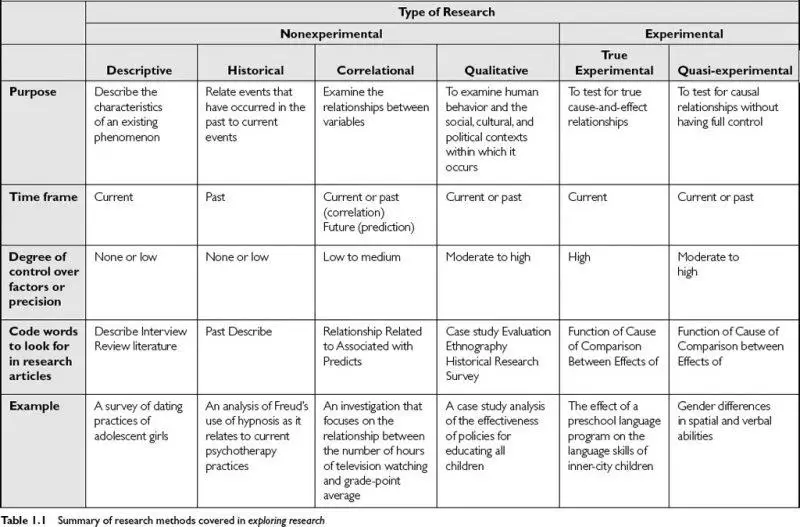
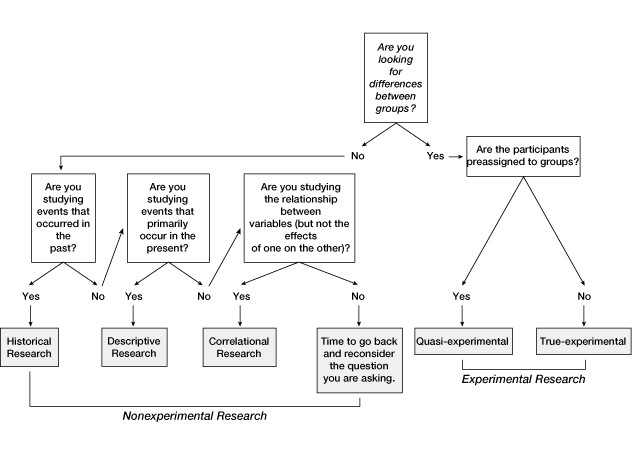
Media Convergence Example- Example of Media Convergence. Media Convergence in Journalism. Who and when established the Media convergence theory? Also, Examples and Elements of Media Convergence. Characteristics of New Media Audiences.
Convergence
Convergence means converging multiple items to unite things to get benefits. It is the process of forming a unique thing by utilizing two or more things. The convergence has been happening in all sectors to meet people’s demands. This world is very famous in the medical discipline. As per the technological revolution, technological and media convergence has been impossible to reverse trends.
Types of Convergence
According to Henry Jenkins, the six types of convergence are technological, media, global, economic, cultural, and organic.
Media Convergence
Media convergence refers to merging diverse media outlets, including traditional and new media, to promote the program and media content. The traditional and new media have been merged to adjust to new technology. There are many types of convergence, such as technological convergence and cultural convergence. The new technology and culture have changed human lifestyles. The revolution of technology stimulates media convergence. Technology adoption theories and models explain why and how people accept new technology excessively. Additionally, technological and cultural convergence forces the mass media to converge with other mainstream and new media.
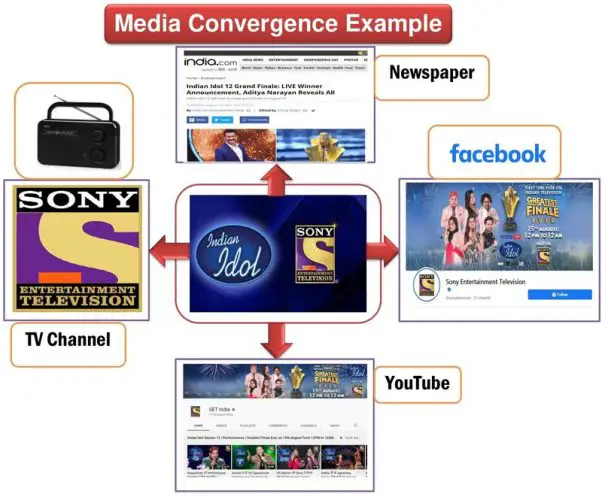
Example of Media Convergence
For example, the most popular Indian reality TV show name is “Indian Idol.” It is a singing competition Television series. Sony Entertainment Television telecasts the full episodes. Firstly, the candidates need to download the Sony liv app for registration. Sony Television has social media pages to promote the programs. The TV authority uses social media platforms to promote upcoming episodes as most people access new media sites more than traditional media. They also request their audiences to vote for their favorite contestants via smartphones. The active and passive audiences can provide their opinions via social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram. Sometimes, they use FM and traditional radio to advertise the program. In sum, the program authority merges Sony Television, smartphones, radio, Facebook, and YouTube channel to promote the program successfully. It is an example of media convergence in the digital era.
Media Convergence in Journalism
Media convergence in journalism means mutually utilizing print, broadcast, and online media to promote the news. Journalists use many media to spread the news among the maximum number of people locally and internationally. Media convergence in journalism appears as a significant step toward survival in the new media age.
