Aristotle’s Model of Communication Example Situation, Elements, and Explanation. Advantages and Disadvantages of Aristotle’s Model of Communication.
Aristotle’s Model of Communication
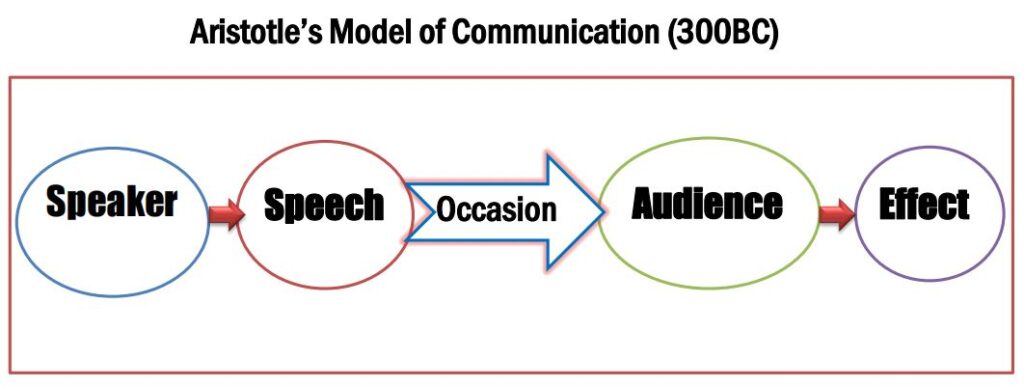
Aristotle’s communication model refers to the linear communication theory focusing on five elements: speaker, speech, occasion, audience, and effect. Greek great scientist Aristotle introduced this one-way communication model in 300 B.C. that mainly focuses on the speech or the message. So it is known as Aristotle’s communication model or Aristotelian model. The Aristotelian model is one of the most recognized communication models globally, emphasizing the speaker’s role in making a powerful speech. The Aristotle model focuses on public speaking, including how the speaker delivers a message to the audience. As this model was proposed before 300 B.C., it is regarded as the first communication model. Aristotle was a well-known Greek scientist and philosopher born in 384 BC in Stagira on the northern frontier of Classical Greece.
The most common three types of communication models are linear, interactive, and transactional. Aristotle’s communication theory is the initial linear model followed by Shannon-Weaver and Lasswell’s communication model. The author explains the model, including elements, examples, and advantages and disadvantages.
Aristotle’s Linear Model of Communication
Aristotle’s communication model explains a one-way communication process, which is a linear communication model. The linear communication model excludes feedback, whereas the transactional (two-way) model includes feedback. There is no feedback in Aristotle’s communication model; hence, it is known as Aristotle’s linear model of communication.
Five Elements of Aristotle’s Communication Model
Aristotle’s communication model is designed to explain delivering a persuasive speech. The five components of Aristotle’s communication model are speaker, speech, occasion, audience, and effect.
Speaker
The speaker refers to the person who delivers the speech. It is the primary element of the communication process that initiates the conversation. Communication cannot be designed without a speaker. So, it is crucial in all verbal and nonverbal communication types.
Speech
Speech is the message of communication that a speaker wants to deliver to audiences. The speaker delivers the speech to accomplish the goal. For example, a political leader produces persuasive speeches to motivate supporters.
Occasion
Occasion means the context in communication that denotes the environment and represents why conversation occurs. The speech pattern can be distinguished based on the occasion. For example, a political leader delivers speeches based on the situation, including political campaigns and social and personal events.
Audience
The audience is the receiver of the speech. The speaker addresses a speech to the audience. So, audiences are known as listeners. For example, supporters are the audience in the political campaign. The audience plays a passive role, impacted by the speech. There are two types of audiences such as active and passive audiences. This limits communication to one direction, from speaker to receiver.
Effect
The effect is positive and negative, the consequences of the speech. It measures whether the audience is persuaded or not. For example, a marketing manager provides a promotional speech to sell a product. Here, the effect refers to buying attitude of the customers.
Example of Aristotle’s Model of Communication
The 5 examples of Aristotle’s communication model are: 1. delivering a speech through Radio, 2. advertisement on Television, 3. delivering written political speech, 4. publishing news through newspapers, 5. receiving a no-reply email.
Delivering Speech through Radio
For example, the NBC radio station(Context) broadcasted American 32nd President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s (Speaker) speech through fireside chats. The president explained (Speech) the new policies directly to the citizens(Audience). Franklin D. Roosevelt was an effective communicator, and his speech created a strong relationship(Effect) between the government and the general people. This situation is the best example of Aristotle’s model.
Advertisement on Television
A salesman (Speaker) advertises on Television (Context) to persuade customers (Audience) to sell a laptop at the best price. He delivers a promotional message (Speech) to convince the customers. Finally, the salesman manages to sell some laptops (Effect) through T.V. advertisement. In this context, the audience listens to the speakers without providing feedback.
Political Speech Physically
Barack Obama (Speaker) delivers a speech to supporters (Audiences) to persuade them to vote for Democratic Party in the general election (C0ntext) of the United States of America. For example, many voters decide to vote (Effect) for Democratic Party after listening to the motivational speech.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Aristotle’s Model of Communication.
