David Berlo’s SMCR Model of Communication Example Situation. Berlo’s Model of Communication Advantages and Disadvantages
David Berlo’s SMCR Model of Communication
The SMCR communication model refers to the Source-Message-Channel-Receiver communication model developed by David Berlo in 1960. In 1960, David Berlo designed the SMCR communication model with four elements: Sender, Message, Channel, and Receiver. SMCR refers to the Source, Message, Channel, and Receiver, which are essential elements of any communication process. Therefore, the SMCR communication model is known as Berlo’s Source-Message-Channel-Receiver model.
Berlo invented this model based on the Shannon-Weaver communication model (1949). He described some factors that make the communication process more effective. SMRC represents the Source, Message, Channel, and Receiver that are also part of the nine essential communication elements of the primary communication process.
There are three types of communication models: linear, interactive, and transactional. The SMCR communication model refers to a one-way communication system. So, the SMCR model is a linear model of communication where feedback is absent.
Berlo’s Model of Communication Published Year: 1960
Who Developed the SMCR Communication Model?
Answer: David Berlo
What Does SMCR Stand For?
SMCR stands for Sender, Message, Channel, and Receiver
Berlo’s Model of Communication Example
Listening to a lecture in a classroom is a real-life example of David Barlo’s SMCR communication model. Lecturer Delivering a Lesson Physically in a Classroom can be an example situation of Berlo’s model of communication. The four essential elements of Barlo’s model are the source, message, channel, and receiver. Firstly, the news lecturer is the source of knowledge who disseminates the information. The lessons are the message, and hearing and seeing are the channel. Finally, the students are receivers of messages who listen to the lecture. In this context, students can be a source of information when they provide feedback. David Berlo did not mention feedback in his model; therefore, it is designed to explain a one-way communication process.
Similarly, reading newspapers, books, and magazines is an example scenario of Barlo’s communication model. Print and broadcast journalism primarily relate to one-way communication.
However, digital journalism generates two-way communication, including social media-based citizen journalism and blogging. The active audience can comment on social media platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp to express their opinions.
Berlo’s Model of Communication Diagram
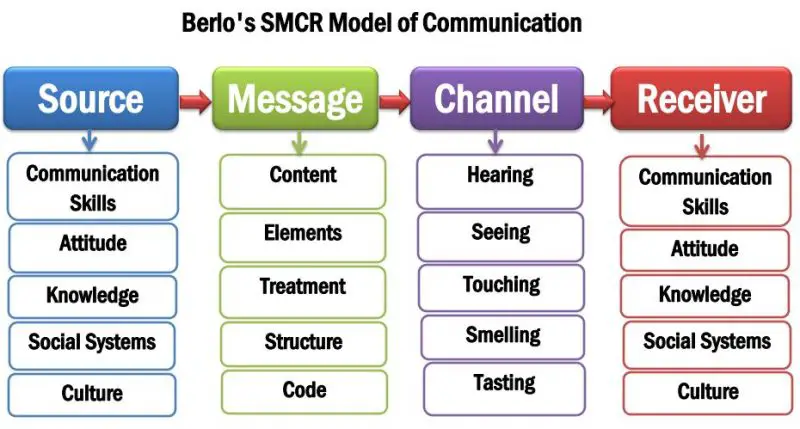
David Berlo’s Communication Model Elements
The Four Key Elements of Berlo’s Model of Communication are:
- Source
- Message
- Channel
- Receiver
1. Source
The source means the message’s sender who initiates the communication process by sending information to the Receiver. David Berlo describes five factors related to the source: Communication Skills, Attitude, Knowledge, Social Systems, and Culture.
Communication skills
Communication skills refer to the ability to speak, read, write, and listen effectively. It also indicates the ability to use verbal and nonverbal communication cues during the interaction. Communication will be more effective if the senders and receivers have excellent communication skills. The most common nonverbal communication examples are eye contact, facial expression, body language, gestures, posture, and so on. The source’s communication skills increase the effectiveness of the communication process.
Attitude
Attitude is the psychological factor of the sender and Receiver that affects the message’s meaning. It is also an established perception of a person, i.e., what they think or feel about something. Thus, the message’s meaning depends on the source’s attitude and the Receiver.
Knowledge
Knowledge indicates the level of actual information, familiarity, and experience on the discussion topic. The discussion topic is the message of the communication process. Therefore, the communicator feels comfortable discussing whether the topic is familiar to them. However, knowledge does not imply the educational qualifications or degrees of the sender or receiver.
For example, a football player will be more interested in talking about football than cricket. On the other hand, a cricket player will surely feel comfortable discussing a cricket game. Here, knowledge indicates familiarity with the subject of the discussion topic or message.
Social Systems
Social systems include values, beliefs, behaviors, rules and regulations, locations, and religions. These factors influence the method of the communication process as well as the message’s meaning.
