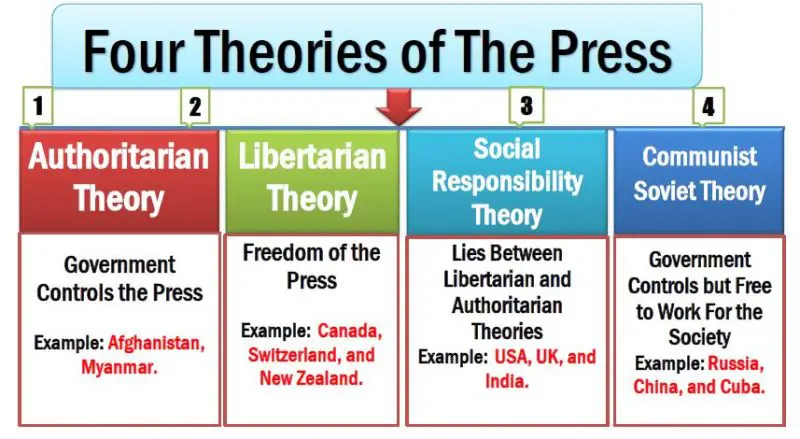
The Four Theories of the Press are Authoritarian, Libertarian, Social Responsibility, and Communist Soviet Theory. Also, 4 Theories of Journalism and Mass Communication.
Four Theories of the Press
The four theories of the press are authoritarian, libertarian, social responsibility, and communist soviet theory. In 1956, three scholars, Schramm, Siebert, and Peterson, published the Four Theories of the Press Book. It is also known as the Four Theories of the Press by Wilbur Schramm 1956.
The press plays different roles in diverse countries globally. The press roles and news values in journalism differ from country to country due to their political ideology. For example, in the USA, the press can focus on all types of news values, including negativity, but in North Korea, the press can not practice freely. The Four Theories of the Press Book describes a framework for understanding the role of the press in different political and social contexts. The four theories of the press are Authoritarian Theory, Libertarian Theory, Social Responsibility Theory, and Communist Soviet Theory.
Who are the Authors of the Four Theories of the Press?
Fred S. Siebert is Director of the School of Journalism and Communications at the University of Illinois.
Theodore Peterson is Associate Professor of Journalism and Communications at the University of Illinois.
Wilbur Schramm, former Dean of the Communications Division of the University of Illinois, is Professor of Journalism and Communications at Stanford University.
Book Title: Four Theories of the Press (The Authoritarian, Libertarian, Social Responsibility, and Soviet Communist Concepts of What the Press Should Be and Do)
What are the Four Theories of the Press?
The 4 Theories of the Press are:
- Authoritarian Theory
- Libertarian Theory
- Social Responsibility Theory
- Communist Soviet Theory
1. Authoritarian Theory of the Press
The authoritarian theory explains that the government authority directly controls the communication outlets. The government controls the press, information, and communication systems directly and indirectly (Siebert, Peterson, & Schramm, 1956). Sometimes, the government assigns authority to regulate the whole process of the information and communication system in the country. The agency controls the press thoroughly on behalf of the government. For example, the Korean Central News Agency controls the mass media outlets in North Korea.
The press cannot work independently. So, it publishes news and information that the government wants to know about the public in the country. The authority sets the code of conduct for the news agencies. Therefore, the news publishing outlets must follow the rules and regulations that the management sets. The authority also has the right to provide a license and cancel it. Usually, they revoke the license when the media violates the policies imposed by the government. The media practitioners thoroughly follow the government’s instructions to publish hard news and feature articles.
Characteristics of Authoritarian Press
- The authoritarian press is subject to censorship and control by the government and the state.
- The government strictly regulates the media outlets to suppress dissent.
- Media outlets are either owned by the government or controlled by government regulation.
- The primary objective of the media outlets is to support government activities and policies locally and internationally.
Authoritarian Theory of the Press Example
During the Second World War, Hitler controlled the news media in Germany; hence, no press could publish news without the authority’s permission.
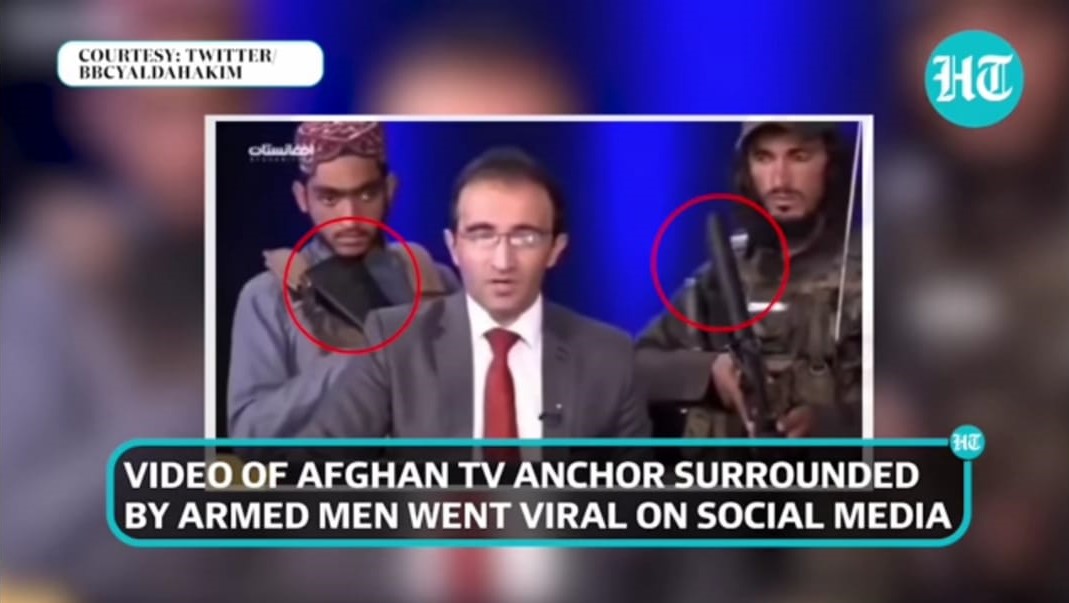
For example, in 2021, the Taliban took over power in Afghanistan, and the management excessively controls all media. Similarly, the army chief Min Aung Hlaing seized power in Myanmar in 2021.