Advantages of Aristotle’s Model of Communication
Aristotle has placed more emphasis on the speaker’s role. Therefore, it benefits anyone looking to develop their public speaking abilities. The Aristotelian model states that the speaker needs to be aware of his intended audience. For instance, the speakers can establish their speech on their socioeconomic status, educational background, etc.
In a corporate context, managers take three steps: Ethos, Pathos, and logos, to enhance organizational productivity.
Aristotle’s model explains how to obtain more supporters with a persuasive speech on a sports team.
Moreover, for researchers and students, Aristotle’s model serves as a motivating outcome of the systematic study of various aspects. It is also an instructive representation of the communication process that assists in system planning. It represents fresh perspectives and ideas on various topics, including verbal, written, and nonverbal communication.
Disadvantages of the Aristotle Communication Model
The three significant criticisms of Aristotle’s model are No Feedback, No Noise, and only Public Speaking Centered.
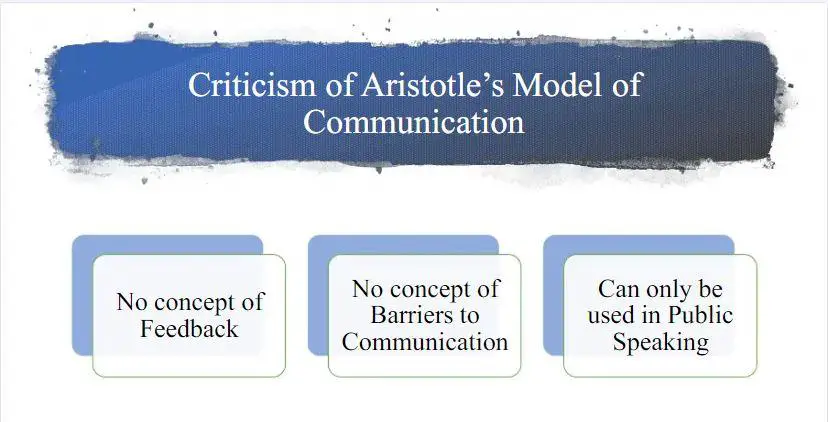
The most crucial weakness of Aristotle’s communication model is that it is a linear communication process. It is considered to be a linear model of one-way communication. It did not include and explain feedback essential for the interactive communication process. Due to the lack of audience feedback and openness in this communication model, the conversation is ineffective.
Additionally, its credibility and usefulness are limited because it is only helpful for public speaking.
Finally, Aristotle’s model shows no concept regarding noise barriers in communication. Noise is an unwanted but paramount element of the communication process.
Aristotle’s Rhetorical Triangle
Aristotle described the rhetorical triangle as comprised of three elements: ethos, pathos, and logos. Any written and spoken speech is generated to persuade audiences. So, the writers and speakers should include the three rhetorical components ethos (speaker’s credibility and trustworthiness), pathos (emotional appeal), and logos (logical message or information).
Ethos(Credibility)
Ethos refers to the information’s credibility and reliability. It ensures that the information comes from reliable sources and is safe to believe. For example, people will consult with an interior designer for office decoration but not with a lawyer. On the other hand, they will consult with lawyers for legal advice. Ethos ensures the person credibility who delivers the message.
Pathos(Emotion)
Pathos refers to the use of emotional appeal to persuade the audience’s attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors. Pathos taps into the audience’s emotions, values, and desires, aiming to evoke sympathy, empathy, anger, fear, or excitement. Unlike logos, which appeals to logic, and ethos, which appeals to ethics and credibility, pathos taps into the audience’s emotions, aiming to create a strong emotional connection and influence their attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors.
In communication and persuasion, pathos plays a significant role in engaging the audience on a deeper level by eliciting emotions such as empathy, sympathy, anger, fear, or joy. By appealing to these emotions, speakers, writers, or advertisers can make their message more relatable, memorable, and persuasive. For example, in a speech advocating for environmental conservation, a speaker might evoke feelings of empathy by describing the impact of pollution on wildlife, stirring the audience’s emotions and inspiring them to take action.
However, it’s essential to use pathos ethically and responsibly, ensuring that emotional appeals are genuine.
Logos (Logic)
Logos refers to the use of logical reasoning, facts, evidence, and arguments to support the speaker’s position or argument. hence, it appeals to the audience’s intellect by presenting rational arguments, data, statistics, examples, and logical deductions.
Conclusion
The five essential elements of Aristotle’s model are speaker, speech, occasion, audience, and effect. Speakers should follow Aristotle’s model to influence the audience positively when speaking in public. It is also a crucial model to motivate audiences. Many scholars extended this theory to establish other theories in different contexts. It is the most ancient model that provided communication concepts initially.
Citation For This Article- APA- 7th Edition:
|
Kobiruzzaman, M. M. (2024). Aristotle’s Model of Communication Example & Explanation. Newsmoor. https://newsmoor.com/aristotles-model-of-communication-example-explanation-elements
In-text citation
According to new research … (Kobiruzzaman, 2024) In research from Kobiruzzaman (2024) |