For example, the speaker delivers an anti-American message in the American parliamentary election campaign. Indeed, the audience will not receive and listen to his message attentively. It is an example of a location factor that is also part of the social system.
Culture
Culture refers to the social background of the Sender and Receiver. The meaning of the same message might be identical when people from different cultures interpret it. It is a significant factor in nonverbal communication cues.
For example, exchanging “Salam” greetings with people is widespread in the Muslim community. Salam conveys a greeting message in the Muslim community; however, handshaking is another activity that also conveys the same meaning. On the other hand, handshaking is a standard greeting among people in Western culture.
2. Message
The message is the primary substance conveyed by the source or sender of the communication to the Receiver. David Berlo proposed another five factors related to the message: Content, Elements, Treatment, Structure, and Code.
Content
Content refers to the entire body of the message from beginning to end. It is essential information for the discussion. Content is the whole script of the conversation.
For example, the lecturer is teaching students about noise in communication. So, the full speech about communication noise is the message’s content.
Elements
Elements refer to nonverbal communication cues such as facial expression, eye contact, gesture, posture, and body movement. It makes the conversation more effective and productive. So, communication might get boring without elements.
For example, the lecturer raises five fingers when mentioning the five basic noises in the communication process.
Treatment
Treatment refers to how the message is conveyed to the audience. The communication method affects the communication system. It represents the message packaging. Examples of therapy in communication are delivering messages formally and casually.
For example, teachers speak formally when delivering classroom speeches. However, the lecturer talks very casually when meeting students outside of class.
Structure
The structure of the message describes how the information is arranged. The effectiveness of the message depends on the message structure.
For example, the lecturer talks about the definition, types, and examples of communication noise. The students clearly perceive the message because of its good organization.
Code
Code in the message refers to the form of the message transmitted from sender to receiver. Examples of code include text, audio, video, visual, and more.
For example, the teacher is speaking in front of the students; hence, the message’s code is audio.
3. Channel
A channel is the medium that carries the message from the sender to the Receiver. There are many communication channels, such as radio, newspapers, TV, phone calls, and social media. Berlo highlighted the five senses as the communication channel: hearing, seeing, touching, smelling, and tasting. These five channels are crucial to the human communication process.
For example, a face-to-face class is more effective than an online class. The students can see the lecturer physically and hear the lecture. Nowadays, many institutes conduct virtual classes through premium platforms. The channels denote the physical and virtual means of conveying messages.
David Berlo mentions only five human senses as communication channels: hearing, seeing, touching, smelling, and tasting.
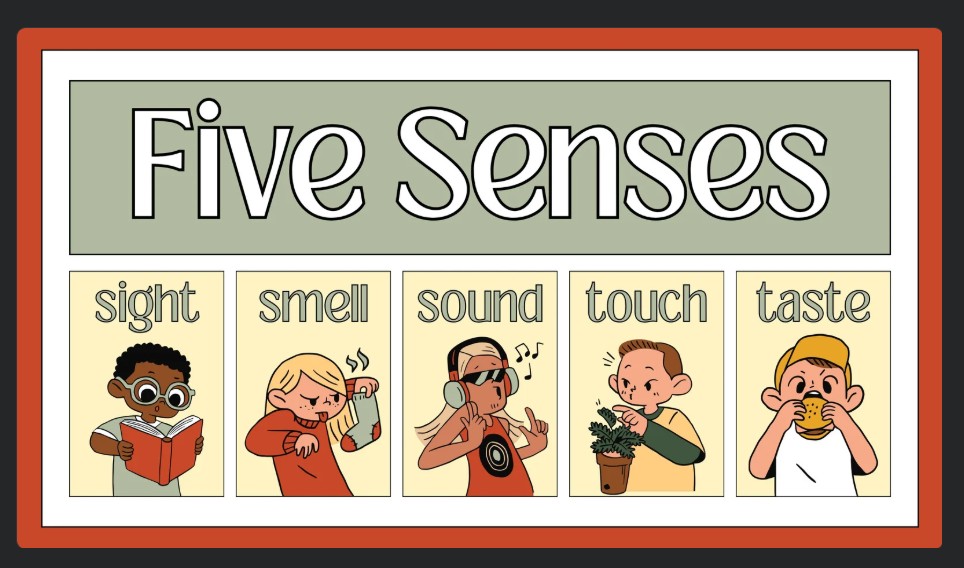
Hearing
People receive messages through listening. It is the most effective channel in the communication process. For example, students hear lectures in the classroom.
Seeing
People accept messages through seeing. It is one of the crucial channels in nonverbal communication. People take less than 1 second to judge others based on appearance. The audiences form a conception of the speaker based on body movement, facial expression, eye contact, and gesture. A proverb says that people can lie, but eyes never lie. It means people believe what they see more than what they hear.