There are two types of media convergence in journalism: (1) media convergence in collecting news and (2) media convergence in reporting the news.
Firstly, journalists collect information from other media and cite the source name when publishing information. It enhances the news value in print journalism. Television channels disseminate news from other channels such as radio, TV, newspapers, and social media.
Secondly, media authority uses multiple media to publish the news. People prefer to read online newspapers from social media sites rather than printed papers. Therefore, journalists publish the news via a printed newspaper and website portal and share them on social media platforms to reach more audiences.
Example of Media Convergence in Journalism
For example, The Star is the most popular newspaper outlet in Malaysia. A journalist for “The Star” has collected information from Malaysiakini. The Star has published the news via printed newspapers and online portals. They have also shared the news link via their Facebook page to reach the news among social media users. The authority has converged a few media to spread the news among a maximum number of audiences.
Technology Convergence
A long time ago, people used to listen to the radio to get news, Television to watch drama, cameras to capture photos, and bookshelves to keep books. Nowadays, people use only smartphones and computers to fulfill all their needs.
Who and when established Media convergence theory?
Henry Jenkins introduced media convergence theory in 2006 via his book Convergence Culture: Where Old and new media collide.
Elements of Media Convergence
The five essential elements of media convergence are technological, social, industrial, textual, and political.
Technological Convergence
Technology convergence has brought computer, communication, and content together, which is called 3 C. Here, 3 C refers to a computer, communication, and content. Computers and smartphones have digitilized the content, and digital content has changed the process of communication. The revolution of new technology and media convergence has changed the way of generating content and distribution. It has influenced the news production and distribution process totally. For example, now, every newspaper outlet has its own social media fan page, providing breaking news. Technology has allowed these outlets to operate live video programs that provide very authentic news for audiences. Therefore, subscribers are getting instant news through new technology convergence. It is definitely a positive impact of convergence in communication outlets.
Social Convergence
Social media convergence has both positive and negative impacts on society. It is called the double edge sword for the communication sector in society. Social media are a computer and application-based networking system that ease human communication through the internet (Kobiruzzaman, Waheed, Yaakup & Osman, 2018). Social media have emerged as the most convenient and popular communication platform, also known as new media. People are adopting social media for entertaining, imparting knowledge, sharing information, and communicating. There are many types of social media such as Facebook, YouTube, Twitter, WhatsApp, WeChat, Instagram, Zoom, Google meet, TikTok, QQ, Douyin, Sina Weibo, QZone, Snapchat, Reddit, Pinterest, and so more. Social media convergence made the news free of charge, so everyone could watch the news easily.
Many traditional media outlets disseminate the news through social media. For example, a newspaper outlet publishes printed newspapers, and it updates the same news on social media platforms. Thus, anyone can consume news from social media platforms without buying a printed copy of the newspaper. Social media convergence eases the way of reporting news for news reporters and editors. It has enabled news reporters and editors to collect news within a short time and disseminate them. Many journalists share their content on social media so that everyone can know who is the content writer.
Industrial Convergence
Many big industries have been merged into one giant company to dominate the sector. For example, in the 1990s and 2000s, many media companies expanded their business interest and merged with other companies. In the 1990s, industrial convergence is the Viacom-Paramount (1994) and Disney-ABC (1995). In the 2000s, example of the biggest company merger is America On-Line (AOL), Time Warner, Viacom-CBS (2000), and NBC-Universal (2004). They took over the company to expand business in the media sector.
Textual Convergence
Textual convergence refers to the merging of printed media into online news media. For example, books and newspapers have been converted into social media-based writing and reading practices, also known as digital journalism. Anyone can contribute to the media industry by commenting on social media platforms. It is called textual convergence in media. Journalists are earning knowledge and improving themselves through convergence. Now journalists can view others’ content easily because of convergence. They are getting ideas and improving themselves. It lets them learn more about generating media content’s rules and regulations. Media convergence creates a new way to interact between media practitioners and audiences. Readers comment to express their opinion. So, it allows for making interactive communication atmosphere.
Political Convergence
Convergence has managed to increase the similarity between political parties worldwide. It brings the similarity between political parties and policies inside the parties.
Characteristics of New Media
Audiences According to Don Tapscott (2008), new media audiences have the following characteristics:
- New media audiences want liberty in everything they do—for example, freedom of choice and expression.
- New media audiences love to customize, scrutinize, and personalize.
- They look for corporate integrity and openness when deciding what to buy and where to work.
- New media audiences want entertainment and play in their work, education, and social life.
- They are collaborative and relationship generation.
- Audiences are innovators.
Social media availability has formed the characteristic of new media audiences.
In Conclusion, If someone asks me to do I think convergence is essential or not? I will answer: Yes, I think change is always good. Change is part of the natural adoption process that drives the communication industry. The problem will occur when we avoid change. So, we cannot avoid the pace of change.
Citation For This Article (APA 7th Edition)
| Kobiruzzaman, M. M. (2025). Media Convergence Definition, Example Types & Elements. Newsmoor- Educational Website For Online Learning. https://newsmoor.com/media-convergence-example-elements-of-media-convergence-in-communication/ |