Technology Adoption Theories and Models. Explain Models for Technology Adoption. Also, Examples of Technology Adoption Theories and Models.
Technology Adoption Models
The technology adoption models are theories and frameworks that explain why people adopt and use modern technology. It also describes how people adopt modern technology and use it in communication, business, health, education, and other sectors. Technology adoption means confidently accepting and using modern technology. Researchers have introduced several technology adoption models in the recent decade to describe the reasons for technology adoption. They also mention the significant factors of these models that stimulate people to accept modern technology.
On the other hand, academicians consider a few factors that drive users to reject modern technology. The adoption of technology models plays a critical role in further improving technology. The importance of technology adoption has increased in social, political, educational, and business contexts. Therefore, nobody can deny the usefulness of modern technology and its application in personal life.
The Importance of Technology Adoption Models
Technology adoption models answer the most common question, “why do people use the new technology?” In addition, the researchers and practitioners identify factors that influence people’s acceptance of new technology. Technology has become an inevitable part of daily life. Nowadays, students hold virtual classes on platforms such as Google Meet, Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Skype. Additionally, many organizations set corporate meetings via these web conferencing applications. The adoption models for technology are developed to propose the reasons for and consequences of the technology. Technology adoption theories are related to information and communication models.
Technology Adoption Models and Theories
The Models of Technology Adoption are:
- Technology Acceptance Model(TAM)-1986
- Technology Acceptance Model(TAM)-1989
- Final Version of Technology Acceptance Model-1996
- Extended Technology Acceptance Model (TAM 2) (ETAM)- 2002
- Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT)- 2003
- Technology Acceptance Model-3 (TAM 3)-2008
- Extending Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT2, 2012)
- Motivational Model (MM)-1992
- Motivational Model of Microcomputer Usage-1996
- Uses and Gratification Theory (U&G)-1974
- Diffusion of Innovation Theory- 1962
- Perceived Characteristics of Innovating Theory (PCIT)
- The Model of PC Utilization (MPCU)-1991
These are examples of technology adoption models and theories.
1. Technology Acceptance Model(TAM)-1986
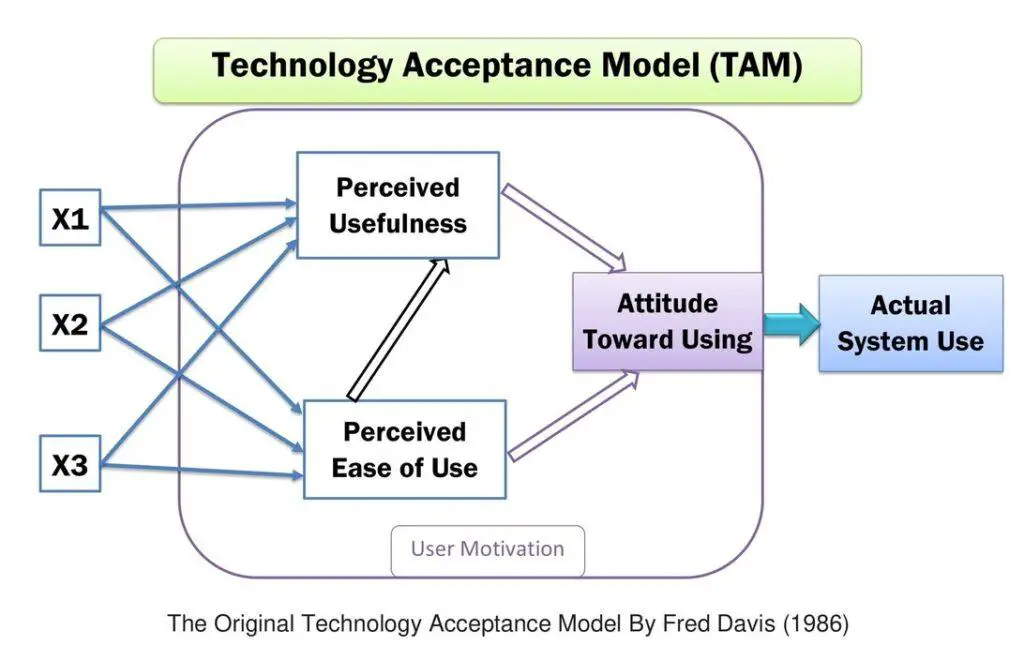
Fred D. Davis introduced the technology acceptance model(TAM) in 1986 in his Ph.D. thesis paper titled “A TECHNOLOGY ACCEPTANCE MODEL FOR EMPIRICALLY TESTING NEW END-USER INFORMATION SYSTEMS: THEORY AND RESULTS.” In 1986, Fred D. Davis initially included three elements: perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and attitude toward using the system. The technology acceptance model outlines three factors: perceived usefulness, ease of use, and attitude toward using the system. It also represents the design feature with X1, X2, and X3.
2. Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) (Davis, 1989)
Fred D. Davis published the technology acceptance model “Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology ” in the Management Information Systems Research Center, the University of Minnesota, 1989. So, the model is familiar as the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) (Davis, 1989).
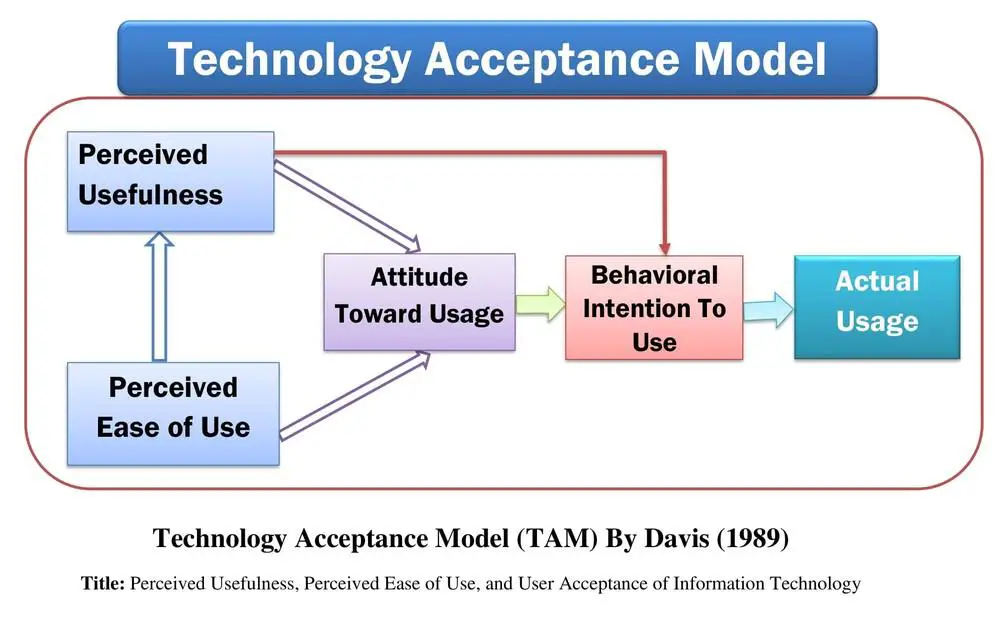
2. Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) (Davis et al., 1989)
However, in 1989, Fred D. Davis, Richard P. Bagozzi, and Paul R. Warshaw presented the technology acceptance model in the research paper “User Acceptance of Computer Technology: A Comparison of Two Theoretical Models,” published by the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS) located in Maryland, USA.
Fred D. Davis is a University of Michigan School of Business Administration professor. His research interests include user acceptance of technology, technology support for decision-making, and motivational factors in computer acceptance. The TAM model was undoubtedly derived from the Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA), which describes the factors that stimulate people to change their behavior. It has also been designated as the most cited model in the field of information and communication technology(ICT). The technology acceptance model (TAM) is undoubtedly one of the most significant models of technology adoption.
3. TAM-1: Final Version of Technology Acceptance Model- 1996
The Final Version of the Technology Acceptance Model was developed by Venkatesh and Davis in 1996. The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) explains users’ intention to adopt technology through three variables: perceived usefulness, ease of use, and attitude toward use. The additional factors of the TAM are user education, system features, user participation in the design, and the nature of the execution method. However, it excludes the social influence factor on the acceptance of modern technology. So, the researchers and practitioners term this a limitation of the model for implementation beyond the workplace.