For example, a lecturer asks students about their final exam. The student replied that the exam was excellent; however, they looked very worried during the interaction with the lecturer. So, the lecturer does not believe the statement due to seeing the anxious face. Watching television is another example of seeing channels in communication.
Touching
Touch is an effective nonverbal communication channel that conveys messages through physical contact. It is also known as Haptics in Nonverbal Communication. The most common examples of touching channels in communication are holding hands, hugging, tickling, and kissing. These touching styles represent different messages.
Smelling
Smelling is another channel of the intrapersonal communication process. Intrapersonal communication is communicating with yourself. It is also known as olfactory nonverbal communication. People judge others based on the Fragrance they have used. A pleasant smell creates a positive impression of the person. Perspiration odors create a negative perception of the person. A pleasing fragrance represents a good personality.
For example, people smell flowers and other fragrances to determine whether a flavor is good or bad.
Tasting
Tasting refers to nonverbal communication through the act of tasting something. For example, people test food to identify its deliciousness.
4. Receiver
Finally, R-Receiver is the person who receives the message or information in the communication process. David Berlo adds the same factors from the sources to the Receiver: Communication skills, Attitudes, Knowledge, Social Systems, and Culture. Communication gets more effective when senders and receivers have similar skills, attitudes, and knowledge. Communication among people from the same culture and social system reduces communication noise during the interaction.
Berlo’s Model of Communication: Example Situation
A Marketing Officer Selling a New Television
1. Source (S)
In this scenario, the marketing manager is the source of information who initiates the communication.
- Communication Skills: The marketing manager should be a verbal and non-verbal communicator to convey the message effectively.
- Attitude: The marketing manager should maintain a positive attitude and provide details about the new television.
- Knowledge: The sales manager should study the new product and the customer’s demographic and psychographic background.
- Social System: The manager works within the organizational structure and culture.
- Culture: The manager’s approach and style may be influenced by the organization’s culture and the audience’s background.
2. Message (M)
The promotional information about the new television is the message.
- Content: information about the new television, including components, features, pricing, and launch date.
- Elements: Verbal and non-verbal communication cues, including artifacts, presentation slides, statistical report charts, and television images.
- Treatment: The way of conveying information, including a formal presentation with a Q&A session.
- Structure: The whole session includes an executive summary, product features, market analysis, and conclusion.
- Code: The marketing manager uses language in promotional presentations, including technical terms, and possibly visual and audio elements.
3. Channel (C)
In this scenario, hearing and seeing are the channels through which a message is transmitted.
- Hearing: The customers and sales team listen to the manager’s speech about the new television.
- Seeing: Customers see visual aids and observe nonverbal cues.
- Touching: Some audiences touch the new television to know more about it.
- Smelling and Tasting: It does not apply to this product. However, it might be applicable for food items.
4. Receiver (R)
In this scenario, the clients are receivers of the information.
- Communication Skills: The customers and sales team must have strong listening skills and minimal product knowledge.
- Attitude: It indicates the customer’s willingness to buy the new products. It might be positive or negative towards the new television. It is also relevant to psychological noise in communication.
- Knowledge: Similar to the marketing manager, the customers and sales team should have knowledge and positive attitudes toward the new television.
- Social System: The marketing session is designed and operated in accordance with the company’s hierarchical structure and social norms.
- Culture: The customer’s cultural background and corporate culture may influence their perception of the message.
Berlo’s Model of Communication Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Berlo’s SMCR Communication Model
Berlo’s communication model explains the communication system with four primary and 15 sub-components. It presents a comprehensive diagram of the communication process. The SMCR model describes the communication process elaborately.
The source (sender) and receiver contain similar components. This model articulates that the sender and receiver convey and receive messages simultaneously. It indicates interactive communication even though it is a linear communication model.
It focuses on human communication, emphasizing the skills, attitudes, knowledge, and social systems of both the sender and receiver.
Disadvantages of Berlo’s SMCR Communication Model
The criticisms of David Berlo’s SMCR Model are that it is a linear model, provides a complex explanation, and lacks noise.
Linear Model
David Berlo’s SMCR Model of Communication is the linear communication model; therefore, feedback is absent. Hence, the SMCR model can’t explain transactional communication processes, such as speaking over a smartphone.
Complex Model
Additionally, it illustrates a complex communication model that is difficult to understand. This model troubles students in their understanding of the process.
Noise
Moreover, Berlo’s SMCR communication model avoids noise, a significant source of communication error. It excludes another communication element- context. It is impossible to describe the communication process without noise and context.
Conclusion
SMCR is one of the significant linear communication models that describes the communication process through four elements: the Sender, the Message, the Channel, and the Receiver. Although this model mentions various components, it is a one-way directed model. Berlo’s SMCR model is known as the one-step communication model; whereas, the two-step flow of communication is the interactive model. In sum, the SMCR model is also a linear model of communication, as it excludes feedback.