way. For example, Television, radio, and newspapers are communication channels in mass media. In contrast, hearing, seeing, smelling, and touching are message-transmitting channels in face-to-face communication. In non-verbal communication, the communication channels are “Physical Appearance, Paralinguistics, Body Movement, Gestures, Posture, Facial Expression, Eye Contact, Proxemics, Haptics, Chronemics, Artifacts, and Environment.”
Example: The politician’s speech may be delivered through various channels, such as live television broadcasts, social media platforms, or public appearances.
To Whom
To Whom describes the individuals to whom the message is delivered; it is also known as the receiver of the communication process. The receiver is the audience who receives the information. The sender disseminates the message through a particular channel to reach receivers (To Whom). For example, the news reporter conveys information to the audience who listens to them.
Example: The audience for the politician’s speech may consist of supporters, undecided voters, members of the opposing party, and journalists covering the event.
With What Effect
With What Effect illustrates the message’s output and validates whether the receivers comprehend the message or not. Sometimes, the sender cannot persuade the audience due to communication noise, faulty channels, and lack of speaker capability. Initially, Aristotle mentioned effects as a significant communication component in his Rhetorical Triangle model. In 1948, Lasswell included this element to explain the one-way communication process.
Example: The effect of the politician’s speech may vary among different audience segments. Supporters may feel inspired and energized, undecided voters may be swayed, opponents may become more entrenched in their views, and journalists may report on the speech in the media, influencing public opinion.
Lasswell Model of Communication Examples
1. For example, if a news presenter broadcasts the FIFA World Cup information to inform Football lovers, we can relate the Lasswell model to this event. It analyzes who is disseminating information (News Presenter), What is saying (FIFA World Cup information), Which channel the news presenter is using to transfer information (Television), and “Effect” is the objective of the news.
2. Another Lasswell model example of a situation is the newspaper advertisement. We can see that the organization promotes its products via newspaper channels to inform customers.
3. Politicians address speeches on the Radio to motivate voters to vote for their parties.
4. Lecturers send assignment instructions to students via email to get their information.
6. An organization sends appointment letters to candidates through postal and courier services.
7. Students submit assignments to the lecturer on an A4 paper sheet.
8. The HR manager posts current company rules and regulations on the notice board to inform all employees.
9. A writer publishes his latest book series for readers.
10. A motivational speaker gives a speech on how to lead a happy life with limited wealth through a YouTube channel.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Lasswell Model of Communication
Advantages of the Lasswell Model
Firstly, the Lasswell model explains the information-transmitting process by throwing five questions to the readers. The answer to these questions indeed describes the whole communication process.
Secondly, the model is suitable for all verbal communication processes, including human communication.
In addition, this model has excellent heuristic significance, and the concept has been utilized in several types of research.
Disadvantages of the Lasswell Model
Firstly, the Lasswell formula is an outdated model of communication. Lasswell model does not indicate the feedback clearly to this model; hence, it is suitable to explain only one-way conversation but not transactional interaction like face-to-face interaction.
In addition, the Lasswell theory does not appropriately explain the nonverbal communication process since it mentions the “Who Say” component. In the nonverbal communication context, senders convey messages without spoken words.
Moreover, the Lasswell model cannot explain effective communication adequately, such as the interaction between two individuals. In face-to-face communication, both the sender and receiver provide feedback simultaneously. No feedback in the Lasswell model can explain interpersonal and group interaction.
Furthermore, Lasswell’s model completely ignores the communication noise barriers to effective communication.
Finally, it is a propaganda-based linear model. This model focused on describing social and political propaganda.
Despite having advantages and disadvantages of the Lasswell model, it is still a famous model for students to study linear communication.
Lasswell’s Communication Model Explanation
Who and when establishes the Lasswell communication model?
Harold Dwight Lasswell’s short name (Harold Lasswell) established the Lasswell model in 1948.
What Type of Model is it?
Lasswell’s communication model explains a one-way communication process; therefore, it is linear, like Aristotle’s communication model, Shannon-Weaver’s communication model, and Berlo’s SMCR communication model. The linear communication model excludes feedback; in contrast, the transactional model includes it to explain two-way discussion.
Reference For This Article- APA 7th Edition
Kobiruzzaman, M. M. (2024). Lasswell Model of Communication 1948 Examples & Components. Newsmoor. https://newsmoor.com/lasswell-model-of-communication-1948-examples-components/In-text citation |