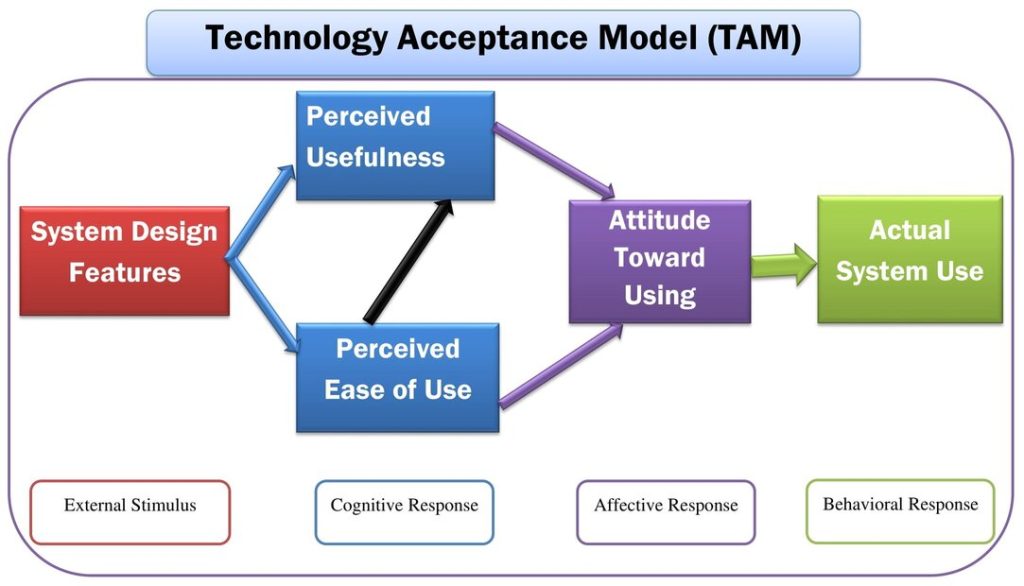
However, in 1996, Viswanath Venkatesh and Fred D. Davis included an additional variable, “External Variables”, to the previous model and outlined the final version of the Technology Acceptance Model.
“The TAM, TAM2, ETAM, TAM3, and UTAUT have been used over the years by various researchers to explain the adoption of technology systems”.
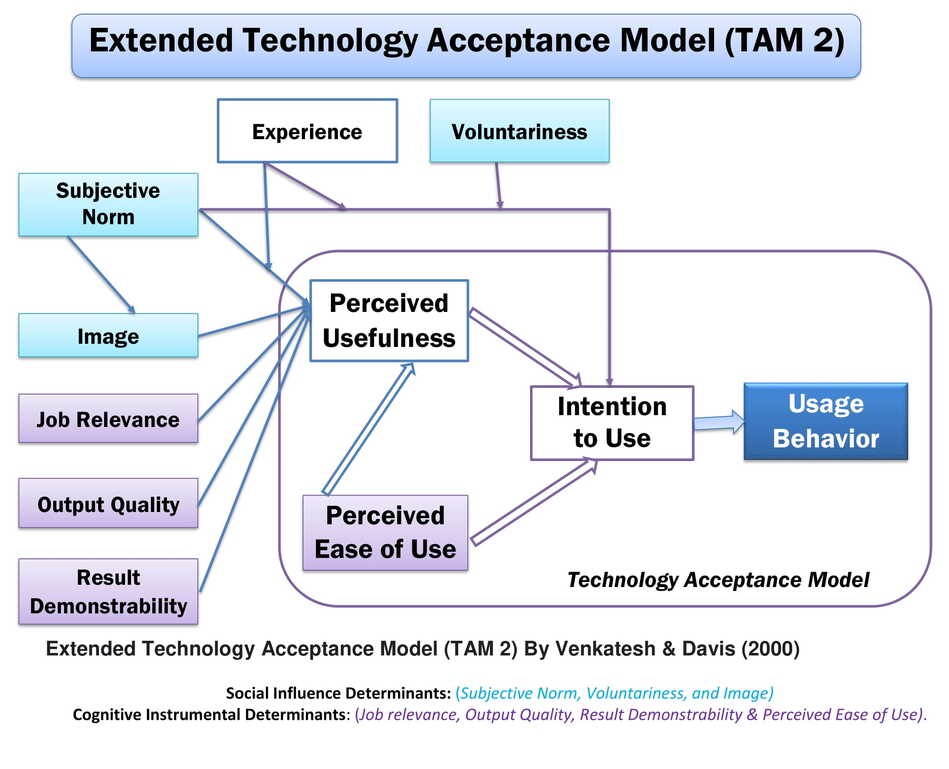
4. Extended Technology Acceptance Model (TAM 2) (2000)
Venkatesh and Davis added new factors to the Technology Acceptance Model and established the Extended Technology Acceptance Model (TAM 2) in 2000. The extended technology acceptance model is also known as the TAM2 and ETAM. ETAM described two groups of constructs, for example, social influence processes and cognitive instrumental determinants.
