Eugene White's Model of Communication Example, Explanation, Components, Advantages, and Disadvantages. Examples of Eugene White's Model of Communication.
Eugene White's Model of Communication
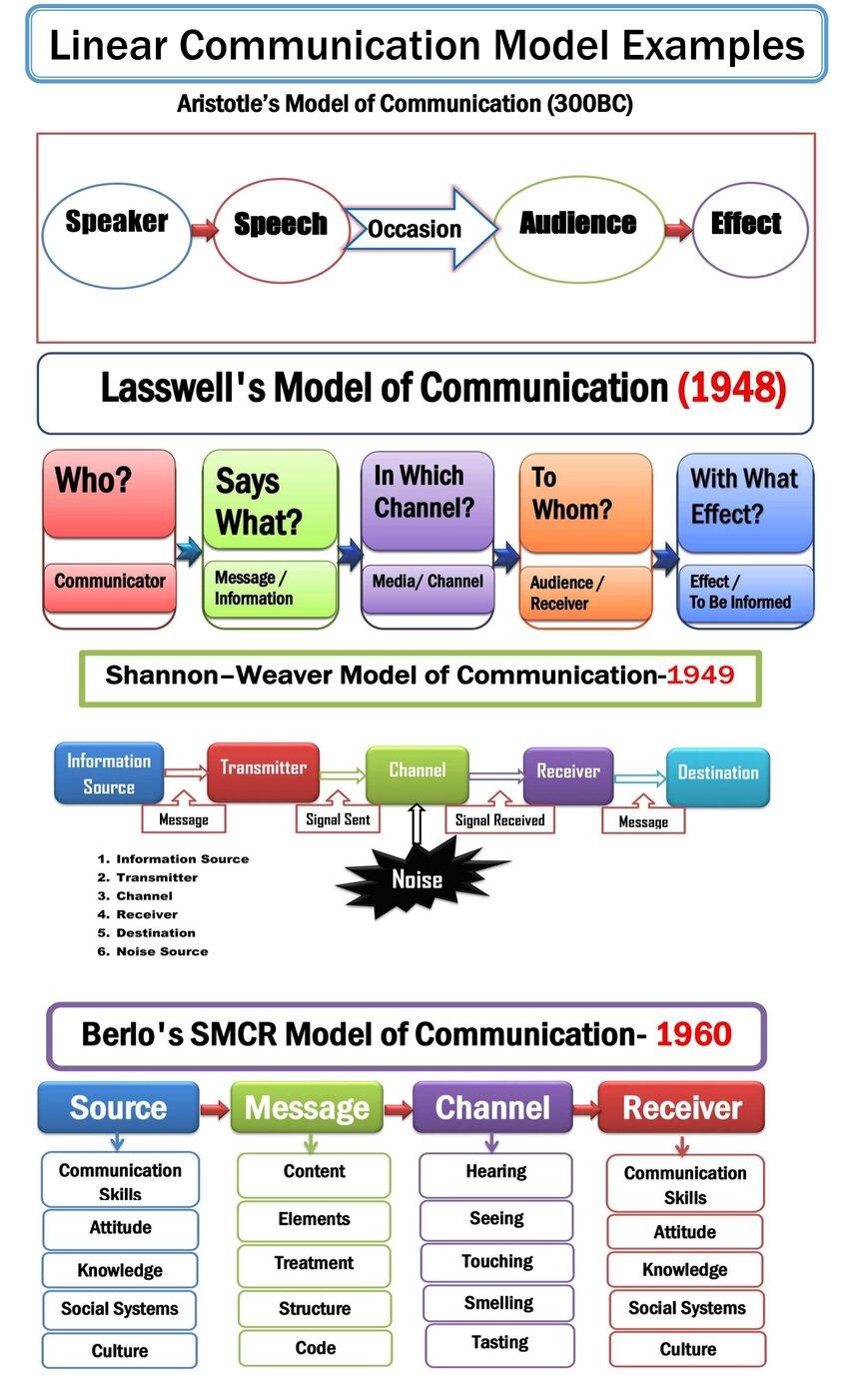
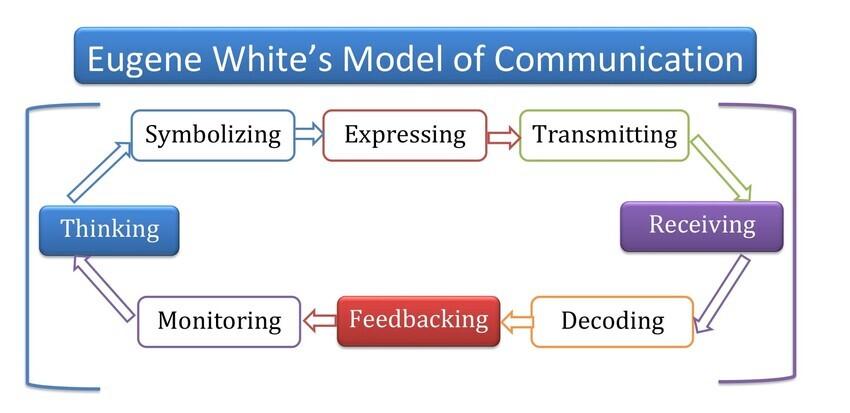
In 1960, scientist Eugene White introduced a transactional communication model with eight elements including feedback. Therefore, it is known as Eugene White's transactional model of communication. It is a perfect model to explain oral communication between senders and receivers. Consequently, it is known as Eugene White's model of oral communication or verbal discussion. The most important component of this theory is feedback to make it a transactional model of communication.
According to Eugene White's model, the communication process is circular, not linear. Feedback exists as the most important component of the oral discussion.