The Global Investigative Journalism Network published the World Press Freedom Index country ranking list in 2024. According to the report, Eritrea ranked 180th and fell at the bottom of the list.
For example, Eritrea, Syria, Afghanistan, North Korea, Iran, Vietnam, Myanmar, and Turkmenistan.
2. Libertarian Theory
Libertarian theory refers to the freedom of the press to disseminate information (Siebert et al., 1956). Therefore, it is also known as the normative theory of mass communication. Mass media outlets are entirely free to publish any ethical news and information. The press works as the watchdog of the community and society in the country.
John Milter was the first introducer of the libertarian press concept. Firstly, in the 1700s, authorities in the USA applied the libertarian theory of the press. After that, and in the 1900s, Europe accepted it. According to the Libertarian Press, human beings have the right to access accurate information published by mass media outlets. The press should disseminate the actual news to society’s people.
Sometimes, the WikiLeaks platform publishes confidential documents to the public. Therefore, the governments of many countries worldwide do not allow to practice libertarian press system, and it can impact the political parties to form the government.
Characteristics of Libertarian Theory
- The owners of the media outlets are the masses of people, and they operate the press freely under government policy.
- The primary objective of media outlets is to express opinions freely.
- The press serves as a watchdog for society and the country, maintaining government policy.
- The press prioritizes public debate and opinion.
Example: The United States and other democratic countries where the press operates independently, and freedom of the press is protected by law.
Libertarian Theory of the Press Examples
Firstly, mass media and communication systems are free from the government to publish news. The government does not control the press when it disseminates information, even though it criticizes its activities. Therefore, journalists and media practitioners manage the press directly.
For example, Canada, Switzerland, and New Zealand
3. Social Responsibility Theory of the Press
Social responsibility theory explains that the press media do not need permission from the government to distribute news and information; however, they consider society when publishing news. Therefore, the social responsibility theory of the press has linked the libertarian and authoritarian theories. It lies between those two theories. The media are somewhat free from the government but controlled by the people of the country’s society.
Characteristics of Social Responsibility Press
- The media outlets are free to disseminate information, but are self-regulated to ensure ethical standards.
- The press is not biased by government agencies or the masses.
- The media publish authentic, balanced, and appropriate information for society and the country.
- The media outlets highlight social responsibility, avoiding causing harm.
Social Responsibility Theory of the Press Example
In mid mid-20th century, many countries applied the social responsibility theory, incorporating “the Commission of the Freedom of Press” in the United States in 1949. Anyone can express their opinion through mass media. Additionally, mass media play an essential role in raising a voice against discrimination and corruption. The BBC in the United Kingdom operates under a public service mandate, aiming to inform, educate, and entertain while adhering to high ethical standards.
For example, in the USA, UK, and India
4. Communist Soviet Theory
Communist Soviet Theory describes that the ministry of the respective government controls the press media, but they are free to work for society. The government regulates and guides mass media outlets for the benefit of the people. They can publish any news without obtaining permission from the authorities, but the government agency controls the entire system at the end of the day.
Communist Soviet Theory Example
The Soviet Union was reconstructed with the new norms based on the Marxist-Leninist beliefs in the 1917th revolution. Communist Soviet Theory is also known as Soviet Media Theory. This theory is generated from authoritarian theory but contradicted by the libertarian theory. The government agency owns the press media, but they are free to work for society. Finally, the government set up official media to deliver the information to society.
Characteristics of Communist Soviet Theory
- The media outlets are owned and regulated by the ruling Communist Party.
- The media play a role as a wing of the state, highlighting socialist values.
- They do not support dissenting opinions; they focus on the ideology of the state.
- The primary role of the media is to educate people and mobilize public support for the communist government
Example: The Soviet Union and other communist states, where the media outlet functions to promote the ideology of the Communist Party.
For example, in Russia, China, and Cuba.

Citation For This Article (APA 7th Edition)
| Kobiruzzaman, M. M. (2025). Four Theories of the Press- Authoritarian, Libertarian, Social Responsibility & Communist Soviet. Newsmoor- Educational Website For Online Learning. https://newsmoor.com/four-theories-of-the-press-authoritarian-libertarian-social-responsibility-theory/ |
Reference
| Siebert, F., Peterson, T. B., & Schramm, W. (1956). Four theories of the press: The authoritarian, libertarian, social responsibility, and Soviet communist concepts of what the press should be and do (Vol. 10). University of Illinois Press. |