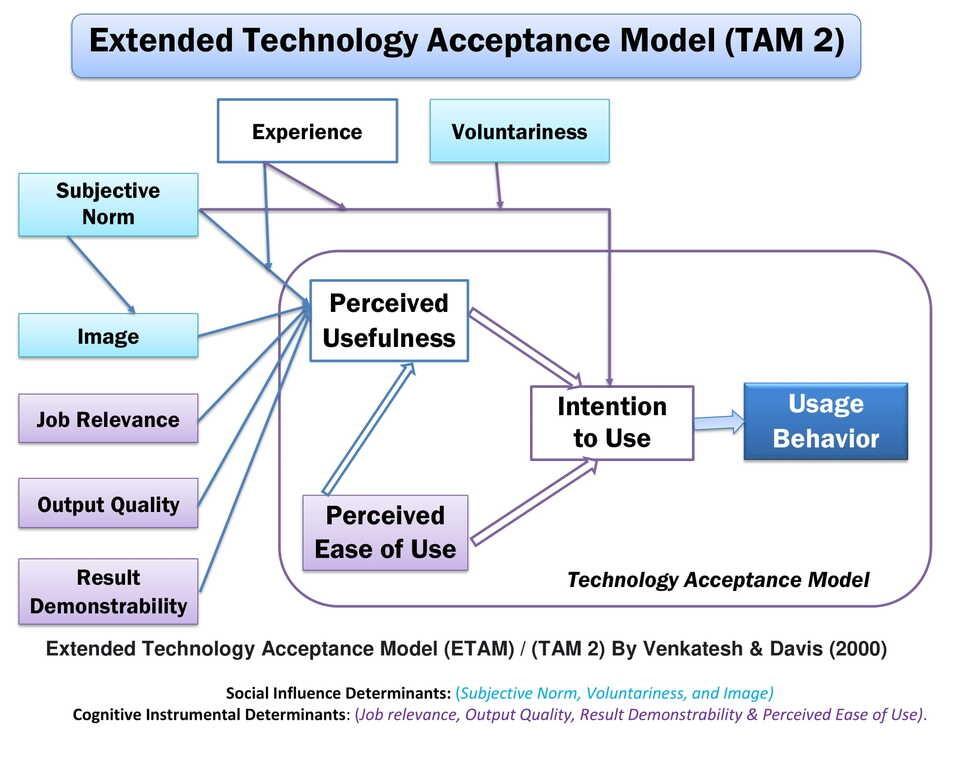
The three social influence determinants are subjective norm, voluntariness, and image. Additionally, the four cognitive instrumental processes of perceived usefulness are Job relevance, Output quality, Result demonstrability, and perceived ease of use. Both social influence and cognitive instrumental determinants stimulate users to accept and use the system.
5. Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) (2003)
The unified theory of acceptance and use of technology refers to the UTAUT model introduced in 2003. Viswanath Venkatesh, Michael Morris, Gordon Davis, and Fred Davis established the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) in 2003, under the title of “User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View”.
The Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) was developed from eight well-established models of technology acceptance. “The eight models are the theory of reasoned action (TRA), the technology acceptance model (TAM), the motivational model (MM), the theory of planned behavior (TPB), a model combining the technology acceptance model and the theory of planned behavior, the model of PC utilization (MPCU), the innovation diffusion theory, and the social cognitive theory (SCT).”
Firstly, the authors analyze the eight models and review the literature on user acceptance. Secondly, they investigate and compare the extensions of those models. Additionally, they developed a unified model based on the components of the eight models. Finally, the unified model was empirically tested and validated using longitudinal data. The UTAUT model has become the most significant framework for understanding the determinants of acceptance and use of a new system.
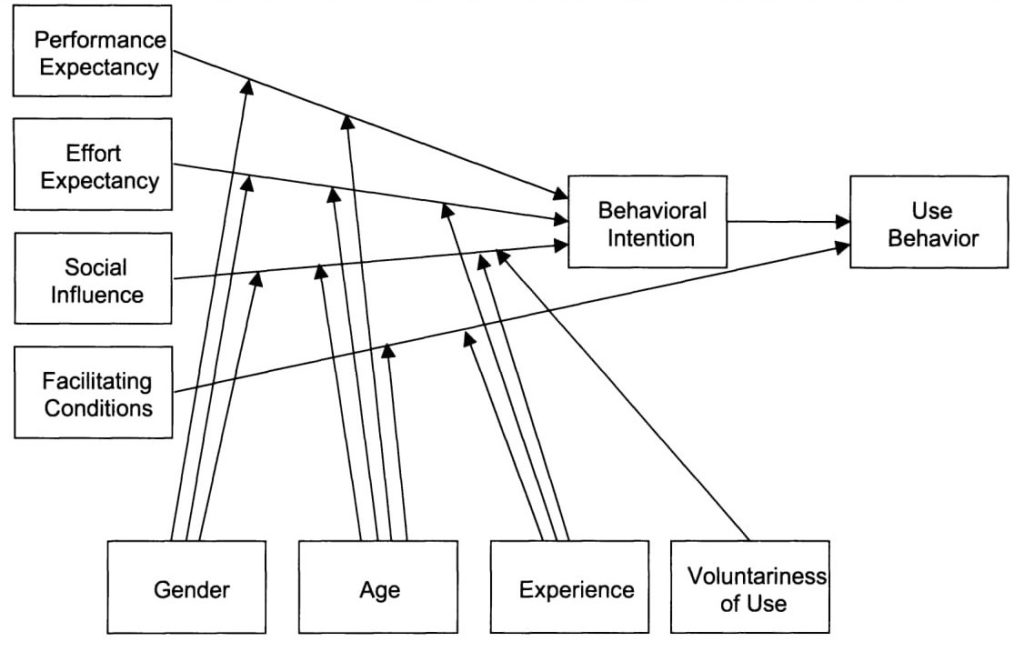
The four prime constructs of UTAUT are 1) Performance Expectancy, 2) Effort Expectancy, 3) Social Influence, and 4) Facilitating Conditions.
The first three constructs (Performance Expectancy, Effort Expectancy, and Social Influence) determine user intention and behavior. However, the fourth element (Facilitating Conditions) directly determines user behavior. Besides, the four moderate variables are Gender, age, experience, and voluntariness.
6. Technology Acceptance Model 3 (2008)
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM3) was introduced by Venkatesh and Bala in 2008. TAM-3 provides valuable rational explanations of how and why individuals decide to adopt and use ITs, particularly the work on the determinants of perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use.
7. Extending Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT2) (2012)
Venkatesh, Thong, and Xu established the Extending Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT2) in 2012. They added three additional variables, including hedonic motivation, price value, and
habit, to the UTAUT to explain customer technology adoption. The Extending Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology includes age, gender, and experience as moderating variables; however, it excludes voluntariness.