Eugene White's model shows communication occurs in two directions. It also indicates communication is a circular, not a linear process. The discussion occurs between two people, and it is reciprocal.
According to Eugene White's model (1960), people think to symbolize the speech; they then speak to send the message to receivers. The receivers decode the message to provide feedback to senders. The sender and receiver monitor the context to continue the conversation. It is the best communication mode to describe a talk show and debating program.
Examples of Eugene White's Model of Communication
The five examples of Eugene White's model are the talk-show program, debating, bargaining between buyer and seller, small group discussion, and interview session discussion.
Talk-show program
The talk show program is an example situation of Eugene White's stages of oral communication. In talk show programs, the speaker and host follow eight stages of communication, including thinking, symbolizing, expressing, transmitting, receiving, decoding, feedbacking, and monitoring the context.
Debating among Student
Debating among students is another example of White's communication model. The speaker and receiver follow a cyclical communication process in this context. Sometimes, the senders play the role of receiver. Consequently, the receivers play the role of the sender. They speak and listen simultaneously.
Negotiation Between Buyer and Seller
The bargaining between buyers and sellers is an example situation of Eugene White's model. In hardball negotiation, a circular conversation occurs reciprocally.
Group Discussion
In addition, small group discussion is an example situation of White's model of communication. Many people converse recurrently. The group members monitor the discussion and provide their thoughts.
Interview Session
Finally, the interview session is an example situation for White's communication model. The interviewer asks several questions to assess the applicant. Similarly, the applicants reply to the interviewer which produces two-way communication. The communication process is circular and both parties provide feedback.
Eugene White's Model of Communication Explanation
The eight elements of White's model of oral communication are:
- Thinking
- Symbolizing
- Expressing
- Transmitting
- Receiving
- Decoding
- Feedbacking
- Monitoring
Eugene White's model describes the face-to-face communication process with eight communication components: thinking, symbolizing, expressing, transmitting, receiving, decoding, feedbacking, and also monitoring. Communication is a recurring process in which the sender and receiver work simultaneously.
Thinking
Thinking is the sender's thoughts and perceptions. The sender thinks to organize and deliver messages to receivers. Thinking is the initial stage of the communication process.
Symbolizing
Symbolizing means representing something to express thoughts. People symbolize words and utter them to communicate. For example, every word of a speech is a symbol of communication. In written communication, letters are the symbol of communication.
Expressing
Expressing is the process of articulating thoughts and messages to receivers. People express ideas by symbolizing them. For example, a physician delivers his speech to stop people from smoking. He expresses a persuasive speech to influence people.
Transmitting
Transmitting is the process of conveying messages or thoughts from senders to listeners. In face-to-face communication, the sender transmits the message directly to the receiver without a channel. In mass communication, the sender uses TV, radio, or newspaper to transmit the message.
Receiving
Receiving is the process of receiving messages from the receivers. The receiver accepts ideas and decodes them to provide feedback. Usually, listeners receive messages from senders and they respond to deliver opinions.
Decoding
Decoding is the way of interpreting an encoded symbol into intelligible language. It is an invisible process that we can not see.
It involves extracting the intended message from the symbols, words, or signals transmitted by the sender and making sense of it based on one's knowledge, experiences, and cultural background.
In the communication process, decoding occurs after the receiver has received the message through the chosen channel
Feedbacking
Feedback is the process of responding to the sender's message. It validates the communication process is transactional, not linear. Feedback ensures that the communication is transactional and both parties respond. It also validates that Eugene's communication model is the transactional model of communication.
In the verbal communication process, the sender and receiver respond orally for feedback. In the non-verbal communication process, communicators provide feedback with a smile, yawn, nod, posture, gesture, sweating, and covert behavior like a fast heartbeat.
Monitoring
Speakers try to understand whether the listener accomplishes the message or not. It is all about observation. The speaker observes how the message impacts the audience. A good speaker should have monitoring skills to persuade his or her listeners. This skill assists them in staying away from providing stereotyping, prejudice, and discriminating speech.
Eugene White's Model Advantages and Disadvantages
White's Model of Communication Advantages
Firstly, White's communication model can explain the transaction communication process with feedback. It is the perfect model to explain oral communication.
Additionally, this model shows how two-way communication occurs, like debating and talk shows.
Moreover, White's model suits effective communication processes; therefore, organizations use this model to communicate with clients. For example, the marketing team discusses with clients over smartphones to motivate them.
White's Model of Communication Disadvantages
Unable To Explain One-Way Communication
Firstly, the White model cannot describe the one-way communication process; because it is a transactional model with feedback. Whereas, the linear communication models can explain the linear or one-way communication process. For example, it cannot explain communication with radio, television, books, newspapers, and no-reply email.
Complexity
Eugene White's model presents a complex framework compared to linear models such as Aristotle's model of communication with five elements. White's model is difficult to understand and apply in real-life communication because of its multiple stages.
Overemphasis on Feedback
White's model highlights feedback that is not compulsory for one-way communication like print media and no-reply email.
Lack of Contextual Sensitivity
Eugene White's model avoids communication contexts such as intrapersonal, interpersonal, group, and mass communication. This model does not explain the setting in which communication occurs.
Ignores Non-Verbal Communication
Eugene White's model does not highlight nonverbal communication cues including facial expressions, smiles, posture, and gestures. However, feedback can be part of nonverbal cues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Eugene White's model is a transactional communication theory with feedback. It is one of the significant models to describe the two-way oral communication process with eight elements (Thinking, Symbolizing, Expressing, Transmitting, Receiving, Decoding, Feedbacking, and Monitoring). This article provides eugene white's model of communication explanation, examples, strengths, and weaknesses.