8. Motivation Model (MM) (1992)
Davis, Bagozzi, and Warshaw introduced the motivational model (MM) in 1992. The Motivational Model describes the external and natural stimulants that influence users’ behaviors. According to the Motivation Model, the two crucial elements of motivation are extrinsic and intrinsic motivation. Firstly, extrinsic motivation includes perceived usefulness, ease of use, and subjective norm. It is the acknowledgment that stimulates the users to act. On the other hand, intrinsic motivation includes the magnitude of enjoyment derived from recreating with a computer.
9. Motivational Model of Microcomputer Usage (1996)
The Motivational Model of Microcomputer Usage was introduced by Magid Igbaria, Saroj Parasuraman, and Jack J. Baroudi in 1996. It is also known as Igbaria’s model.
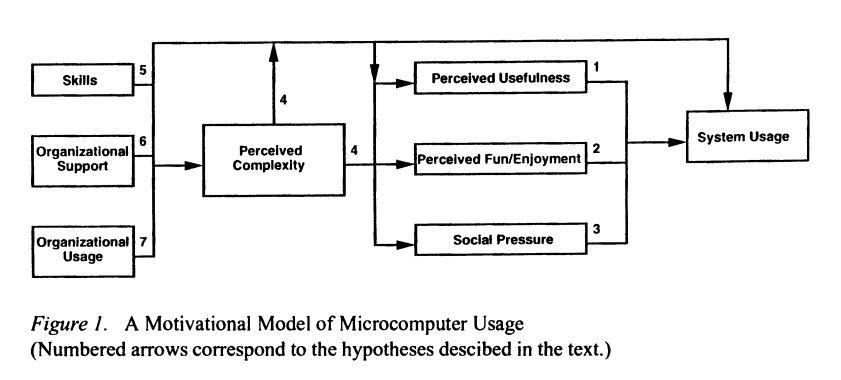
According to the Motivational Model of Microcomputer Usage, intrinsic and extrinsic motivators influence people’s acceptance or rejection of new technologies. This model views perceived fun as the intrinsic motivator; however, perceived usefulness is the extrinsic motivator that influences people’s behavior toward computer use.
10. Uses and Gratifications Theory (1974)
Katz, Blumler, and Gurevitch established the uses and gratifications theory in 1974. It explains why people utilize specific kinds of communication media. It is an active-audience theory that describes the gratification people derive from these media compared to others. The U & G theory explains why people use certain media and the benefits they derive from them. The U&G theory includes three constructs: motivations, behavioral usage, and gratifications/ satisfaction.
11. Diffusion of Innovations Theory (DOI) (1962)
Diffusion of Innovations Theory explains why people accept or reject new ideas and technology. It also describes how technology spreads quickly among people. In 1962, Everett M. Rogers published the diffusion of innovation theory in his book Diffusion of Innovations. Therefore, it is known as Rogers’ theory of technology adoption.
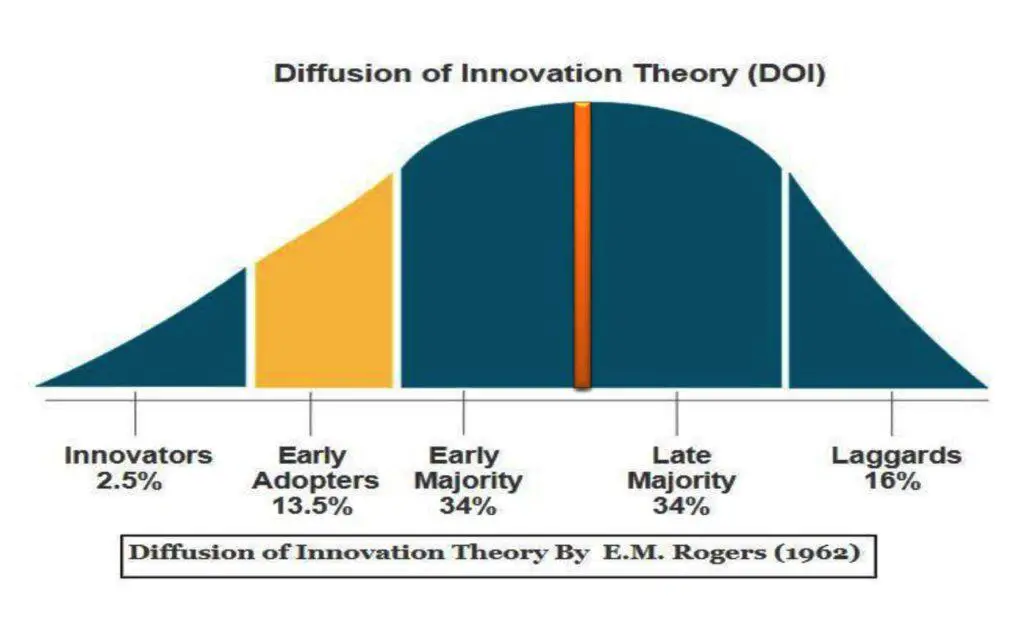
The five elements of the diffusion of innovation theory are Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, and Laggards.
12. Perceived Characteristics of Innovating Theory (PCIT) (1991)
Moore and Benbasat introduced the perceived characteristics and innovation theory in 1991. Perceived Characteristics of Innovating Theory is certainly developed from Rogers’s Perceived Attributes Innovation (PAI) theory. Perceived Characteristics of Innovating Theory added two additional factors: Image and voluntariness. It also separates the constructs of observability into Visibility and Results Demonstrability. Additionally, PCI renamed Rogers’ complexity to ease of use and kept other characteristics the same as before.
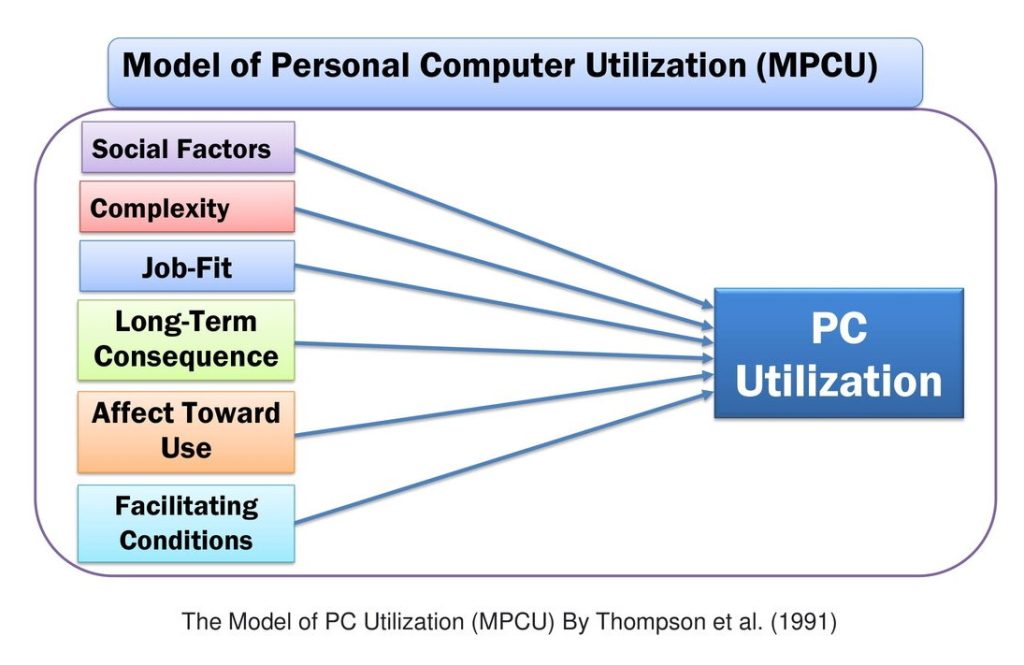
13. Model of PC Utilization (MPCU)-(1991)
Thompson, Higgins, and Howell established the PC Utilization (MPCU) model in 1991. They extended Triandis’ model to explain attitudes toward PC utilization. The Model of PC utilization describes six elements of personal computer utilization, such as job fit, complexity, long-term consequences, effect towards use, social factors, facilitating conditions, and experience to predict PC utilization behavior. However, it differs from the Theory of Reasoned Action by distinguishing between cognitive and affective elements of attitudes.